Abstract
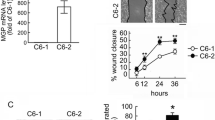
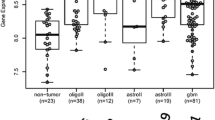
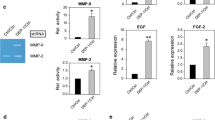
High grade gliomas invariably recur due in a large part to tumor cells permeating normal brain in an inaccessible, diffuse manner. Previous work demonstrates that the expression of matrix metalloproteinases (MMP) contributes to this characteristic. Not only can MMPs assist a cell in traversing its environment by clearing extracellular matrix molecules, but they can also impact non-traditional downstream signals that affect a cell’s ability to interact and respond to its surroundings. Contributions to the induction of MMP expression and functional significance in glioma are still under investigation. Evidence in other cancer settings indicates that nitric oxide (NO) may play a role in tumor/cell progression that can influence MMP production. Matrix metalloproteinase-1 (MMP-1), also known as interstitial collagenase, and the constitutive nitric oxide synthases (NOS) have been shown to be over-expressed in high grade gliomas. In the current study we investigated the potential involvements of NO with regard to MMP-1 and functional glioma cell movement. With the treatment of the NO donor sodium nitroprusside (SNP), there was significant induction of MMP-1 mRNA, secreted MMP-1 protein and motility of glioma cell lines within 48 h. RNA inhibition of MMP-1 through transient transfection of three MMP-1 specific siRNAs revealed a marked abrogation of the NO-mediated induction of motility. In addition, application of the NOS inhibitor Nω-Nitro-l-arginine methyl ester (l-NAME) impaired movement of glioma cells. These data provide evidence for a regulatory axis of high grade glioma cell movement from NO through MMP-1, with NOS inhibitor results showing promise for future pharmacologic investigation.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Buckner JC, Brown PD, O’Neil BP, Meyer FB, Wetmore CJ, Uhm JH (2007) Central nervous system tumors. Mayo Clin Proc 82:1271–1286
McKinney PA (2004) Brain tumors: incidence, survival, and aetiology. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 75((Suppl. 2)):12–17
Fisher JL, Schwartzbaum JA, Wrensch M, Wiemels JL (2007) Epidemiology of brain tumors. Neurol Clin 25:867–890
Krex D, Klink B, Hartmann C et al (2007) Long-term survival with glioblastoma multiforme. Brain 130:2596–2606
Louis DN, Pomeroy SL, Cairncross JG (2002) Focus on central nervous system neoplasia. Cancer Cell 1:125–128
Lam-Himlin D, Espey MG, Perry G, Smith MA, Castellani RJ (2006) Malignant glioma progression and nitric oxide. Neurochem Int 49:764–768
VanMeter TE, Rooprai HK, Kibble MM, Fillmore HL, Broaddus WC, Pilkington GJ (2001) The role of matrix metalloproteinase genes in glioma invasion: co-dependent and interactive proteolysis. J Neurooncol 53:213–235
Fillmore HL, VanMeter TE, Broaddus WC (2001) Membrane-type metalloproteinases (MT-MMPs): expression and function during glioma invasion. J Neurooncol 53:187–202
Nakano A, Tani E, Miyazaki K, Yamamoto Y, Furuyama J (1995) Matrix metalloproteinases and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases in human gliomas. J Neurosurg 83(2):298–307
Stojic J, Hagemann C, Haas S et al (2008) Expression of matrix metalloproteinases MMP-1, MMP-11 and MMP-19 is correlated with the WHO-grading of human malignant gliomas. Neurosci Res 60(1):40–49
McCawley LJ, Matrisian LM (2001) Matrix metalloproteinases: they’re not just for matrix anymore! Curr Opin Cell Biol 13:534–540
McCready J, Broaddus WC, Sykes V, Fillmore HL (2005) Association of a single nucleotide polymorphism in the matrix metalloproteinase-1 promoter with glioblastoma. Int J Cancer 117:781–785
Yoshida M, Sagawa N, Itoh H et al (2001) Nitric oxide increases matrix metalloproteinase-1 production in human uterine cervical fibroblast cells. Mol Hum Reprod 7:979–985
Choe T, Lee B, Park I, Hong S (2003) Inhibition of matrix metalloproteinase-1 and -2 expression using nitric oxide synthase inhibitors in UV-irradiated human dermal fibroblasts. J Cosmet Sci 54:229–238
