Abstract
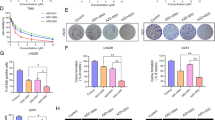
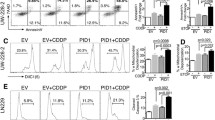
Glioblastoma is the most frequent and malignant glioma in adults. To develop an effective gene therapy strategy for glioblastoma, we investigated the anti-proliferative effects of phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN) restoration and siRNAs specifically targeting PIK3CB and PIK3CA on PTEN-deficient glioblastoma cells in vitro and in subcutaneous xenografts. Restoration of PTEN or knockdown of PIK3CB, but not PIK3CA, in glioblastoma cells markedly down-regulates the phosphorylation level of AKT, inhibits cell proliferation and colony formation, arrests the cell cycle at the G0/G1 stage, and promotes caspase-dependent apoptosis. Combined treatment with PTEN restoration and PIK3CB knockdown shows strong synergy. PTEN restoration or PIK3CB knockdown is also able to efficiently inhibit the growth of human U251 glioblastoma xenografts in nude mice, while tumor growth is entirely suppressed by a combination of the two treatments. In addition, we found that the mRNA levels of inhibitors of apoptosis proteins (IAPs) are reduced in U251 cells by PTEN restoration, suggesting that combined antitumor effects may also be partly attributed to the inhibition of the IAP pathway by PTEN restoration. Collectively, our results demonstrate that PI3 K isoforms play specific roles in tumorigenesis, and that combined treatment of PTEN restoration and PIK3CB siRNA is a promising gene therapy strategy for PTEN-deficient gliomas.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Legler JM, Ries LA, Smith MA et al (1999) Brain and other central nervous system cancers: recent trends in incidence and mortality. J Natl Cancer Inst 91:1382–1390
Wrensch M, Minn Y, Chew T et al (2002) Epidemiology of primary brain tumors: current concepts and review of the literature. Neuro Oncol 4:278–299
Davis FG, McCarthy BJ, Freels S et al (1999) The conditional probability of survival of patients with primary malignant brain tumors surveillance, epidemiology, and end results (SEER) data. Cancer 85:485–491
Bigner SH, Wong AJ, Mark J et al (1987) Relationship between gene amplification and chromosomal deviations in malignant human gliomas. Cancer Genet Cytogenet 29:165–170
Inda MM, Fan X, Muñoz J et al (2003) Chromosomal abnormalities in human glioblastomas: gain in chromosome 7p correlating with loss in chromosome 10q. Mol Carcinog 36:6–14
Furnari FB, Fenton T, Bachoo RM et al (2007) Malignant astrocytic glioma: genetics, biology, and paths to treatment. Genes Dev 21:2683–2710
Li J, Yen C, Liaw D et al (1997) PTEN a putative protein tyrosine phosphatase gene mutated in human brain, breast, and prostate cancer. Science 275:1943–1947
Steck PA, Pershouse MA, Jasser SA et al (1997) Identication of a candidate tumor suppressor gene, MMAC1, at chromosome 10q23.3 that is mutated in multiple advanced cancers. Nat Genet 15:356–362
Li DM, Sun H (1997) TEP1, encoded by a candidate tumor suppressor locus, is a novel protein tyrosine phosphatase regulated by transforming growth factor beta. Cancer Res 57:2124–2129
Narita Y, Nagane M, Mishima K et al (2002) Mutant epidermal growth factor receptor signaling down-regulates p27 through activation of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/AKT pathway in glioblastomas. Cancer Res 62:6764–6769
Haas-Kogan D, Shalev N, Wong M et al (1998) Protein kinase B (PKB/AKT) activity is elevated in glioblastoma cells due to mutation of the tumor suppressor PTEN/MMAC. Curr Biol 8:1195–1198
West KA, Castillo SS, Dennis PA (2002) Activation of the PI3 K/AKT pathway and chemotherapeutic resistance. Drug Resist Updat 5:234–238
Koul D (2008) PTEN signaling pathways in glioblastoma. Cancer Biol Ther 7:1321–1325
Ihle NT, Powis G (2009) Take your PIK: phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase inhibitors race through the clinic and toward cancer therapy. Mol Cancer Ther 8:1–9
