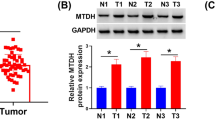
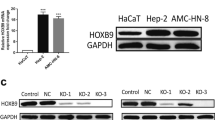
Abstract
Degradation and remodelling of the extracellular matrix has been investigated, with the main focus on the balance between matrix metalloproteinases (MMP) and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases (TIMP). Recent reports disclose the presence of a novel MMP-inhibiting cell membrane-anchored glycoprotein designated ‘reversion-inducing cysteine-rich protein with Kazal motifs’ (RECK). Our main aim in this study was to elucidate the role of RECK in cell invasion of pituitary adenomas and its contribution to signal transduction. The function of RECK in cell invasion was investigated by comparing data obtained from full-length RECK clone transfection and gene silencing with RECK mRNA-targeting siRNA. RECK expression was confirmed using real-time RT-PCR and Western blotting. Levels of matrix metalloproteinases (MMP-2 and -9) and TIMP-1 were measured by zymography and reverse zymography, respectively. Cell invasion was examined with a 3-D invasion assay. The signal cascade was investigated by cDNA microarray analysis. As expected, expression of RECK was elevated upon cDNA transfection, and diminished using siRNA. We observed elevation of MMP-2 and -9 expression and consequent 3-D cell invasion in cells under-expressing RECK. However, TIMP expression was not affected by RECK. Analysis with cDNA microarray revealed that RECK additionally upregulates growth hormone-releasing hormone receptor (GHRHR) and latrophilin 2 at the transcriptional level. Our findings collectively suggest that RECK regulates the cell signalling pathway, playing a critical neuroendocrinological role in the pituitary adenoma cell line.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kim YY, Chae SY, Kim S, Byun Y, Bae YH (2005) Improved phenotype of rat islets in a macrocapsule by co-encapsulation with cross-linked Hb. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed 16:1521–1535
Tischer T, Vogt S, Aryee S, Steinhauser E, Adamczyk C, Milz S, Martinek V, Imhoff AB (2007) Tissue engineering of the anterior cruciate ligament: a new method using acellularized tendon allografts and autologous fibroblasts. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 127:735–741
Tunuguntla R, Ripley D, Sang QX, Chegini N (2003) Expression of matrix metalloproteinase-26 and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases TIMP-3 and -4 in benign endometrium and endometrial cancer. Gynecol Oncol 89:453–459
Bendardaf R, Buhmeida A, Ristamaki R, Syrjanen K, Pyrhonen S (2007) MMP-1 (collagenase-1) expression in primary colorectal cancer and its metastases. Scand J Gastroenterol 1–6 (Epub ahead of print)
Bister V, Skoog T, Virolainen S, Kiviluoto T, Puolakkainen P, Saarialho-Kere U (2007) Increased expression of matrix metalloproteinases-21 and -26 and TIMP-4 in pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Mod Pathol 20:1128–1140
Delgado-Enciso I, Cepeda-Lopez FR, Monrroy-Guizar EA, Bautista-Lam JR, Andrade-Soto M, Jonguitud-Olguin G, Rodriguez-Hernandez A, Anaya-Ventura A, Baltazar-Rodriguez LM, Orozco-Ruiz M, Soriano-Hernandez AD, Rodriguez-Sanchez IP, Lugo-Trampe A, Espinoza-Gomez F, Michel-Peregrina ML (2007) Matrix metalloproteinase-2 promoter polymorphism is associated with breast cancer in a Mexican population. Gynecol Obstet Invest 65:68–72
Takagi S, Kato Y, Asano K, Ohsaki T, Bosnakovski D, Hoshino Y, Okumura M, Kadosawa T, Fujinaga T (2005) Matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor RECK expression in canine tumors. J Veter Med Sci/Jpn Soc Veter Sci 67:761–767
Accorsi-Mendonca T, Paiva KB, Zambuzzi WF, Cestari TM, Lara VS, Sogayar MC, Taga R, Granjeiro JM (2007) Expression of matrix metalloproteinases-2 and -9 and RECK during alveolar bone regeneration in rat. J Mol Histol 39(2):201–208