Ishii Y, Ogura T, Tatemichi M, Fujisawa H, Otsuka F, Esumi H (2002) Induction of matrix metalloproteinase gene transcription by nitric oxide and mechanisms of MMP-1 gene induction in human melanoma cell lines. Int J Cancer 103:161–168
Cobbs CS, Brenman JE, Aldape KD, Bredt DS, Israel MA (1995) Expression of nitric oxide synthase in human central nervous system tumors. Cancer Res 55:727–730
Kao CL, Chiou SH, Chen HS et al (2003) Elevated nitric oxide levels in childhood brain tumors. Childs Nerv Syst 19:744–749
Bakshi A, Nag TC, Wadhwa S, Mahapatra AK, Sarkar C (1998) The expression of nitric oxide synthases in human brain tumours and peritumoral areas. J Neurol Sci 155:196–203
Iwata S, Nakagawa K, Harada H, Oka Y, Kumon Y, Sakaki S (1999) Endothelial nitric oxide synthase expression in tumor vasculature is correlated with malignancy in human supratentorial astrocytic tumors. Neurosurgery 45:24–28
Ludwig HC, Feiz-Erfan I, Bockermann V, Behnke-Mursch J, Schallock K, Markakis E (2000) Expression of nitric oxide synthase (NOS I-III) by immunohistochemistry and DNA in situ hybridization. Correlation with macrophage presence, vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and oedema volumetric data in 220 glioblastomas. Anticancer Res 20:299–304
Ludwig HC, Ahkavan-Shigari R, Rausch S et al (2000) Oedema extension in cerebral metastasis and correlation with the expression of nitric oxide synthase isozymes (NOS I-III). Anticancer Res 20:305–310
Erdamar S, Bagci P, Oz B, Dirican A (2006) Correlation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase and vascular endothelial growth factor expression with malignancy in patients with astrocytic tumors. J BUON 11:213–216
Broholm H, Braendstrup O, Lauritzen M (2001) Nitric oxide synthase expression of oligodendrogliomas. Clin Neuropathol 20:233–238
Broholm H, Rubin I, Kruse A et al (2003) Nitric oxide synthase expression and enzymatic activity in human brain tumors. Clin Neuropathol 22:273–281
Fukumura D, Kashiwagi S, Jain RK (2006) The role of nitric oxide in tumour progression. Nat Rev Cancer 6:521–534
Ridnour LA, Thomas DD, Donzelli S et al (2006) The biphasic nature of nitric oxide responses in tumor biology. Antioxid Redox Signal 8:1329–1337
Ederli L, Reale L, Madeo L et al (2009) NO release by nitric oxide donors in vitro and in planta. Plant Physiol Biochem 47(1):42–48
Jaffrey SR, Erdjument-Bromage H, Ferris CD, Tempst P, Snyder SH (2001) Protein S-nitrosylation: a physiological signal for neuronal nitric oxide. Nat Cell Biol 3(2):193–197
Limb GA, Matter K, Murphy G et al (2005) Matrix metalloproteinase-1 associates with intracellular organelles and confers resistance to lamin A/C degradation during apoptosis. Am J Pathol 166(5):1555–1563
Hodgson JG, Yeh RF, Ray A et al. (2009) Comparative analyses of gene copy number and mRNA expression in GBM tumors and GBM xenografts. Neuro Oncol [Epub ahead of print]
Lin YM, Jan HJ, Lee CC et al (2008) Dexamethasone reduced invasiveness of human malignant glioblastoma cells through a MAPK phosphatase-1 (MKP-1) dependent mechanism. Eur J Pharmacol 593:1–9
Wang F, Zhang R, Xia T et al (2007) Inhibitory effects of nitric oxide on invasion of human cancer cells. Cancer Lett 257(2):274–282
Kaur B, Khwaja FW, Severson EA, Matheny SL, Brat DJ, Van Meir EG (2005) Hypoxia and the hypoxia-inducible-factor pathway in glioma growth and angiogenesis. Neuro Oncol 7(2):134–153
Gu Z, Kaul M, Yan B et al (2002) S-nitrosylation of matrix metalloproteinases: signaling pathway to neuronal cell death. Science 297:1186–1190
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the Nucleic Acids Research Facilities of the Massey Cancer Center, VCU for their performance of the real time PCR assays. Funding for this work was provided by the Hord Fund of the MCV Foundation. We are also grateful for the continued support of Dr. Harold Young, Chairman, Department of Neurosurgery at VCUHS.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pullen, N.A., Fillmore, H.L. Induction of matrix metalloproteinase-1 and glioma cell motility by nitric oxide. J Neurooncol 96, 201–209 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-009-9965-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-009-9965-6