Cheng CK, Fan QW, Weiss WA (2009) PI3 K signaling in glioma–animal models and therapeutic challenges. Brain Pathol 19:112–120
Scheid MP, Woodgett JR (2001) PKB/AKT: functional insights from genetic models. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2:760–768
Stambolic V, Suzuki A, de la Pomps JL et al (1998) Negative regulation of PKB/AKT-dependent cell survival by the tumor suppressor PTEN. Cell 95:29–39
Maehama T, Dixon JE (1998) The tumor suppressor, PTEN/MMAC1, dephosphorylates the lipid second messenger, phosphatidylinositol 3, 4, 5-trisphosphate. J Biol Chem 273:13375–13378
Wu XY, Neshat MS, Whang YE et al (1998) The Pten/MMAC1 tumor suppressor phosphatase functions as a negative regulator of the phosphoinositide 3-kinase/AKT pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:15587–15591
Sano T, Lin H, Chen X et al (1999) Differential expression of MMAC/PTEN in glioblastoma multiforme: relationship to localization and prognosis. Cancer Res 59:1820–1824
Furnari FB, Lin H, Huang HS et al (1997) Growth suppression of glioma cells by PTEN requires a functional phosphatase catalytic domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:12479–12484
Cheney IW, Johnson DE, Vaillancourt MT et al (1998) Suppression of tumorigenicity of glioblastoma cells by adenovirus-mediated MMAC1/PTEN gene transfer. Cancer Res 58:2331–2334
Kang CS, Zhang ZY, Jia ZF et al (2006) Suppression of EGFR expression by antisense or small interference RNA inhibits U251 glioma cell growth in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Gene Ther 13:530–538
Pu P, Kang C, Zhang Z et al (2006) Downregulation of PIK3CB by siRNA suppresses malignant glioma cell growth in vitro and in vivo. Technol Cancer Res Treat 5:271–280
Yu S, Pu P, Jiang D (1998) A study of gene expression of PDGFBB and PDGFR as well as level of PDGFR activity in human gliomas. Chin J Pathol 27:109–112
Li J, Huang Q, Pu P (2000) IGF1 gene expression in human brain tumors. Chin J Clin Cancer Res 27:375–376
Joensuu H, Puputti M, Sihto H et al (2005) Amplification of genes encoding KIT, PDGF alpha, and VEGFR2 receptor tyrosine kinases is frequent in glioblastoma multiforme. J Pathol 207:224–231
Hirano H, Lopes MB, Laws ER Jr et al (1999) Insulin-like growth factor-1 content and pattern of expression correlates with histopathologic grade in diffusely infiltrating astrocytomas. Neuro Oncol 1:109–119
Vivanco I, Sawyers CL (2002) The phosphotidylinositol-3-kinase-AKT signaling pathway in human cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 2:489–501
Fruman DA, Meyers RE, Cantley LC (1998) Phosphoinositide kinases. Annu Rev Biochem 67:481–507
Wee S, Lengauer C, Wiederschain D (2008) Class IA phosphoinositide 3-kinase isoforms and human tumorigenesis: implications for cancer drug discovery and development. Curr Opin Oncol 20:77–82
Shayesteh L, Lu Y, Kuo WL et al (1999) PIK3CA is implicated as an oncogene in ovarian cancer. Nat Genet 21:99–102
Ma YY, Wei SJ, Lin YC et al (2000) PIK3CA as an oncogene in cervical cancer. Oncogene 19:2739–2744
Samuels Y, Wang Z, Bardelli A et al (2004) High frequency of mutations of the PIK3CA gene in human cancers. Science 304:554
Campbell IG, Russell SE, Choong DY et al (2004) Mutation of the PIK3CA gene in ovarian and breast cancer. Cancer Res 64:7678–7681
Wu G, Mambo E, Guo Z et al (2005) Uncommon mutation, but common amplifications, of the PIK3CA gene in thyroid tumors. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 90:4688–4693
Phillips WA, Russell SE, Ciavarella ML et al (2006) Mutation analysis of PIK3CA and PIK3CB in esophagus cancer and Barrett’s esophagus. Int J Cancer 118:2644–2646
Broderick DK, Di C, Parrett TJ et al (2004) Mutations of PIK3CA in anaplastic oligodendrogliomas, high grade astrocytomas, and medulloblastomas. Cancer Res 64:5048–5054
Torbett NE, Luna-Moran A, Knight ZA et al (2008) A chemical screen in diverse breast cancer cell lines reveals genetic enhancers and suppressors of sensitivity to PI3 K isoform-selective inhibition. Biochem J 415:97–110
