Abstract
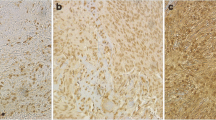
Aquaporins (AQP) are a growing family of water-channel proteins, numbering 13 to date. Recent studies have reported AQP1 and AQP4 to be involved in the development and resorption of brain edemas of different origin. Other AQPs have also been detected in brain tissue, but their impact on brain edema remains to be shown. To evaluate a possible role of AQP5 in brain edema, we investigated the association of AQP5 expression and the functional AQP5 promoter polymorphism A(-1364)C with occurrence and intensity of peritumoral edema in meningioma patients. Peritumoral edema was classified in three degrees based on preoperative imaging in 89 meningioma patients treated at the University Hospital Essen between 2003 and 2006. AQP5 expression was assessed immunohistochemically in tumor tissue obtained during neurosurgical tumor resection. Genotypes of the A(-1364)C polymorphism were determined using the “slowdown” polymerase chain reaction. Higher levels of AQP5 expression were significantly correlated with the AQP5-1364 AA genotype (P = 0.02). AQP5 expression was positively correlated with edema (P = 0.04). AQP5 genotypes were not significantly associated with the occurrence, but with the intensity of peritumoral brain edema (P = 0.04). In our cohort, 40 % of patients with grade I, 66.7 % with grade II, and 76.5 % with grade III edema possessed at least one A allele. Development and intensity of peritumoral edema in meningiomas are associated with AQP5 expression. The intensity of edema correlates with the AQP5 A(-1364)C genotype. This suggests AQP5 as an interesting new candidate involved in peritumoral brain edema in meningioma patients.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Oya S, Kawai K, Nakatomi H, Saito N (2012) Significance of Simpson grading system in modern meningioma surgery: integration of the grade with MIB-1 labeling index as a key to predict the recurrence of WHO grade I meningiomas. J Neurosurg 117(1):121–128. doi:10.3171/2012.3.JNS111945
Riemenschneider MJ, Perry A, Reifenberger G (2006) Histological classification and molecular genetics of meningiomas. Lancet Neurol 5(12):1045–1054. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(06)70625-1
Claus EB, Bondy ML, Schildkraut JM, Wiemels JL, Wrensch M, Black PM (2005) Epidemiology of intracranial meningioma. Neurosurgery 57(6):1088–1095. doi: 00006123-200512000-00003 (discussion 1088–1095)
Wiemels J, Wrensch M, Claus EB (2010) Epidemiology and etiology of meningioma. J Neurooncol 99(3):307–314. doi:10.1007/s11060-010-0386-3
Vignes JR, Sesay M, Rezajooi K, Gimbert E, Liguoro D (2008) Peritumoral edema and prognosis in intracranial meningioma surgery. J Clin Neurosci 15(7):764–768. doi: S0967-5868(07)00351-7 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jocn.2007.06.001
Paek SH, Kim CY, Kim YY, Park IA, Kim MS, Kim DG, Jung HW (2002) Correlation of clinical and biological parameters with peritumoral edema in meningioma. J Neurooncol 60(3):235–245
Badaut J, Brunet JF, Grollimund L, Hamou MF, Magistretti PJ, Villemure JG, Regli L (2003) Aquaporin 1 and aquaporin 4 expression in human brain after subarachnoid hemorrhage and in peritumoral tissue. Acta Neurochir Suppl 86:495–498
Verkman AS, Binder DK, Bloch O, Auguste K, Papadopoulos MC (2006) Three distinct roles of aquaporin-4 in brain function revealed by knockout mice. Biochim Biophys Acta 1758(8):1085–1093. doi:S0005-2736(06)00045-9 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamem.2006.02.018