Clark JC, Thomas DM, Choong PF, Dass CR (2007) RECK-a newly discovered inhibitor of metastasis with prognostic significance in multiple forms of cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev 26:675–683
Kawashima S, Imamura Y, Chandana EP, Noda T, Takahashi R, Adachi E, Takahashi C, Noda M (2007) Localization of the membrane-anchored MMP-regulator RECK at the neuromuscular junctions. J Neurochem 104(2):376–385
Takagi S, Hoshino Y, Osaki T, Okumura M, Fuginaga T (2007) Expression of membrane-anchored matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor reversion inducing cysteine rich protein with Kazal motifs in murine cell lines. Exp Oncol 29:30–34
Ong EK, Suphioglu C, Singh MB, Knox RB (1990) Immunodetection methods for grass pollen allergens on western blots. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol 93:338–343
Le QT, Ohashi A, Hirose S, Katunuma N (2005) Reverse zymography using fluorogenic substrates for protease inhibitor detection. Electrophoresis 26:1038–1045
Patel BP, Shah PM, Rawal UM, Desai AA, Shah SV, Rawal RM, Patel PS (2005) Activation of MMP-2 and MMP-9 in patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma. J Surg Oncol 90:81–88
Yoshida D, Teramoto A (2007) The use of 3-D culture in peptide hydoegel for analysis of discoidin domain receptor 1-collagen interaction. Cell Adhesion Migrat 1:92–98
Esposito V, Santoro A, Minniti G, Salvati M, Innocenzi G, Lanzetta G, Cantore G (2004) Transsphenoidal adenomectomy for GH-, PRL- and ACTH-secreting pituitary tumours: outcome analysis in a series of 125 patients. Neurol Sci 25:251–256
Karavitaki N, Collison K, Halliday J, Byrne JV, Price P, Cudlip S, Wass JA (2007) What is the natural history of nonoperated nonfunctioning pituitary adenomas? Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 67:938–943
Chang CZ, Huang YH, Howng SL (2000) Follow-up of invasive pituitary macroadenoma in 56 patients within a duration of 5 years. Kaohsiung J Med Sci 16:339–344
Gong J, Zhao Y, Abdel-Fattah R, Amos S, Xiao A, Lopes MB, Hussaini IM, Laws ER (2008) Matrix metalloproteinase-9, a potential biological marker in invasive pituitary adenomas. Pituitary 11:37–48
Hussaini IM, Trotter C, Zhao Y, Abdel-Fattah R, Amos S, Xiao A, Agi CU, Redpath GT, Fang Z, Leung GK, Lopes MB, Laws ER Jr (2007) Matrix metalloproteinase-9 is differentially expressed in nonfunctioning invasive and noninvasive pituitary adenomas and increases invasion in human pituitary adenoma cell line. Am J Pathol 170:356–365
Knappe UJ, Hagel C, Lisboa BW, Wilczak W, Ludecke DK, Saeger W (2003) Expression of serine proteases and metalloproteinases in human pituitary adenomas and anterior pituitary lobe tissue. Acta Neuropathol 106:471–478
Liu W, Kunishio K, Matsumoto Y, Okada M, Nagao S (2005) Matrix metalloproteinase-2 expression correlates with cavernous sinus invasion in pituitary adenomas. J Clin Neurosci 12:791–794
Liu W, Matsumoto Y, Okada M, Miyake K, Kunishio K, Kawai N, Tamiya T, Nagao S (2005) Matrix metalloproteinase 2 and 9 expression correlated with cavernous sinus invasion of pituitary adenomas. J Med Invest 52:151–158
Turner HE, Nagy Z, Esiri MM, Harris AL, Wass JA (2000) Role of matrix metalloproteinase 9 in pituitary tumor behavior. J Clin Endocrinol Metabol 85:2931–2935
Yoshida D, Teramoto A (2007) Enhancement of pituitary adenoma cell invasion and adhesion is mediated by discoidin domain receptor-1. J Neuro-oncol 82:29–40
Takagi S, Kitamura T, Hosaka Y, Ohsaki T, Bosnakovski D, Kadosawa T, Okumura M, Fujinaga T (2005) Molecular cloning of canine membrane-anchored inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinase, RECK. J Veter Med Sci/Jpn Soc Veter Sci 67:385–391
Welm B, Mott J, Werb Z (2002) Developmental biology: vasculogenesis is a wreck without RECK. Curr Biol 12:R209–211
Chang HC, Cho CY, Hung WC (2007) Downregulation of RECK by promoter methylation correlates with lymph node metastasis in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Sci 98:169–173
