Abstract
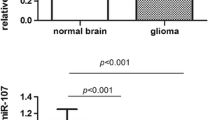
High-mobility group A1 (HMGA1) protein is an architectural transcription factor widely expressed during embryonic development and tumor progression. The purpose of this research was to investigate the expression of HMGA1 in malignant gliomas with different WHO classification and to study the correlation of HMGA1 expression with tumor proliferation, invasion, and angiogenesis. Expression of HMGA1, Ki-67, MMP-9, VEGF-A, and MVD in malignant gliomas and their correlation were studied in 60 samples of different WHO classification by use of immunohistochemistry, and in 27 randomly selected samples by use of real-time quantitative PCR. Immunohistochemistry results showed that nuclear immunostaining of HMGA1 protein was not observed in normal brain tissues but was observed in 96.7% (58 of 60) of malignant gliomas including high (+++) in 15 (25.0%), moderate (++) in 28 (46.7%), and negligible to low (0–+) in 17 (28.3%) samples. Expression of HMGA1 protein was significantly higher in glioblastoma multiforme than in WHO grade II (P = 0.002) and WHO grade III gliomas (P = 0.024). HMGA1 protein expression correlated significantly with expression of Ki-67 (r = 0.530, P = 0.000), MMP-9 (r = 0.508, P = 0.000), VEGF-A (r = 0.316, P = 0.014), and MVD (r = 0.321, P = 0.012), but not with sex (r = 0.087, P = 0.510) and age (r = −0.121, P = 0.358). Real-time quantitative PCR results, also, were indicative of HMGA1 overexpression in glioblastoma multiforme compared with WHO grade II (P = 0.043) and WHO grade III (P = 0.031) gliomas. HMGA1 gene expression correlated significantly with gene expression of Ki-67 (r = 0.429, P = 0.025), MMP-9 (r = 0.443, P = 0.024), and VEGF-A (r = 0.409, P = 0.034). These results indicated that expression of HMGA1 correlates significantly with malignancy, proliferation, invasion, and angiogenesis of gliomas. We conclude that HMGA1 may be a potential biomarker and rational therapeutic target for human tumors.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Davis FG, McCarthy BJ, Freels S, Kupelian V, Bondy ML (1999) The conditional probability of survival of patients with primary malignant brain tumors: surveillance, epidemiology, and end results (SEER) data. Cancer 85:485–491
Ranuncolo SM, Varela M, Morandi A, Lastiri J, Christiansen S, Bal de Kier Joffe E, Pallotta MG, Puricelli L (2004) Prognostic value of Mdm2, p53 and p16 in patients with astrocytomas. J Neurooncol 68:113–121
Wen PY, Kesari S (2008) Malignant gliomas in adults. N Engl J Med 359:492–507
Matsuda M, Nimura K, Shimbo T, Hamasaki T, Yamamoto T, Matsumura A, Kaneda Y (2010) Immunogene therapy using immunomodulating HVJ-E vector augments anti-tumor effects in murine malignant glioma. J Neurooncol. dio:10.1007/s11060-010-0355-x
Germano IM, Binello E (2009) Gene therapy as an adjuvant treatment for malignant gliomas: from bench to bedside. J Neurooncol 93:79–87
Chiocca EA, Broaddus WC, Gillies GT, Visted T, Lamfers ML (2004) Neurosurgical delivery of chemotherapeutics, targeted toxins, genetic and viral therapies in neuro-oncology. J Neurooncol 69:101–117
Jacobs AH, Voges J, Kracht LW, Dittmar C, Winkeler A, Thomas A, Wienhard K, Herholz K, Heiss WD (2003) Imaging in gene therapy of patients with glioma. J Neurooncol 65:291–305
Grasser KD (2003) Chromatin-associated HMGA and HMGB proteins: versatile co-regulators of DNA-dependent processes. Plant Mol Biol 53:281–295
Fan H, Guo H, Zhang IY, Liu B, Luan L, Xu S, Hou X, Liu W, Zhang R, Wang X, Pang Q (2011) The different HMGA1 expression of total population of glioblastoma cell line U251 and glioma stem cells isolated from U251. Brain Res 1384:9–14