Jia S, Liu Z, Zhang S et al (2008) Essential roles of PI(3)K-p110beta in cell growth, metabolism and tumorigenesis. Nature 454:776–779
An HJ, Cho NH, Yang HS et al (2007) Targeted RNA interference of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase p110-beta induces apoptosis and proliferation arrest in endometrial carcinoma cells. J Pathol 212:161–169
Oda K, Okada J, Timmerman L et al (2008) PIK3CA cooperates with other phosphatidylinositol 30-kinase pathway mutations to effect oncogenic transformation. Cancer Res 68:8127–8136
Wee S, Wiederschain D, Maira SM et al (2008) PTEN-deficient cancers depend on PIK3CB. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:13057–13062
Ziegler DS, Kung AL, Kieran MW (2008) Anti-apoptosis mechanisms in malignant Gliomas. J Clin Oncol 26:493–500
Wagenknecht B, Glaser T, Naumann U et al (1999) Expression and biological activity of X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis (XIAP) in human malignant glioma. Cell Death Differ 6:370–376
Chen Z, Naito M, Hori S et al (1999) A human IAP-family gene, apollon, expressed in human brain cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 264:847–854
Adida C, Berrebi D, Peuchmaur M et al (1998) Antiapoptosis gene, survivin and prognosis of neuroblastoma. Lancet 351:882–883
Krakstad C, Chekenya M (2010) Survival signalling and apoptosis resistance in glioblastomas: opportunities for targeted therapeutics. Mol Cancer 9:135
Dai Y, Qiao L, Chan KW et al (2008) Loss of XIAP sensitizes rosiglitazone-induced growth inhibition of colon cancer in vivo. Int J Cancer 122:2858–2863
Van Themsche C, Leblanc V, Parent S et al (2009) X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein (XIAP) regulates PTEN ubiquitination, content, and compartmentalization. J Biol Chem 284:20462–20466
Vasudevan KM, Gurumurthy S, Rangnekar VM (2004) Suppression of PTEN expression by NF-kappa B prevents apoptosis. Mol Cell Biol 24:1007–1021
Schwab M, Reynders V, Loitsch S et al (2008) PPARγ is involved in mesalazine-mediated induction of apoptosis and inhibition of cell growth in colon cancer cells. Carcinogenesis 29:1407–1414
Guha M, Plescia J, Leav I et al (2009) Endogenous tumor suppression mediated by PTEN involves survivin gene silencing. Cancer Res 69:4954–4958
Koul D, Takada Y, Shen R et al (2006) PTEN enhances TNF-induced apoptosis through modulation of nuclear factor-kappaB signaling pathway in human glioma cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 350:463–471
Dasari VR, Kaur K, Velpula KK et al (2010) Upregulation of PTEN in glioma cells by cord blood mesenchymal stem cells inhibits migration via downregulation of the PI3 K/Akt pathway. PLoS One 5:e10350
Natarajan M, Hecker TP, Gladson CL (2003) FAK signaling in anaplastic astrocytoma and glioblastoma tumors. Cancer J 9:126–133
Cai XM, Tao BB, Wang LY et al (2005) Protein phosphatase activity of PTEN inhibited the invasion of glioma cells with epidermal growth factor receptor mutation type III expression. Int J Cancer 117:905–912
Acknowledgments
We are grateful for the fundings (to L.H.) from the Shenzhen Municipal Government and Bureau of Science Technology and Information through the programs of Shenzhen National Key Lab of Health Science and Technology and the Key Lab of Gene and Antibody Therapy; from the Ministry of Science and Technology of China through the National “973” Key Research Program grant 2005CCA03500; and from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) through grant 30570960.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, H., Mei, L., Zhou, L. et al. PTEN restoration and PIK3CB knockdown synergistically suppress glioblastoma growth in vitro and in xenografts. J Neurooncol 104, 155–167 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-010-0492-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-010-0492-2