Abstract
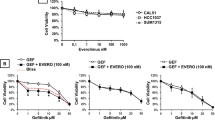
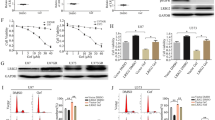
The antiproliferative effect of tandem somatostatin receptor (SSTR) activation, epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) inhibition, and induction of DNA damage was analyzed using octreotide (OCT), a SSTR agonist, the clinical DNA methylating agent temozolomide (TMZ), Iressa, an EGFR inhibitor, and dual EGFR-DNA targeting agents termed “combi-molecules”. Using SSTR-expressing glioma cells harbouring low levels of EGFR (U87MG) or transfected to overexpress EGFR (U87/EGFR) or a variant (U87/EGFRvIII), we showed that Iressa, alone or in combination with the DNA damaging agent TMZ, and combi-molecules RA2 and RA5 inhibited EGF-induced phosphorylation of EGFR in U87MG and more moderately in U87/EGFR and U87/EGFRvIII transfected cells. This translated into equivalent levels of Erk 1/2 inhibition. Activation of SSTRs with OCT did not modulate the effects of the various treatments on Erk 1/2 phosphorylation. Likewise, SSTR activation did not alter TMZ- or DNA-damaging combi-molecules, RA2 and RA5, induced p53 activation nor upregulation. However, SSTR activation significantly shifted TMZ-, RA2- and RA5-induced cell-cycle arrest to earlier phases (i.e., G2/M to late S, late S to S, S to G1). Further analysis showed that apoptosis was not induced. This was in agreement with the fact that p53 activation did not induce Bax upregulation nor did EGFR inhibition promote Bad dephosphorylation. Moreover, enhancement of survivin, an anti-apoptotic protein, expression was observed. The results in toto suggest that the combination of SSTR activation with EGFR inhibition and DNA damage affects cell-cycle progression but a disconnection between the targeted signalling pathways in these brain tumour cells precludes synergistic cell-killing by the triple growth inhibitory events.











Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ATM:
-
Ataxia-telangiectasia
- ATR:
-
ATM and Rad-3-related
- BER:
-
Base excision repair
- DMSO:
-
Dimethyl sulfoxide
- EGF:
-
Epidermal growth factor
- ErbBs:
-
Epidermal growth factor receptors
- GPCR:
-
G protein-coupled receptors
- MAPK:
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinase
- NER:
-
Nucleotide excision repair
- OCT:
-
Octreotide
- PBST:
-
0.1% Tween 20 (v/v) in phosphate-buffered saline
- PGT:
-
Poly(L-glutamic acid–L-tyrosine 4:1)
- PI:
-
Propidium iodide
- PVDF:
-
Poly(vinylidene difluoride)
- RTK:
-
Receptor tyrosine kinase
- SST:
-
Somatostatin
- SSTR:
-
Somatostatin receptor
- TK:
-
Tyrosine kinase
- TKI:
-
Tyrosine kinase inhibitor
- TMB:
-
Tetramethylbenzidine peroxidase substrate
- TMZ:
-
Temozolomide
References
Merayo N, Rachid Z, Qiu Q, Brahimi F, Jean-Claude BJ (2006) The combi-targeting concept: evidence for the formation of a novel inhibitor in vivo. Anticancer Drugs 17:165–171
Banerjee R, Rachid Z, McNamee J, Jean-Claude BJ (2003) Synthesis of a prodrug designed to release multiple inhibitors of the epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase and an alkylating agent: a novel tumor targeting concept. J Med Chem 46:5546–5551
Qiu Q, Dudouit F, Matheson SL, Brahimi F, Banerjee R, McNamee JP, Jean-Claude BJ (2003) The combi-targeting concept: a novel 3,3-disubstituted nitrosourea with EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitory properties. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 51:1–10
Brahimi F, Matheson SL, Dudouit F, McNamee JP, Tari AM, Jean-Claude BJ (2002) Inhibition of epidermal growth factor receptor-mediated signaling by “Combi-triazene” BJ2000, a new probe for Combi-Targeting postulates. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 303:238–246
