Abstract
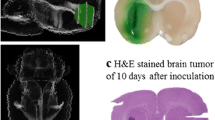
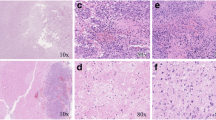
The objective of the present study was to investigate the interest of convection-enhanced delivery (CED) for the administration of a nanocarrier-based radiosensitizing chemotherapy in the rat brain. Pursuing on newly developed lipid nanocapsules (LNC) that can be internalised within brain tumour cells, we studied their intracerebral distribution when labelled with fluorescent Nile red (NR). As paclitaxel (Px) represents an interesting radiosensitiser, we also evaluated the potential radiosensitising effects of Px-loaded LNC administered through CED in the 9L intracranial rat glioblastoma model. The distribution study demonstrated that CED injection of NR-loaded LNC (NR-LNC) improved significantly the volume of distribution of NR when matched with simple injection (by about 150 fold). It also reveals that the LNC perfusion of a whole tumour forming area inside the CNS (6 days after implantation of 103 9L cells) is achievable through CED injection, whilst preserving the ability of LNC to reach the intracellular space of encountered tumour cells. Having established an animal model of encephalic irradiation close to the clinic (18 Gray in three fractions of six Gray at days 8, 11 and 14 after 9L cell implantation) we proved the feasibility of the combination of CED for the administration of drug-loaded LNC with external beam therapy. Although a single CED injection of Px-LNC at low Px dose (375 μg/kg of bodyweight) gave the best median survival (twice that of untreated controls), it underlines the need for optimisation. Hence, the possibility of grafting recognition moieties onto the LNC surface combined to their biocompatibility must be beneficial.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
De Angelis LM (2001) Brain tumors. N Engl J Med 344:114–123
Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, Weller M, Fisher B, Taphoorn MJ, Belanger K, Brandes AA, Marosi C, Bogdahn U, Curschmann J, Janzer RC, Ludwin SK, Gorlia T, Allgeier A, Lacombe D, Cairncross JG, Eisenhauer E, Mirimanoff RO (2005) Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med 352:987–996
Pardridge WM (2002) Drug and gene targeting to the brain with molecular Trojan horses. Nat Rev Drug Discov 1:131–139
Wang PP, Frazier J, Brem H (2002) Local drug delivery to the brain. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 54:987–1013
Kreuter J (2001) Nanoparticulate systems for brain delivery of drugs. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 47:65–81
Tiwari SB, Amiji MM (2006) A review of nanocarrier-based CNS delivery systems. Curr Drug Deliv 3:219–232
Jain KK (2007) Use of nanoparticles for drug delivery in glioblastoma multiforme. Expert Rev Neurother 7:363–372
Garcion E, Lamprecht A, Heurtault B, Paillard A, Aubert-Pouessel A, Denizot B, Menei P, Benoit JP (2006) A new generation of anticancer, drug-loaded, colloidal vectors reverses multidrug resistance in glioma and reduces tumor progression in rats. Mol Cancer Ther 5:1710–1722
Heurtault B, Saulnier P, Pech B, Proust JE, Benoit JP (2002) A novel phase inversion-based process for the preparation of lipid nanocarriers. Pharm Res 19:875–880
Bobo RH, Laske DW, Akbasak A, Morrison PF, Dedrick RL, Oldfield EH (1994) Convection-enhanced delivery of macromolecules in the brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:2076–2080
Tishler RB, Geard CR, Hall EJ, Schiff PB (1992) Taxol sensitizes human astrocytoma cells to radiation. Cancer Res 52:3495–3497
Greenspan P, Mayer EP, Fowler SD (1985) Nile red: a selective fluorescent stain for intracellular lipid droplets. J Cell Biol 100:965–973
Hed J, Hallden G, Johansson SG, Larsson P (1987) The use of fluorescence quenching in flow cytofluorometry to measure the attachment and ingestion phases in phagocytosis in peripheral blood without prior cell separation. J Immunol Methods 101:119–125
Saini M, Bellinzona M, Meyer F, Cali G, Samii M (1999) Morphometrical characterization of two glioma models in the brain of immunocompetent and immunodeficient rats. J Neurooncol 42:59–67
Chen MY, Lonser RR, Morrison PF, Governale LS, Oldfield EH (1999) Variables affecting convection-enhanced delivery to the striatum: a systematic examination of rate of infusion, cannula size, infusate concentration, and tissue-cannula sealing time. J Neurosurg 90:315–320