Hu H, Yao HT, Zhang WP, Zhang L, Ding W, Zhang SH, Chen Z, Wei EQ (2005) Increased expression of aquaporin-4 in human traumatic brain injury and brain tumors. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B 6(1):33–37. doi:10.1631/jzus.2005.B0033
Ng WH, Hy JW, Tan WL, Liew D, Lim T, Ang BT, Ng I (2009) Aquaporin-4 expression is increased in edematous meningiomas. J Clin Neurosci 16(3):441–443. doi:S0967-5868(08)00249-X 10.1016/j.jocn.2008.04.028
Badaut J, Lasbennes F, Magistretti PJ, Regli L (2002) Aquaporins in brain: distribution, physiology, and pathophysiology. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 22(4):367–378. doi:10.1097/00004647-200204000-00001
Chae YK, Woo J, Kim MJ, Kang SK, Kim MS, Lee J, Lee SK, Gong G, Kim YH, Soria JC, Jang SJ, Sidransky D, Moon C (2008) Expression of aquaporin 5 (AQP5) promotes tumor invasion in human non small cell lung cancer. PLoS One 3(5):e2162. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0002162
Kang SK, Chae YK, Woo J, Kim MS, Park JC, Lee J, Soria JC, Jang SJ, Sidransky D, Moon C (2008) Role of human aquaporin 5 in colorectal carcinogenesis. Am J Pathol 173(2):518–525. doi:10.2353/ajpath.2008.071198
Woo J, Lee J, Kim MS, Jang SJ, Sidransky D, Moon C (2008) The effect of aquaporin 5 overexpression on the Ras signaling pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 367(2):291–298. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2007.12.073
Lee MD, Bhakta KY, Raina S, Yonescu R, Griffin CA, Copeland NG, Gilbert DJ, Jenkins NA, Preston GM, Agre P (1996) The human aquaporin-5 gene. Molecular characterization and chromosomal localization. J Biol Chem 271(15):8599–8604
Adamzik M, Frey UH, Bitzer K, Jakob H, Baba HA, Schmieder RE, Schneider MP, Heusch G, Peters J, Siffert W (2008) A novel-1364A/C aquaporin 5 gene promoter polymorphism influences the responses to salt loading of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system and of blood pressure in young healthy men. Basic Res Cardiol 103(6):598–610. doi:10.1007/s00395-008-0750-z
Adamzik M, Frey UH, Mohlenkamp S, Scherag A, Waydhas C, Marggraf G, Dammann M, Steinmann J, Siffert W, Peters J (2011) Aquaporin 5 gene promoter–1364A/C polymorphism associated with 30-day survival in severe sepsis. Anesthesiology 114(4):912–917. doi:10.1097/ALN.0b013e31820ca91100000542-201104000-00027
Kasimir-Bauer S, Heubner M, Otterbach F, Kimmig R, Siffert W, Adamzik M (2009) Prognostic relevance of the AQP5-1364C>A polymorphism in primary breast cancer. Mol Med Report 2(4):645–650. doi:10.3892/mmr_00000151
Nomura J, Hisatsune A, Miyata T, Isohama Y (2007) The role of CpG methylation in cell type-specific expression of the aquaporin-5 gene. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 353(4):1017–1022. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2006.12.126
Hammoud MA, Sawaya R, Shi W, Thall PF, Leeds NE (1996) Prognostic significance of preoperative MRI scans in glioblastoma multiforme. J Neurooncol 27(1):65–73
Ide M, Jimbo M, Kubo O, Yamamoto M, Takeyama E, Imanaga H (1994) Peritumoral brain edema and cortical damage by meningioma. Acta Neurochir Suppl (Wien) 60:369–372
Mattei TA, Mattei JA, Ramina R, Aguiar PH, Plese JP, Marino R Jr (2005) Edema and malignancy in meningiomas. Clinics (Sao Paulo) 60(3):201–206. doi: S1807-59322005000300004.
