Abstract
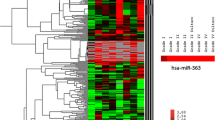
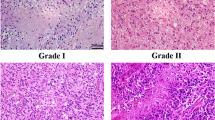
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small noncoding regulatory RNAs that reduce stability and/or translation of fully or partially sequence-complementary target mRNAs. Recent evidence indicates that miRNAs can function both as tumor suppressors and as oncogenes. It has been demonstrated that in glioblastoma multiforme miR-21 and 221 are upregulated whereas miR-128 and 181 are downregulated. Expression of miR-21, 221, 128a, 128b, 128c, 181a, 181b, 181c was studied using real-time quantitative reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction and northern blotting for human astrocytic tumors with different grade of malignancy. miR-21 and 221 were overexpressed in glioma samples, whereas miRNA 181b was downregulated compared with normal brain tissue. miRNA-21 was hyperexpressed in all tumor samples whereas higher levels of miRNA-221 were found in high-grade gliomas. This study is the first analysis of miRNAs in astrocytic tumor at different stages of malignancy. The different expression pattern observed in tumors at different stages of malignancy is probably dependent on the cell-specific repertoire of target genes of tumors sharing different molecular pathways activity and suggests miRNAs may have also a place in diagnosis and staging of brain tumors.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
de Moor CH, Meijer H, Lissenden S (2005) Mechanisms of translational control by the 3′ UTR in development and differentiation. Semin Cell Dev Biol 16:49–58. doi:10.1016/j.semcdb.2004.11.007
Lai EC (2002) Micro RNAs are complementary to 3′ UTR sequence motifs that mediate negative post-transcriptional regulation. Nat Genet 30:363–364. doi:10.1038/ng865
Robins H, Press WH (2005) Human microRNAs target a functionally distinct population of genes with AT-rich 3′ UTRs. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:15557–15562. doi:10.1073/pnas.0507443102
Stark A, Brennecke J, Bushati N, Russell RB, Cohen SM (2005) Animal microRNAs confer robustness to gene expression and have a significant impact on 3′UTR evolution. Cell 123:1133–1146. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2005.11.023
Sun M, Hurst LD, Carmichael GG, Chen J (2005) Evidence for a preferential targeting of 3′-UTRs by cis-encoded natural antisense transcripts. Nucleic Acids Res 33:5533–5543. doi:10.1093/nar/gki852
Meltzer PS (2005) Cancer genomics: small RNAs with big impacts. Nature 435:745–746. doi:10.1038/435745a
Ro S, Park C, Young D, Sanders KM, Yan W (2007) Tissue-dependent paired expression of miRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res 35:5944–5953. doi:10.1093/nar/gkm641
Denli AM, Tops BB, Plasterk RH, Ketting RF, Hannon GJ (2004) Processing of primary microRNAs by the Microprocessor complex. Nature 432:231–235. doi:10.1038/nature03049
Hammond SM, Bernstein E, Beach D, Hannon GJ (2000) An RNA-directed nuclease mediates post-transcriptional gene silencing in Drosophila cells. Nature 404:293–296. doi:10.1038/35005107
Berezikov E, Guryev V, van de Belt J, Wienholds E, Plasterk RH, Cuppen E (2005) Phylogenetic shadowing and computational identification of human microRNA genes. Cell 120:21–24. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2004.12.031
Lewis BP, Burge CB, Bartel DP (2005) Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell 120:15–20. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2004.12.035
Reinhart BJ, Slack FJ, Basson M, Pasquinelli AE, Bettinger JC, Rougvie AE, Horvitz HR, Ruvkun G (2000) The 21-nucleotide let-7 RNA regulates developmental timing in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature 403:901–906. doi:10.1038/35002607
