Abstract
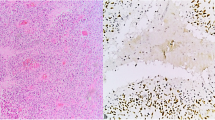
Signal transducer and activator of transcription protein 3 (STAT3) is a regulator of central nervous system (CNS) development and a promising therapeutic target in human cancers. Activation of STAT3 promotes oncogenesis in a variety of tissues, but knowledge of its role in glioblastoma is still limited. Recent results indicate that STAT3 acts as a tumor suppressor or an oncogene depending upon the genetic background of the tumor. Here we immunohistochemically assessed Y705-phosphorylated STAT3 (pY705-STAT3) in formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded specimens of 111 patients with supratentorial glioblastomas and 25 patients with supratentorial grade III gliomas. We found that glioblastoma patients with high or very high numbers of pY705-STAT3-positive tumor cells had significantly shorter overall survival than those with no or low numbers (P = 0.001, Cox regression). Interestingly the proportion of grade III glioma cases with high or very high numbers of pY705-STAT3-positive tumor cells was similar to that in glioblastoma. Our findings provide evidence that activation of STAT3 by Y705 phosphorylation is linked with clinically more aggressive behavior in glioblastomas, but is most likely not associated with tumor progression of grade III gliomas. In sum, our results suggest that STAT3 inhibition should be considered as a therapeutic approach in malignant gliomas.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bromberg JF, Darnell JE Jr (1999) Potential roles of Stat1 and Stat3 in cellular transformation. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol 64:425–428
Germain D, Frank DA (2007) Targeting the cytoplasmic and nuclear functions of signal transducers and activators of transcription 3 for cancer therapy. Clin Cancer Res 13:5665–5669
Kamakura S, Oishi K, Yoshimatsu T, Nakafuku M, Masuyama N, Gotoh Y (2004) Hes binding to STAT3 mediates crosstalk between Notch and JAK-STAT signalling. Nat Cell Biol 6:547–554
Levy DE, Lee CK (2002) What does Stat3 do? J Clin Invest 109:1143–1148
Schlessinger K, Levy DE (2005) Malignant transformation but not normal cell growth depends on signal transducer and activator of transcription 3. Cancer Res 65:5828–5834
Brantley EC, Benveniste EN (2008) Signal transducer and activator of transcription-3: a molecular hub for signaling pathways in gliomas. Mol Cancer Res 6:675–684
Schaefer LK, Menter DG, Schaefer TS (2000) Activation of stat3 and stat1 DNA binding and transcriptional activity in human brain tumour cell lines by gp130 cytokines. Cell Signal 12:143–151
Schaefer LK, Ren Z, Fuller GN, Schaefer TS (2002) Constitutive activation of Stat3alpha in brain tumors: localization to tumor endothelial cells and activation by the endothelial tyrosine kinase receptor (VEGFR-2). Oncogene 21:2058–2065
Wang H, Wang H, Zhang W, Huang HJ, Liao WS, Fuller GN (2004) Analysis of the activation status of Akt, NFkappaB, and Stat3 in human diffuse gliomas. Lab Invest 84:941–951
Weissenberger J, Loeffler S, Kappeler A et al (2004) IL-6 is required for glioma development in a mouse model. Oncogene 23:3308–3316
Dasgupta A, Raychaudhuri B, Haqqi T et al (2009) Stat3 activation is required for the growth of U87 cell-derived tumours in mice. Eur J Cancer 45:677–684
Zhang L, Alizadeh D, Van Handel M, Kortylewski M, Yu H, Badie B (2009) Stat3 inhibition activates tumor macrophages and abrogates glioma growth in mice. Glia 57:1458–1467
Peñuelas S, Anido J, Prieto-Sánchez R et al (2009) TGF-beta increases glioma-initiating cell self-renewal through the induction of LIF in human glioblastoma. Cancer Cell 15:315–327
Sherry MM, Reeves A, Wu JK, Cochran BH (2009) STAT3 is required for proliferation and maintenance of multipotency in glioblastoma stem cells. Stem Cells 27:2383–2392