Pistolesi S, Fontanini G, Camacci T, De Ieso K, Boldrini L, Lupi G, Padolecchia R, Pingitore R, Parenti G (2002) Meningioma-associated brain oedema: the role of angiogenic factors and pial blood supply. J Neurooncol 60(2):159–164
Yoshioka H, Hama S, Taniguchi E, Sugiyama K, Arita K, Kurisu K (1999) Peritumoral brain edema associated with meningioma: influence of vascular endothelial growth factor expression and vascular blood supply. Cancer 85(4):936–944. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-0142(19990215)85:4<936:AID-CNCR23>3.0.CO;2-J
Bachmann HS, Siffert W, Frey UH (2003) Successful amplification of extremely GC-rich promoter regions using a novel ‘slowdown PCR’ technique. Pharmacogenetics 13(12):759–766. doi:10.1097/01.fpc.0000054140.14659.61
Rodriguez S, Gaunt TR, Day IN (2009) Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium testing of biological ascertainment for Mendelian randomization studies. Am J Epidemiol 169(4):505–514. doi:10.1093/aje/kwn359
Puttmann S, Senner V, Braune S, Hillmann B, Exeler R, Rickert CH, Paulus W (2005) Establishment of a benign meningioma cell line by hTERT-mediated immortalization. Lab Invest 85(9):1163–1171. doi:10.1038/labinvest.3700307
Regelsberger J, Hagel C, Emami P, Ries T, Heese O, Westphal M (2009) Secretory meningiomas: a benign subgroup causing life-threatening complications. Neuro Oncol 11(6):819–824. doi:15228517-2008-109 https://doi.org/10.1215/15228517-2008-109
Manley GT, Fujimura M, Ma T, Noshita N, Filiz F, Bollen AW, Chan P, Verkman AS (2000) Aquaporin-4 deletion in mice reduces brain edema after acute water intoxication and ischemic stroke. Nat Med 6(2):159–163. doi:10.1038/72256
Nag S, Manias JL, Stewart DJ (2009) Pathology and new players in the pathogenesis of brain edema. Acta Neuropathol 118(2):197–217. doi:10.1007/s00401-009-0541-0
Verkman AS, Yang B, Song Y, Manley GT, Ma T (2000) Role of water channels in fluid transport studied by phenotype analysis of aquaporin knockout mice. Exp Physiol 85 Spec No: 233S–241S
Ben Y, Chen J, Zhu R, Gao L, Bai C (2008) Upregulation of AQP3 and AQP5 induced by dexamethasone and ambroxol in A549 cells. Respir Physiol Neurobiol 161(2):111–118. doi:10.1016/j.resp.2007.12.007
Wu BJ, Zhu J, Tan WP, Mai XD, Huang HR, Li J, Li WY (2008) Effect of dexamethasone on the expression of aquaporin-5 in the lungs of mice with acute allergic asthma. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao 28(9):1670–1673
Gu YT, Zhang H, Xue YX (2007) Dexamethasone treatment modulates aquaporin-4 expression after intracerebral hemorrhage in rats. Neurosci Lett 413(2):126–131. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2006.11.072
Kobayashi H, Yokoo H, Yanagita T, Satoh S, Kis B, Deli M, Niwa M, Wada A (2006) Induction of aquaporin 1 by dexamethasone in lipid rafts in immortalized brain microvascular endothelial cells. Brain Res 1123(1):12–19. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2006.09.066
Cuevas IC, Slocum AL, Jun P, Costello JF, Bollen AW, Riggins GJ, McDermott MW, Lal A (2005) Meningioma transcript profiles reveal deregulated notch signaling pathway. Cancer Res 65(12):5070–5075. doi: https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-0240
Johnson MD, Okediji E, Woodard A (2004) Transforming growth factor-beta effects on meningioma cell proliferation and signal transduction pathways. J Neurooncol 66(1–2):9–16
Pham MH, Zada G, Mosich GM, Chen TC, Giannotta SL, Wang K, Mack WJ (2011) Molecular genetics of meningiomas: a systematic review of the current literature and potential basis for future treatment paradigms. Neurosurg Focus 30(5):E7. doi:10.3171/2011.2.FOCUS1117
Shu J, Lee JH, Harwalkar JA, Oh-Siskovic S, Stacey DW, Golubic M (1999) Adenovirus-mediated gene transfer of dominant negative Ha-Ras inhibits proliferation of primary meningioma cells. Neurosurgery 44(3):579–587 (discussion 587–578)
Woo J, Lee J, Chae YK, Kim MS, Baek JH, Park JC, Park MJ, Smith IM, Trink B, Ratovitski E, Lee T, Park B, Jang SJ, Soria JC, Califano JA, Sidransky D, Moon C (2008) Overexpression of AQP5, a putative oncogene, promotes cell growth and transformation. Cancer Lett 264(1):54–62. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2008.01.029
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the WTZ Research Support Service (supported in part by the Deutsche Krebshilfe Comprehensive Cancer Center financing) for comments on and editing of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lambertz, N., Hindy, N.E., Adler, C. et al. Expression of aquaporin 5 and the AQP5 polymorphism A(-1364)C in association with peritumoral brain edema in meningioma patients. J Neurooncol 112, 297–305 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-013-1064-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-013-1064-z