Cheng LC, Tavazoie M, Doetsch F (2005) Stem cells: from epigenetics to microRNAs. Neuron 46:363–367. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2005.04.027
Hatfield SD, Shcherbata HR, Fischer KA, Nakahara K, Carthew RW, Ruohola-Baker H (2005) Stem cell division is regulated by the microRNA pathway. Nature 435:974–978. doi:10.1038/nature03816
Cimmino A, Calin GA, Fabbri M, Iorio MV, Ferracin M, Shimizu M, Wojcik SE, Aqeilan RI, Zupo S, Dono M, Rassenti L, Alder H, Volinia S, Liu CG, Kipps TJ, Negrini M, Croce CM (2005) miR-15 and miR-16 induce apoptosis by targeting BCL2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:13944–13949. doi:10.1073/pnas.0506654102
Abelson JF, Kwan KY, O’Roak BJ, Baek DY, Stillman AA, Morgan TM, Mathews CA, Pauls DL, Rasin MR, Gunel M, Davis NR, Ercan-Sencicek AG, Guez DH, Spertus JA, Leckman JF, Dure LS, Kurlan R, Singer HS, Gilbert DL, Farhi A, Louvi A, Lifton RP, Sestan N, State MW (2005) Sequence variants in SLITRK1 are associated with Tourette’s syndrome. Science 310:317–320. doi:10.1126/science.1116502
Alvarez-Garcia I, Miska EA (2005) MicroRNA functions in animal development and human disease. Development 132:4653–4662. doi:10.1242/dev.02073
Volinia S, Calin GA, Liu CG, Ambs S, Cimmino A, Petrocca F, Visone R, Iorio M, Roldo C, Ferracin M, Prueitt RL, Yanaihara N, Lanza G, Scarpa A, Vecchione A, Negrini M, Harris CC, Croce CM (2006) A microRNA expression signature of human solid tumors defines cancer gene targets. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:2257–2261. doi:10.1073/pnas.0510565103
Dalmay T (2008) MicroRNAs and cancer. J Intern Med 263:366–375. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2796.2008.01926.x
Cho WC (2007) OncomiRs: the discovery and progress of microRNAs in cancers. Mol Cancer 6:60. doi:10.1186/1476-4598-6-60
Calin GA, Liu CG, Sevignani C, Ferracin M, Felli N, Dumitru CD, Shimizu M, Cimmino A, Zupo S, Dono M, Dell’Aquila ML, Alder H, Rassenti L, Kipps TJ, Bullrich F, Negrini M, Croce CM (2004) MicroRNA profiling reveals distinct signatures in B cell chronic lymphocytic leukemias. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:11755–11760. doi:10.1073/pnas.0404432101
Michael MZ, O’ Connor SM, van Holst Pellekaan NG, Young GP, James RJ (2003) Reduced accumulation of specific microRNAs in colorectal neoplasia. Mol Cancer Res 1:882–891
Takamizawa J, Konishi H, Yanagisawa K, Tomida S, Osada H, Endoh H, Harano T, Yatabe Y, Nagino M, Nimura Y, Mitsudomi T, Takahashi T (2004) Reduced expression of the let-7 microRNAs in human lung cancers in association with shortened postoperative survival. Cancer Res 64:3753–3756. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-0637
Nicoloso MS, Calin GA (2008) MicroRNA involvement in brain tumors: from bench to bedside. Brain Pathol 18:122–129. doi:10.1111/j.1750-3639.2007.00119.x
Ciafre SA, Galardi S, Mangiola A, Ferracin M, Liu CG, Sabatino G, Negrini M, Maira G, Croce CM, Farace MG (2005) Extensive modulation of a set of microRNAs in primary glioblastoma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 334:1351–1358. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2005.07.030
Chan JA, Krichevsky AM, Kosik KS (2005) MicroRNA-21 is an antiapoptotic factor in human glioblastoma cells. Cancer Res 65:6029–6033. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-0137
Louis DN, Ohgaki H, Wiestler OD, Cavenee WK, Burger PC, Jouvet A, Scheithauer BW, Kleihues P (2007) The 2007 WHO classification of tumours of the central nervous system. Acta Neuropathol 114:97–109. doi:10.1007/s00401-007-0243-4