Lieberman DM, Laske DW, Morrison PF, Bankiewicz KS, Oldfield EH (1995) Convection-enhanced distribution of large molecules in gray matter during interstitial drug infusion. J Neurosurg 82:1021–1029
Mamot C, Nguyen JB, Pourdehnad M, Hadaczek P, Saito R, Bringas JR, Drummond DC, Hong K, Kirpotin DB, McKnight T, Berger MS, Park JW, Bankiewicz KS (2004) Extensive distribution of liposomes in rodent brains and brain tumors following convection-enhanced delivery. J Neurooncol 68:1–9
MacKay JA, Deen DF, Szoka FC Jr (2005) Distribution in brain of liposomes after convection enhanced delivery; modulation by particle charge, particle diameter, and presence of steric coating. Brain Res 1035:139–153
Occhiogrosso G, Edgar MA, Sandberg DI, Souweidane MM (2003) Prolonged convection-enhanced delivery into the rat brainstem. Neurosurgery 52:388–393 (discussion 393–384)
Fleming AB, Saltzman WM (2002) Pharmacokinetics of the carmustine implant. Clin Pharmacokinet 41:403–419
Jordan MA, Toso RJ, Thrower D, Wilson L (1993) Mechanism of mitotic block and inhibition of cell proliferation by taxol at low concentrations. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:9552–9556
Glantz MJ, Choy H, Kearns CM, Mills PC, Wahlberg LU, Zuhowski EG, Calabresi P, Egorin MJ (1995) Paclitaxel disposition in plasma and central nervous systems of humans and rats with brain tumors. J Natl Cancer Inst 87:1077–1081
Fellner S, Bauer B, Miller DS, Schaffrik M, Fankhanel M, Spruss T, Bernhardt G, Graeff C, Farber L, Gschaidmeier H, Buschauer A, Fricker G (2002) Transport of paclitaxel (Taxol) across the blood–brain barrier in vitro and in vivo. J Clin Invest 110:1309–1318
Cahan MA, Walter KA, Colvin OM, Brem H (1994) Cytotoxicity of taxol in vitro against human and rat malignant brain tumors. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 33:441–444
Gottesman MM, Fojo T, Bates SE (2002) Multidrug resistance in cancer: role of ATP-dependent transporters. Nat Rev Cancer 2:48–58
Lidar Z, Mardor Y, Jonas T, Pfeffer R, Faibel M, Nass D, Hadani M, Ram Z (2004) Convection-enhanced delivery of paclitaxel for the treatment of recurrent malignant glioma: a phase I/II clinical study. J Neurosurg 100:472–479
Noble CO, Krauze MT, Drummond DC, Yamashita Y, Saito R, Berger MS, Kirpotin DB, Bankiewicz KS, Park JW (2006) Novel nanoliposomal CPT-11 infused by convection-enhanced delivery in intracranial tumors: pharmacology and efficacy. Cancer Res 66:2801–2806
Yamashita Y, Krauze MT, Kawaguchi T, Noble CO, Drummond DC, Park JW, Bankiewicz KS (2007) Convection-enhanced delivery of a topoisomerase I inhibitor (nanoliposomal topotecan) and a topoisomerase II inhibitor (pegylated liposomal doxorubicin) in intracranial brain tumor xenografts. Neuro Oncol 9:20–28
Saito R, Krauze MT, Noble CO, Drummond DC, Kirpotin DB, Berger MS, Park JW, Bankiewicz KS (2006) Convection-enhanced delivery of Ls-TPT enables an effective, continuous, low-dose chemotherapy against malignant glioma xenograft model. Neuro Oncol 8:205–214
Voges J, Reszka R, Gossmann A, Dittmar C, Richter R, Garlip G, Kracht L, Coenen HH, Sturm V, Wienhard K, Heiss WD, Jacobs AH (2003) Imaging-guided convection-enhanced delivery and gene therapy of glioblastoma. Ann Neurol 54:479–487
Hadaczek P, Kohutnicka M, Krauze MT, Bringas J, Pivirotto P, Cunningham J, Bankiewicz K (2006) Convection-enhanced delivery of adeno-associated virus type 2 (AAV2) into the striatum and transport of AAV2 within monkey brain. Hum Gene Ther 17:291–302
Saito R, Bringas JR, McKnight TR, Wendland MF, Mamot C, Drummond DC, Kirpotin DB, Park JW, Berger MS, Bankiewicz KS (2004) Distribution of liposomes into brain and rat brain tumor models by convection-enhanced delivery monitored with magnetic resonance imaging. Cancer Res 64:2572–2579
Neeves KB, Sawyer AJ, Foley CP, Saltzman WM, Olbricht WL (2007) Dilation and degradation of the brain extracellular matrix enhances penetration of infused polymer nanoparticles. Brain Res 1180:121–132
Heimberger AB, Archer GE, McLendon RE, Hulette C, Friedman AH, Friedman HS, Bigner DD, Sampson JH (2000) Temozolomide delivered by intracerebral microinfusion is safe and efficacious against malignant gliomas in rats. Clin Cancer Res 6:4148–4153
Bruce JN, Falavigna A, Johnson JP, Hall JS, Birch BD, Yoon JT, Wu EX, Fine RL, Parsa AT (2000) Intracerebral clysis in a rat glioma model. Neurosurgery 46:683–691