Matheson SL, McNamee JP, Jean-Claude BJ (2001) Design of a chimeric 3-methyl-1,2,3-triazene with mixed receptor tyrosine kinase and DNA damaging properties: a novel tumor targeting strategy. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 296:832–840
He Y, Yuan XM, Lei P, Wu S, Xing W, Lan XL, Zhu HF, Huang T, Wang GB, An R, Zhang YX, Shen GX (2009) The antiproliferative effects of somatostatin receptor subtype 2 in breast cancer cells. Acta Pharmacol Sin 30:1053–1059
Watt HL, Kharmate GD, Kumar U (2009) Somatostatin receptors 1 and 5 heterodimerize with epidermal growth factor receptor: agonist-dependent modulation of the downstream MAPK signalling pathway in breast cancer cells. Cell Signal 21:428–439
Burghardt B, Barabás K, Marcsek Z, Flautner L, Gress TM, Varga G (2000) Inhibitory effect of a long-acting somatostatin analogue on EGF-stimulated cell proliferation in Capan-2 cells. J Physiol Paris 94:57–62
Lev DC, Kim LS, Melnikova V, Ruiz M, Ananthaswamy HN, Price JE (2004) Dual blockade of EGFR and ERK1/2 phosphorylation potentiates inhibition of breast cancer cells. Br J Cancer 91:795–802
Okubo S, Kurebayashi J, Otsuki T, Yamamoto Y, Tanaka K, Sonoo H (2004) Additive antitumor effect of the epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor gefinitib (Iressa, ZD1839) and the antioestrogen fulvestrant (Faslodex, ICI 182, 780) in breast cancer cells. Br J Cancer 90:236–244
Olayioye MA, Neve RM, Lane H, Hynes NE (2000) The ErbB signaling network: receptor heterodimerization in development and cancer. EMBO J 19:3159–3167
Huang S, Armstrong EA, Benavente S, Chinnaiyan P, Harari PM (2004) Dual-agent molecular targeting of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR): combining anti-EGFR with tyrosine kinase inhibitor. Cancer Res 64:5355–5362
Matheson SL (2003) The combi-targeting concept: a novel tumour targeting strategy. Medicine. McGill University, Montreal, p 229
Dragowska WH, Verreault M, Yapp DTT, Warburton C, Edwards L, Ramsay EC, Huxham LA, Minchinton AI, Gelmon K, Bally MB (2006) Gefitinib treatment decreases energy and metabolic stress and increases activation of the mTOR pathway in ER+ HER-2-overexpressing breast cancer. Reasons for Hope Fourth Scientific Conference, 2006, Toronto, Ontario, Canada (Canadian Breast Cancer Research Alliance), 180
Patel YC, Greenwood MT, Panetta R, Demschyshyn L, Niznik H, Srikant CB (1995) Mini review: the somatostatin receptor family. Life Sci 57:1249–1265
Csaba Z, Dournaud P (2001) Cellular biology of somatostatin receptors. Neuropeptides 35:1–23
Florio T, Thellung S, Arena S, Corsaro A, Spaziante R, Gussoni G, Acuto G, Giusti M, Giordano G, Schettini G (1999) Somatostatin and its analog lanreotide inhibit the proliferation of dispersed human non-functioning pituitary adenoma cells in vitro. Eur J Endocrinol 141:396–408
Lahlou H, Guillermet J, Hortala M, Vernejoul F, Pyronnet S, Bousquet C, Susini C (2004) Molecular signaling of somatostatin receptors. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1014:121–131
Rachid Z, Brahimi F, Qiu Q, Williams C, Hartley JM, Hartley JA, Jean-Claude BJ (2007) Novel nitrogen mustard-armed combi-molecules for the selective targeting of epidermal growth factor receptor overexpressing solid tumors: discovery of an unusual structure-activity relationship. J Med Chem 50:2605–2608
Matheson SL, McNamee J, Jean-Claude BJ (2003) Differential responses of EGFR-/AGT-expressing cells to the “combi-triazene” SMA41. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 51:11–20