Johnson KR, Lehn DA, Reeves R (1989) Alternative processing of mRNAs encoding mammalian chromosomal high-mobility-group proteins HMG-I and HMG-Y. Mol Cell Biol 9:2114–2123
Reeves R, Nissen MS (1990) The A.T-DNA-binding domain of mammalian high mobility group I chromosomal proteins. A novel peptide motif for recognizing DNA structure. J Biol Chem 265:8573–8582
Lovell-Badge R (1995) Developmental genetics. Living with bad architecture. Nature 376:725–726
Reeves R, Beckerbauer L (2001) HMGI/Y proteins: flexible regulators of transcription and chromatin structure. Biochim Biophys Acta 1519:13–29
Sgarra R, Rustighi A, Tessari MA, Di Bernardo J, Altamura S, Fusco A, Manfioletti G, Giancotti V (2004) Nuclear phosphoproteins HMGA and their relationship with chromatin structure and cancer. FEBS Lett 574:1–8
Fedele M, Fusco A (2010) HMGA and cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta 1799:48–54
Fusco A, Fedele M (2007) Roles of HMGA proteins in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 7:899–910
Chiappetta G, Avantaggiato V, Visconti R, Fedele M, Battista S, Trapasso F, Merciai BM, Fidanza V, Giancotti V, Santoro M, Simeone A, Fusco A (1996) High level expression of the HMGI (Y) gene during embryonic development. Oncogene 13:2439–2446
Hirning-Folz U, Wilda M, Rippe V, Bullerdiek J, Hameister H (1998) The expression pattern of the Hmgic gene during development. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 23:350–357
Zhou X, Benson KF, Ashar HR, Chada K (1995) Mutation responsible for the mouse pygmy phenotype in the developmentally regulated factor HMGI-C. Nature 376:771–774
Chiappetta G, Bandiera A, Berlingieri MT, Visconti R, Manfioletti G, Battista S, Martinez-Tello FJ, Santoro M, Giancotti V, Fusco A (1995) The expression of the high mobility group HMGI (Y) proteins correlates with the malignant phenotype of human thyroid neoplasias. Oncogene 10:1307–1314
Fedele M, Bandiera A, Chiappetta G, Battista S, Viglietto G, Manfioletti G, Casamassimi A, Santoro M, Giancotti V, Fusco A (1996) Human colorectal carcinomas express high levels of high mobility group HMGI(Y) proteins. Cancer Res 56:1896–1901
Chiappetta G, Tallini G, De Biasio MC, Manfioletti G, Martinez-Tello FJ, Pentimalli F, de Nigris F, Mastro A, Botti G, Fedele M, Berger N, Santoro M, Giancotti V, Fusco A (1998) Detection of high mobility group I HMGI(Y) protein in the diagnosis of thyroid tumors: HMGI(Y) expression represents a potential diagnostic indicator of carcinoma. Cancer Res 58:4193–4198
Kim DH, Park YS, Park CJ, Son KC, Nam ES, Shin HS, Ryu JW, Kim DS, Park CK, Park YE (1999) Expression of the HMGI(Y) gene in human colorectal cancer. Int J Cancer 84:376–380
Chiappetta G, Botti G, Monaco M, Pasquinelli R, Pentimalli F, Di Bonito M, D’Aiuto G, Fedele M, Iuliano R, Palmieri EA, Pierantoni GM, Giancotti V, Fusco A (2004) HMGA1 protein overexpression in human breast carcinomas: correlation with ErbB2 expression. Clin Cancer Res 10:7637–7644
Frasca F, Rustighi A, Malaguarnera R, Altamura S, Vigneri P, Del Sal G, Giancotti V, Pezzino V, Vigneri R, Manfioletti G (2006) HMGA1 inhibits the function of p53 family members in thyroid cancer cells. Cancer Res 66:2980–2989
Hristov AC, Cope L, Di Cello F, Reyes MD, Singh M, Hillion JA, Belton A, Joseph B, Schuldenfrei A, Iacobuzio-Donahue CA, Maitra A, Resar LM (2010) HMGA1 correlates with advanced tumor grade and decreased survival in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Mod Pathol 23:98–104
Mu G, Liu H, Zhou F, Xu X, Jiang H, Wang Y, Qu Y (2010) Correlation of overexpression of HMGA1 and HMGA2 with poor tumor differentiation, invasion, and proliferation associated with let-7 down-regulation in retinoblastomas. Hum Pathol 41:493–502