Morrison PF, Lonser RR, Oldfield EH (2007) Convective delivery of glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor in the human putamen. J Neurosurg 107:74–83
Lacoeuille F, Garcion E, Benoit JP, Lamprecht A (2007) Lipid nanocapsules for intracellular drug delivery of anticancer drugs. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 7:4612–4617
Vogelbaum MA (2005) Convection enhanced delivery for the treatment of malignant gliomas: symposium review. J Neurooncol 73:57–69
Kaiser MG, Parsa AT, Fine RL, Hall JS, Chakrabarti I, Bruce JN (2000) Tissue distribution and antitumor activity of topotecan delivered by intracerebral clysis in a rat glioma model. Neurosurgery 47:1391–1398 (discussion 1398–1399)
Kroin JS, Penn RD (1982) Intracerebral chemotherapy: chronic microinfusion of cisplatin. Neurosurgery 10:349–354
Mardor Y, Roth Y, Lidar Z, Jonas T, Pfeffer R, Maier SE, Faibel M, Nass D, Hadani M, Orenstein A, Cohen JS, Ram Z (2001) Monitoring response to convection-enhanced taxol delivery in brain tumor patients using diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging. Cancer Res 61:4971–4973
Popperl G, Goldbrunner R, Gildehaus FJ, Kreth FW, Tanner P, Holtmannspotter M, Tonn JC, Tatsch K (2005) O-(2-[18F]fluoroethyl)-L-tyrosine PET for monitoring the effects of convection-enhanced delivery of paclitaxel in patients with recurrent glioblastoma. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 32:1018–1025
Jin C, Bai L, Wu H, Tian F, Guo G (2007) Radiosensitization of paclitaxel, etanidazole and paclitaxel + etanidazole nanoparticles on hypoxic human tumor cells in vitro. Biomaterials 28:3724–3730
Fountzilas G, Karavelis A, Capizzello A, Kalogera-Fountzila A, Karkavelas G, Zamboglou N, Selviaridis P, Foroglou G, Tourkantonis A (1999) Radiation and concomitant weekly administration of paclitaxel in patients with glioblastoma multiforme. A phase II study. J Neurooncol 45:159–165
Kortmann RD, Jeremic B, Weller M, Plasswilm L, Bamberg M (2003) Radiochemotherapy of malignant glioma in adults. Clinical experiences. Strahlenther Onkol 179:219–232
Langer CJ, Ruffer J, Rhodes H, Paulus R, Murray K, Movsas B, Curran W (2001) Phase II radiation therapy oncology group trial of weekly paclitaxel and conventional external beam radiation therapy for supratentorial glioblastoma multiforme. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 51:113–119
Walter KA, Cahan MA, Gur A, Tyler B, Hilton J, Colvin OM, Burger PC, Domb A, Brem H (1994) Interstitial taxol delivered from a biodegradable polymer implant against experimental malignant glioma. Cancer Res 54:2207–2212
Korystov YN, Shaposhnikova VV, Korystova AF, Emel’yanov MO, Kublik LN (2008) Modification of multidrug resistance of tumor cells by ionizing radiation. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 61:15–21
Bao S, Wu Q, McLendon RE, Hao Y, Shi Q, Hjelmeland AB, Dewhirst MW, Bigner DD, Rich JN (2006) Glioma stem cells promote radioresistance by preferential activation of the DNA damage response. Nature 444:756–760
Merighi S, Benini A, Mirandola P, Gessi S, Varani K, Leung E, Maclennan S, Baraldi PG, Borea PA (2007) Hypoxia inhibits paclitaxel-induced apoptosis through adenosine-mediated phosphorylation of bad in glioblastoma cells. Mol Pharmacol 72:162–172
Beduneau A, Saulnier P, Hindre F, Clavreul A, Leroux JC, Benoit JP (2007) Design of targeted lipid nanocapsules by conjugation of whole antibodies and antibody Fab’ fragments. Biomaterials 28:4978–4990
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by funding from the Institut National de la Santé et de la Recherche Médicale, from the Cancéropôle Grand Ouest, from the Ligue Nationale Contre le Cancer (Equipe Labellisée 2007) and from the Comité Départemental de Maine et Loire de la Ligue Contre le Cancer through a PhD fellowship to Archibald Paillard. We are also grateful to Pierre Legras and Jérôme Roux from the Service Commun d’Animalerie Hospitalo-Universitaire (SCAHU, Angers, France) for skilful technical support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vinchon-Petit, S., Jarnet, D., Paillard, A. et al. In vivo evaluation of intracellular drug-nanocarriers infused into intracranial tumours by convection-enhanced delivery: distribution and radiosensitisation efficacy. J Neurooncol 97, 195–205 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-009-0012-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-009-0012-4