Heravi M, Rachid Z, Goudarzi A, Schlisser A, Jean-Claude BJ, Radzioch D, Muanza TM (2009) Interaction of ionizing radiation and ZRBA1, a mixed EGFR/DNA-targeting molecule. Anticancer Drugs 20:659–667
Qiu Q, Domarkas J, Banerjee R, Katsoulas A, McNamee JP, Jean-Claude BJ (2007) Type II combi-molecules: design and binary targeting properties of the novel triazolinium-containing molecules JDD36 and JDE05. Anticancer Drugs 18:171–177
Qiu Q, Dudouit F, Banerjee R, McNamee JP, Jean-Claude BJ (2004) Inhibition of cell signaling by the combi-nitrosourea FD137 in the androgen independent DU145 prostate cancer cell line. Prostate 59:13–21
Brahimi F, Rachid Z, Qiu Q, McNamee JP, Li YJ, Tari AM, Jean-Claude BJ (2004) Multiple mechanisms of action of ZR2002 in human breast cancer cells: a novel combi-molecule designed to block signaling mediated by the ERB family of oncogenes and to damage genomic DNA. Int J Cancer 112:1066–1073
Brahimi F, Rachid Z, McNamee JP, Alaoui-Jamali MA, Tari AM, Jean-Claude BJ (2005) Mechanism of action of a novel “combi-triazene” engineered to possess a polar functional group on the alkylating moiety: evidence for enhancement of potency. Biochem Pharmacol 70:511–519
Banerjee R, Rachid Z, Qiu Q, McNamee JP, Tari AM, Jean-Claude BJ (2004) Sustained antiproliferative mechanisms by RB24, a targeted precursor of multiple inhibitors of epidermal growth factor receptor and a DNA alkylating agent in the A431 epidermal carcinoma of the vulva cell line. Br J Cancer 91:1066–1073
Kumar U, Grigorakis SI, Watt HL, Sasi R, Snell L, Watson P, Chaudhari S (2005) Somatostatin receptors in primary human breast cancer: quantitative analysis of mRNA for subtypes 1–5 and correlation with receptor protein expression and tumor pathology. Breast Cancer Res Treat 92:175–186
Kumar U, Sasi R, Suresh S, Patel A, Thangaraju M, Metrakos P, Patel SC, Patel YC (1999) Subtype-selective expression of the five somatostatin receptors (hSSTR1–5) in human pancreatic islet cells. Diabetes 48:77–85
Tian XX, Zhang YG, Du J, Fang WG, Ng HK, Zheng J (2006) Effects of cotransfection of antisense-EGFR and wild-type PTEN cDNA on human glioblastoma cells. Neuropathology 26:178–187
Geoerger B, Vassal G, Opolon P, Dirven CM, Morizet J, Laudani L, Grill J, Giaccone G, Vandertop WP, Gerritsen WR, van Beusechem VW (2004) Oncolytic activity of p53-expressing conditionally replicative adenovirus AdDelta24–p53 against human malignant glioma. Cancer Res 64:5753–5759
Sawa H, Kamada H, Ohshima TA, Noguchi A, Itoh N, Saruta K, Hara M, Saito I (1999) Exogenous expression of p16INK4a is associated with decrease in telomerase activity. J Neurooncol 42:45–57
Matheson SL, McNamee JP, Wang T, Alaoui-Jamali MA, Tari AM, Jean-Claude BJ (2004) The combi-targeting concept: dissection of the binary mechanism of action of the combi-triazene SMA41 in vitro and antitumor activity in vivo. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 311:1163–1170
Cattaneo MG, Gentilini D, Vicentini LM (2006) Deregulated human glioma cell motility: inhibitory effect of somatostatin. Mol Cell Endocrinol 256:34–39
Beutler D, Avoledo P, Reubi J-C, Macke HR, Muller-Brand J, Merlo A, Kuhne T (2005) Three-year recurrence-free survival in a patient with recurrent medulloblastoma after resection, high-dose chemotherapy, and intrathecal Yttrium-90-labeled DOTA0-D-Phe1-Tyr3-octreotide radiopeptide brachytherapy. Cancer 103:869–873
Cervera P, Videau C, Viollet C, Petrucci C, Lacombe J, Winsky-Sommerer R, Csaba Z, Helboe L, Daumas-Duport C, Reubi J-C, Epelbaum J (2002) Comparison of somatostatin receptor expression in human gliomas and medulloblastomas. J Neuroendocrinol 14:458–471