Cho CY, Wang JH, Chang HC, Chang CK, Hung WC (2007) Epigenetic inactivation of the metastasis suppressor RECK enhances invasion of human colon cancer cells. J Cell Physiol 213:65–69
Cho YB, Lee WY, Song SY, Shin HJ, Yun SH, Chun HK (2007) Matrix metalloproteinase-9 activity is associated with poor prognosis in T3–T4 node-negative colorectal cancer. Hum Pathol 38:1603–1610
Kang HG, Kim HS, Kim KJ, Oh JH, Lee MR, Seol SM, Han I (2007) RECK expression in osteosarcoma: correlation with matrix metalloproteinases activation and tumor invasiveness. J Orthop Res 25:696–702
Ohta S, Lai EW, Morris JC, Pang AL, Watanabe M, Yazawa H, Zhang R, Green JE, Chan WY, Sirajuddin P, Taniguchi S, Powers JF, Tischler AS, Pacak K (2007) Metastasis-associated gene expression profile of liver and subcutaneous lesions derived from mouse pheochromocytoma cells. Mol Carcinog 47:245–251
Takemoto N, Tada M, Hida Y, Asano T, Cheng S, Kuramae T, Hamada JI, Miyamoto M, Kondo S, Moriuchi T (2007) Low expression of reversion-inducing cysteine-rich protein with Kazal motifs (RECK) indicates a shorter survival after resection in patients with adenocarcinoma of the lung. Lung Cancer 58:376–383
Correa TC, Brohem CA, Winnischofer SM, da Silva Cardeal LB, Sasahara RM, Taboga SR, Sogayar MC, Maria-Engler SS (2006) Downregulation of the RECK-tumor and metastasis suppressor gene in glioma invasiveness. J Cell Biochem 99:156–167
Noda M, Oh J, Takahashi R, Kondo S, Kitayama H, Takahashi C (2003) RECK: a novel suppressor of malignancy linking oncogenic signaling to extracellular matrix remodeling. Cancer Metastasis Rev 22:167–175
Doyle SE, Scholz MJ, Greer KA, Hubbard AD, Darnell DK, Antin PB, Klewer SE, Runyan RB (2006) Latrophilin-2 is a novel component of the epithelial–mesenchymal transition within the atrioventricular canal of the embryonic chicken heart. Dev Dyn 235:3213–3221
Osada S, Ikeda T, Xu M, Nishihara T, Imagawa M (1997) Identification of the transcriptional repression domain of nuclear factor 1-A. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 238:744–747
Barnes SL, Vidrich A, Wang ML, Wu GD, Cominelli F, Rivera-Nieves J, Bamias G, Cohn SM (2007) Resistin-like molecule beta (RELMbeta/FIZZ2) is highly expressed in the ileum of SAMP1/YitFc mice and is associated with initiation of ileitis. J Immunol 179:7012–7020
Fainstein Day P, Frohman L, Garcia Rivello H, Reubi JC, Sevlever G, Glerean M, Fernandez Gianotti T, Pietrani M, Rabadan A, Racioppi S, Bidlingmaier M (2007) Ectopic growth hormone-releasing hormone secretion by a metastatic bronchial carcinoid tumor: a case with a non hypophysial intracranial tumor that shrank during long acting octreotide treatment. Pituitary 10:311–319
Horvath E, Kovacs K (2006) Pathology of acromegaly. Neuroendocrinology 83:161–165
Roh SG, Doconto M, Feng DD, Chen C (2006) Differential regulation of GHRH-receptor and GHS-receptor expression by long-term in vitro treatment of ovine pituitary cells with GHRP-2 and GHRH. Endocrine 30:55–62
Annabi B, Bouzeghrane M, Currie JC, Hawkins R, Dulude H, Daigneault L, Ruiz M, Wisniewski J, Garde S, Rabbani SA, Panchal C, Wu JJ, Beliveau R (2005) A PSP94-derived peptide PCK3145 inhibits MMP-9 secretion and triggers CD44 cell surface shedding: implication in tumor metastasis. Clin Exp Metastasis 22:429–439
Acknowledgement
This study was supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research from the Ministry of Education, Science, and Culture of Japan (Nos. 17591536 and 18390405).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yoshida, D., Nomura, R. & Teramoto, A. Regulation of cell invasion and signalling pathways in the pituitary adenoma cell line, HP-75, by reversion-inducing cysteine-rich protein with kazal motifs (RECK). J Neurooncol 89, 141–150 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-008-9606-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-008-9606-5