Enestrom S, Vavruch L, Franlund B, Nordenskjold B (1998) Ki-67 antigen expression as a prognostic factor in primary and recurrent astrocytomas. Neurochirurgie 44:25–30
Johannessen AL, Torp SH (2006) The clinical value of Ki-67/MIB-1 labeling index in human astrocytomas. Pathol Oncol Res 12:143–147
Wild-Bode C, Weller M, Wick W (2001) Molecular determinants of glioma cell migration and invasion. J Neurosurg 94:978–984
Raithatha SA, Muzik H, Rewcastle NB, Johnston RN, Edwards DR, Forsyth PA (2000) Localization of gelatinase-A and gelatinase-B mRNA and protein in human gliomas. Neuro Oncol 2:145–150
Choe G, Park JK, Jouben-Steele L, Kremen TJ, Liau LM, Vinters HV, Cloughesy TF, Mischel PS (2002) Active matrix metalloproteinase 9 expression is associated with primary glioblastoma subtype. Clin Cancer Res 8:2894–2901
Goldbrunner RH, Bernstein JJ, Plate KH, Vince GH, Roosen K, Tonn JC (1999) Vascularization of human glioma spheroids implanted into rat cortex is conferred by two distinct mechanisms. J Neurosci Res 55:486–495
Plate KH, Breier G, Weich HA, Risau W (1992) Vascular endothelial growth factor is a potential tumour angiogenesis factor in human gliomas in vivo. Nature 359:845–848
Rotondo F, Sharma S, Scheithauer BW, Horvath E, Syro LV, Cusimano M, Nassiri F, Yousef GM, Kovacs K (2010) Endoglin and CD-34 immunoreactivity in the assessment of microvessel density in normal pituitary and adenoma subtypes. Neoplasma 57:590–593
Kosem M, Tuncer I, Kotan C, Ibiloglu I, Ozturk M, Turkdogan MK (2009) Significance of VEGF and microvascular density in gastric carcinoma. Hepatogastroenterology 56:1236–1240
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-delta delta C (T)) method. Methods 25:402–408
Reeves R, Edberg DD, Li Y (2001) Architectural transcription factor HMGI(Y) promotes tumor progression and mesenchymal transition of human epithelial cells. Mol Cell Biol 21:575–594
Zhang Y, Ma T, Yang S, Xia M, Xu J, An H, Yang Y, Li S (2011) High-mobility group A1 proteins enhance the expression of the oncogenic miR-222 in lung cancer cells. Mol Cell Biochem. doi: 10.1007/s11010-011-0907-1
Palmieri D, Valentino T, D’Angelo D, De Martino I, Postiglione I, Pacelli R, Croce CM, Fedele M, Fusco A (2011) HMGA proteins promote ATM expression and enhance cancer cell resistance to genotoxic agents. Oncogene doi: 10.1038/onc.2011.21
Cao YD, Huang PL, Sun XC, Ma J, Jin ZL, Cheng HY, Xu RZ, Li F, Qin SK, Deng YX, Ge XL (2011) Silencing of high mobility group A1 enhances gemcitabine chemosensitivity of lung adenocarcinoma cells. Chin Med J (Engl) 124:1061–1068
Yuan S, Pan Q, Fu C, Bi Z (2011) Silencing of HMGA1 expression by RNA interference suppresses growth of osteogenic sarcoma. Mol Cell Biochem doi: 10.1007/s11010-011-0865-7
Scheithauer BW, Fuller GN, VandenBerg SR (2008) The 2007 WHO classification of tumors of the nervous system: controversies in surgical neuropathology. Brain Pathol 18:307–316
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no. 30973109) and the Science and Technology Department of Shandong Province (grant no. 2008BS03044). The authors thank the patients who contributed to this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Bo Pang and Haitao Fan contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pang, B., Fan, H., Zhang, I.Y. et al. HMGA1 expression in human gliomas and its correlation with tumor proliferation, invasion and angiogenesis. J Neurooncol 106, 543–549 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-011-0710-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-011-0710-6