Viollet C, Lepousez G, Loudes C, Videau C, Simon A, Epelbaum J (2008) Somatostatinergic systems in brain: networks and functions. Mol Cell Endocrinol 286:75–87
Caporali S, Falcinelli S, Starace G, Russo MT, Bonmassar E, Jiricny J, D’Atri S (2004) DNA damage induced by temozolomide signals to both ATM and ATR: role of the mismatch repair system. Mol Pharmacol 66:478–491
Senderowicz AM (2004) Targeting cell cycle and apoptosis for the treatment of human malignancies. Curr Opin Cell Biol 16:670–678
Mita AC, Mita MM, Nawrocki ST, Giles FJ (2008) Survivin: key regulator of mitosis and apoptosis and novel target for cancer therapeutics. Clin Cancer Res 14:5000–5005
Altieri DC (2006) The case for survivin as a regulator of microtubule dynamics and cell-death decisions. Curr Opin Cell Biol 18:609–615
Altieri DC (2004) Molecular circuits of apoptosis regulation and cell division control: the survivin paradigm. J Cell Biochem 92:656–663
Altieri DC (2003) Survivin, versatile modulation of cell division and apoptosis in cancer. Oncogene 22:8581–8589
Massa A, Barbieri F, Aiello C, Arena S, Pattarozzi A, Pirani P, Corsaro A, Iuliano R, Fusco A, Zona G, Spaziante R, Florio T, Schettini G (2004) The expression of the phosphotyrosine phosphatase DEP-1/PTPeta dictates the responsivity of glioma cells to somatostatin inhibition of cell proliferation. J Biol Chem 279:29004–29012
Held-Feint J, Forstreuter F, Pufe T, Mentlein R (2001) Influence of the somatostatin receptor sst2 on growth factor signal cascades in human glioma cells. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 87:12–21
Feindt J, Becker I, Blömer U, Hugo HH, Mehdorn HM, Krisch B, Mentlein R (1995) Expression of somatostatin receptor subtypes in cultured astrocytes and gliomas. J Neurochem 65:1997–2005
Sharma K, Srikant CB (1998) Induction of wild-type p53 Bax and acidic endonuclease during somatostatin signaled apoptosis in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells. Int J Cancer 76:259–266
Pagès P, Benali N, Saint-Laurent N, Estève JP, Schally AV, Tkaczuk J, Vaysse N, Susini C, Buscail L (1999) sst2 somatostatin receptor mediates cell-cycle arrest and induction of p27(Kip1). Evidence for the role of SHP-1. J Biol Chem 274:15186–15893
Sharma K, Patel YC, Srikant CB (1996) Subtype-selective induction of p53-dependent apoptosis but not cell-cycle arrest by human somatostatin receptor 3. Mol Endocrinol 10:1688–1696
Milano V, Piao Y, LaFortune T, de Groot J (2009) Dasatinib-induced autophagy is enhanced in combination with temozolomide in glioma. Mol Cancer Ther 8:394–406
Yin D, Wakimoto N, Xing H, Lu D, Huynh T, Wang X, Black KL, Koeffler HP (2008) Cucurbitacin B markedly inhibits growth and rapidly affects the cytoskeleton in glioblastoma multiforme. Int J Cancer 123:1364–1375
Yu C, Friday BB, Yang L, Atadja P, Wigle D, Sarkaria J, Adjei AA (2008) Mitochondrial Bax translocation partially mediates synergistic cytotoxicity between histone deacetylase inhibitors and proteasome inhibitors in glioma cells. Neuro Oncol 10:309–319
Acknowledgements
We would like to acknowledge the Canadian Institute for Health Research (CIHR) and the Brain Tumour Foundation of Canada for financial support. HW was supported by a McGill University Health Centre Research Institute Studentship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Watt, H.L., Rachid, Z. & Jean-Claude, B.J. Receptor activation and inhibition in cellular response to chemotherapeutic combinational mimicries: the concept of divergent targeting. J Neurooncol 100, 345–361 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-010-0196-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-010-0196-7