Lee RC, Feinbaum RL, Ambros V (1993) The C. elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14. Cell 75:843–854. doi:10.1016/0092-8674(93)90529-Y
Pasquinelli AE, Reinhart BJ, Slack F, Martindale MQ, Kuroda MI, Maller B, Hayward DC, Ball EE, Degnan B, Muller P, Spring J, Srinivasan A, Fishman M, Finnerty J, Corbo J, Levine M, Leahy P, Davidson E, Ruvkun G (2000) Conservation of the sequence and temporal expression of let-7 heterochronic regulatory RNA. Nature 408:86–89. doi:10.1038/35040556
Lagos-Quintana M, Rauhut R, Lendeckel W, Tuschl T (2001) Identification of novel genes coding for small expressed RNAs. Science 294:853–858. doi:10.1126/science.1064921
Lau NC, Lim LP, Weinstein EG, Bartel DP (2001) An abundant class of tiny RNAs with probable regulatory roles in Caenorhabditis elegans. Science 294:858–862. doi:10.1126/science.1065062
Lee RC, Ambros V (2001) An extensive class of small RNAs in Caenorhabditis elegans. Science 294:862–864. doi:10.1126/science.1065329
Landgraf P, Rusu M, Sheridan R, Sewer A, Iovino N, Aravin A, Pfeffer S, Rice A, Kamphorst AO, Landthaler M, Lin C, Socci ND, Hermida L, Fulci V, Chiaretti S, Foa R, Schliwka J, Fuchs U, Novosel A, Muller RU, Schermer B, Bissels U, Inman J, Phan Q, Chien M, Weir DB, Choksi R, De Vita G, Frezzetti D, Trompeter HI, Hornung V, Teng G, Hartmann G, Palkovits M, Di Lauro R, Wernet P, Macino G, Rogler CE, Nagle JW, Ju J, Papavasiliou FN, Benzing T, Lichter P, Tam W, Brownstein MJ, Bosio A, Borkhardt A, Russo JJ, Sander C, Zavolan M, Tuschl T (2007) A mammalian microRNA expression atlas based on small RNA library sequencing. Cell 129:1401–1414. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2007.04.040
Calin GA, Croce CM (2006) MicroRNA signatures in human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer 6:857–866. doi:10.1038/nrc1997
Iorio MV, Ferracin M, Liu CG, Veronese A, Spizzo R, Sabbioni S, Magri E, Pedriali M, Fabbri M, Campiglio M, Menard S, Palazzo JP, Rosenberg A, Musiani P, Volinia S, Nenci I, Calin GA, Querzoli P, Negrini M, Croce CM (2005) MicroRNA gene expression deregulation in human breast cancer. Cancer Res 65:7065–7070. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-1783
Si ML, Zhu S, Wu H, Lu Z, Wu F, Mo YY (2007) miR-21-mediated tumor growth. Oncogene 26:2799–2803. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1210083
Lee EJ, Gusev Y, Jiang J, Nuovo GJ, Lerner MR, Frankel WL, Morgan DL, Postier RG, Brackett DJ, Schmittgen TD (2007) Expression profiling identifies microRNA signature in pancreatic cancer. Int J Cancer 120:1046–1054. doi:10.1002/ijc.22394
Chen C, Ridzon DA, Broomer AJ, Zhou Z, Lee DH, Nguyen JT, Barbisin M, Xu NL, Mahuvakar VR, Andersen MR, Lao KQ, Livak KJ, Guegler KJ (2005) Real-time quantification of microRNAs by stem-loop RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res 33:e179. doi:10.1093/nar/gni178
Meng F, Henson R, Wehbe-Janek H, Ghoshal K, Jacob ST, Patel T (2007) MicroRNA-21 regulates expression of the PTEN tumor suppressor gene in human hepatocellular cancer. Gastroenterology 133:647–658. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2007.05.022
Ohgaki H, Kleihues P (2007) Genetic pathways to primary and secondary glioblastoma. Am J Pathol 170:1445–1453. doi:10.2353/ajpath.2007.070011
Frankel LB, Christoffersen NR, Jacobsen A, Lindow M, Krogh A, Lund AH (2008) Programmed cell death 4 (PDCD4) is an important functional target of the microRNA miR-21 in breast cancer cells. J Biol Chem 283:1026–1033. doi:10.1074/jbc.M707224200