Paillaud E, Costa S, Fages C et al (2009) Retinoic acid increases proliferation rate of GL-15 glioma cells, involving activation of STAT-3 transcription factor. J Neurosci Res 67:670–679
Blaskovich MA, Sun J, Cantor A, Turkson J, Jove R, Sebti SM (2003) Discovery of JSI-124 (cucurbitacin I), a selective Janus kinase/signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 signaling pathway inhibitor with potent antitumor activity against human and murine cancer cells in mice. Cancer Res 63:1270–1279
Rahaman SO, Vogelbaum MA, Haque SJ (2005) Aberrant Stat3 signaling by interleukin-4 in malignant glioma cells: involvement of IL-13Ralpha2. Cancer Res 65:2956–2963
Konnikova L, Kotecki M, Kruger MM, Cochran BH (2003) Knockdown of STAT3 expression by RNAi induces apoptosis in astrocytoma cells. BMC Cancer 3:23
Lo HW, Cao X, Zhu H, Ali-Osman F (2008) Constitutively activated STAT3 frequently coexpresses with epidermal growth factor receptor in high-grade gliomas and targeting STAT3 sensitizes them to Iressa and alkylators. Clin Cancer Res 14:6042–6054
Iwamaru A, Szymanski S, Iwado E et al (2007) A novel inhibitor of the STAT3 pathway induces apoptosis in malignant glioma cells both in vitro and in vivo. Oncogene 26:2435–2444
Lee J, Son MJ, Woolard K et al (2008) Epigenetic-mediated dysfunction of the bone morphogenetic protein pathway inhibits differentiation of glioblastoma-initiating cells. Cancer Cell 13:69–80
Halfter H, Friedrich M, Postert C, Ringelstein EB, Stögbauer F (1999) Activation of Jak-Stat and MAPK2 pathways by oncostatin M leads to growth inhibition of human glioma cells. Mol Cell Biol Res Commun 1:109–116
Mizoguchi M, Betensky RA, Batchelor TT, Bernay DC, Louis DN, Nutt CL (2006) Activation of STAT3, MAPK, and AKT in malignant astrocytic gliomas: correlation with EGFR status, tumor grade, and survival. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 65:1181–1188
Fujita M, Zhu X, Sasaki K et al (2008) Inhibition of STAT3 promotes the efficacy of adoptive transfer therapy using type-1 CTLs by modulation of the immunological microenvironment in a murine intracranial glioma. J Immunol 180:2089–2098
Cattaneo E, Magrassi L, De-Fraja C et al (1998) Variations in the levels of the JAK/STAT and ShcA proteins in human brain tumors. Anticancer Res 18:2381–2387
Ehrmann J, Strakova N, Vrzalikova K, Hezova R, Kolar Z (2008) Expression of STATs and their inhibitors SOCS and PIAS in brain tumors. In vitro and in vivo study. Neoplasma 55:482–487
Ghosh MK, Sharma P, Harbor PC, Rahaman SO, Haque SJ (2005) PI3K-AKT pathway negatively controls EGFR-dependent DNA-binding activity of Stat3 in glioblastoma multiforme cells. Oncogene 24:7290–7300
de la Iglesia N, Konopka G, Puram SV et al (2008) Identification of a PTEN-regulated STAT3 brain tumor suppressor pathway. Genes Dev 22:449–462
Yoshimatsu T, Kawaguchi D, Oishi K et al (2006) Non-cell-autonomous action of STAT3 in maintenance of neural precursor cells in the mouse neocortex. Development 133:2553–2563
Singh SK, Hawkins C, Clarke ID et al (2004) Identification of human brain tumour initiating cells. Nature 432:396–401
Yu H, Jove R (2004) The STATs of cancer—new molecular targets come of age. Nat Rev Cancer 4:97–105
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Dr. Johannes Hainfellner, Vienna, for advice and critical discussions. This work was supported by European Union Social Fund Program BG051PO001/07/3.3-02 grant number 80/17.06.2008 and BSF grant number Д01-840/16.10.2007.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Birner, P., Toumangelova-Uzeir, K., Natchev, S. et al. STAT3 tyrosine phosphorylation influences survival in glioblastoma. J Neurooncol 100, 339–343 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-010-0195-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-010-0195-8