Asangani IA, Rasheed SA, Nikolova DA, Leupold JH, Colburn NH, Post S, Allgayer H (2008) MicroRNA-21 (miR-21) post-transcriptionally downregulates tumor suppressor Pdcd4 and stimulates invasion, intravasation and metastasis in colorectal cancer. Oncogene 27:2128–2136. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1210856
Zhang H, Ozaki I, Mizuta T, Hamajima H, Yasutake T, Eguchi Y, Ideguchi H, Yamamoto K, Matsuhashi S (2006) Involvement of programmed cell death 4 in transforming growth factor-beta1-induced apoptosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene 25:6101–6112. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1209634
Gao F, Zhang P, Zhou C, Li J, Wang Q, Zhu F, Ma C, Sun W, Zhang L (2007) Frequent loss of PDCD4 expression in human glioma: possible role in the tumorigenesis of glioma. Oncol Rep 17:123–128
Zhu S, Si ML, Wu H, Mo YY (2007) MicroRNA-21 targets the tumor suppressor gene tropomyosin 1 (TPM1). J Biol Chem 282:14328–14336. doi:10.1074/jbc.M611393200
Gillies JK, Lorimer IA (2007) Regulation of p27Kip1 by miRNA 221/222 in glioblastoma. Cell Cycle 6:2005–2009
le Sage C, Nagel R, Egan DA, Schrier M, Mesman E, Mangiola A, Anile C, Maira G, Mercatelli N, Ciafre SA, Farace MG, Agami R (2007) Regulation of the p27(Kip1) tumor suppressor by miR-221 and miR-222 promotes cancer cell proliferation. EMBO J 26:3699–3708. doi:10.1038/sj.emboj.7601790
Gonzalez T, Seoane M, Caamano P, Vinuela J, Dominguez F, Zalvide J (2003) Inhibition of Cdk4 activity enhances translation of p27kip1 in quiescent Rb-negative cells. J Biol Chem 278:12688–12695. doi:10.1074/jbc.M207530200
Ishii N, Maier D, Merlo A, Tada M, Sawamura Y, Diserens AC, Van Meir EG (1999) Frequent co-alterations of TP53, p16/CDKN2A, p14ARF, PTEN tumor suppressor genes in human glioma cell lines. Brain Pathol 9:469–479
Slingerland J, Pagano M (2000) Regulation of the cdk inhibitor p27 and its deregulation in cancer. J Cell Physiol 183:10–17. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-4652(200004)183:1<10::AID-JCP2>3.0.CO;2-I
He L, Thomson JM, Hemann MT, Hernando-Monge E, Mu D, Goodson S, Powers S, Cordon-Cardo C, Lowe SW, Hannon GJ, Hammond SM (2005) A microRNA polycistron as a potential human oncogene. Nature 435:828–833. doi:10.1038/nature03552
Pallante P, Visone R, Ferracin M, Ferraro A, Berlingieri MT, Troncone G, Chiappetta G, Liu CG, Santoro M, Negrini M, Croce CM, Fusco A (2006) MicroRNA deregulation in human thyroid papillary carcinomas. Endocr Relat Cancer 13:497–508. doi:10.1677/erc.1.01209
Cheng AM, Byrom MW, Shelton J, Ford LP (2005) Antisense inhibition of human miRNAs and indications for an involvement of miRNA in cell growth and apoptosis. Nucleic Acids Res 33:1290–1297. doi:10.1093/nar/gki200
Pekarsky Y, Santanam U, Cimmino A, Palamarchuk A, Efanov A, Maximov V, Volinia S, Alder H, Liu CG, Rassenti L, Calin GA, Hagan JP, Kipps T, Croce CM (2006) Tcl1 expression in chronic lymphocytic leukemia is regulated by miR-29 and miR-181. Cancer Res 66:11590–11593. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-3613
Shi L, Cheng Z, Zhang J, Li R, Zhao P, Fu Z, You Y (2008) hsa-mir-181a and hsa-mir-181b function as tumor suppressors in human glioma cells. Brain Res 1236:185–193. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2008.07.085
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Conti, A., Aguennouz, M., La Torre, D. et al. miR-21 and 221 upregulation and miR-181b downregulation in human grade II–IV astrocytic tumors. J Neurooncol 93, 325–332 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-009-9797-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-009-9797-4