Abstract
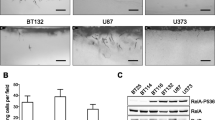
Several recent studies have shown that aberrant constitutive activation of nuclear factor kappaB (NF-κB) is present in a variety of cancers including gliomas. NF-κB is known to play important roles in the physiological regulation of diverse cellular processes such as inflammation, growth and immunity. In contrast, aberrant activation of this latent transcription factor promotes cancer cell migration, invasion and resistance to chemotherapy. Here we show by electro-mobility shift assay (EMSA) and immuno-staining that constitutive NF-κB activation is present in various malignant glioma cell lines as well as in primary cultures derived from tumor tissue. This activation was not serum dependent and it led to high IL-8 gene transcription and protein production. Over-expression of an I-κB super-repressor (I-κB SR) transgene completely blocked constitutive NF-κB activation, nuclear localization and transcription of some but not all NF-κB regulated genes indicating that NF-κB signaling in glioma cells is I-κB dependent. Surprisingly, over-expression of IκBSR did not have any effect on the transcription levels of anti-apoptotic genes in these glioma cultures and cell lines. Down-regulation of NF-κB activation reduced invasion of glioma cells through matrigel. Collectively these data suggest that aberrant constitutive activation of NF-κB in glioblastoma cells promotes their invasive phenotype. Interruption of this aberrant NF-κB activity may help reduce the spread of this infiltrative tumor.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sawaya R, Ligon BL, Bindal AK, Bindal RK, Hess KR (1996) Surgical treatment of metastatic brain tumors. J Neurooncol 27:269–277
Baldwin AS Jr (2001) Series introduction: the transcription factor NF-kappaB, human disease. J Clin Invest 107:3–6
Higgins KA, Perez JR, Coleman TA, Dorshkind K, McComas WA, Sarmiento UM, Rosen CA, Narayanan R (1993) Antisense inhibition of the p65 subunit of NF-kappa B blocks tumorigenicity and causes tumor regression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:9901–9915
Beg AA, Baltimore D (1996) An essential role for NF-kappaB in preventing TNF-alpha-induced cell death. Science 274:782–784
Gilmore TD, Koedood M, Piffat KA, White DW (1996) Rel/NF-kappaB/IkappaB proteins and cancer. Oncogene 13:1367–1378
Van Antwerp DJ, Martin SJ, Kafri T, Green DR, Verma IM (1996) Suppression of TNF-alpha-induced apoptosis by NF-kappaB. Science 274:787–789
Wang CY, Mayo MW, Baldwin AS Jr (1996) TNF- and cancer therapy-induced apoptosis: potentiation by inhibition of NF-kappaB. Science 274:784–787
Duffey DC, Chen Z, Dong G, Ondrey FG, Wolf JS, Brown K, Siebenlist U, Van Waes C (1999) Expression of a dominant-negative mutant inhibitor-kappaBalpha of nuclear factor-kappaB in human head and neck squamous cell carcinoma inhibits survival, proinflammatory cytokine expression, and tumor growth in vivo. Cancer Res 59:3468–3474
Yoshida A, Yoshida S, Ishibashi T, Kuwano M, Inomata H (1999) Suppression of retinal neovascularization by the NF-kappaB inhibitor pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate in mice. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 40:1624–1629
Huang S, DeGuzman A, Bucana CD, Fidler IJ (2000) Nuclear factor-kappaB activity correlates with growth, angiogenesis, and metastasis of human melanoma cells in nude mice. Clin Cancer Res 6:2573–2581
Aggarwal BB Nuclear factor-kappaB: the enemy within (2004) Cancer Cell 6:203–208
Ritchie CK, Giordano A, Khalili K (2000) Integrin involvement in glioblastoma multiforme: possible regulation by NF-kappaB. J Cell Physiol 184:214–221
Bjorklund M, Koivunen E (2005) Gelatinase-mediated migration and invasion of cancer cells. Biochim Biophys Acta 1755:37–69
Griffin JD (2001) Leukemia stem cells and constitutive activation of NK-kappaB. Blood 6:203–208
Feinman R, Koury J, Thames M, Barlogie B, Epstein J, Siegel DS (1999) Role of NF-kappaB in the rescue of multiple myeloma cells from glucocorticoid-induced apoptosis by bcl-2. Blood 93:3044–3052
Kordes U, Krappmann D, Heissmeyer V, Ludwig WD, Scheidereit C (2000) Transcription factor NF-kappaB is constitutively activated in acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells. Leukemia 14:399–402
Baron F, Turhan AG, Giron-Michel J, Azzarone B, Bentires-Alj M, Bours V, Bourhis JH, Chouaib S, Caignard A (2002) Leukemic target susceptibility to natural killer cytotoxicity: relationship with BCR-ABL expression. Blood 99:2107–2113
Palayoor ST, Youmell MY, Calderwood SK, Coleman CN, Price BD (1999) Constitutive activation of IkappaB kinase alpha and NF-kappaB in prostate cancer cells is inhibited by ibuprofen. Oncogene 18:7389–7394
Nakshatri H, Bhat-Nakshatri P, Martin DA, Goulet RJ Jr, Sledge GW Jr (1997) Constitutive activation of NF-kappaB during progression of breast cancer to hormone-independent growth. Mol Cell Biol 17:3629–3639
Bian X, Opipari AW Jr, Ratanaproeksa AB, Boitano AE, Lucas PC, Castle VP (2002) Constitutively active NFkappa B is required for the survival of S-type neuroblastoma. J Biol Chem 277:42144–42150
Nagai S, Washiyama K, Kurimoto M, Takaku A, Endo S, Kumanishi T (2002) Aberrant nuclear factor-kappaB activity and its participation in the growth of human malignant astrocytoma. J Neurosurg 96:909–917
Gill JS, Zhu X, Moore MJ, Lu L, Yaszemski MJ, Windebank AJ (2002) Effects of NFkappaB decoy oligonucleotides released from biodegradable polymer microparticles on a glioblastoma cell line. Biomaterials 23:2773–2781
Hata N, Yoshimoto K, Yokoyama N, Mizoguchi M, Shono T, Guan Y, Tahira T, Kukita Y, Higasa K, Nagata S, Iwaki T, Sasaki T, Hayashi K (2006) Allelic losses of chromosome 10 in glioma tissues detected by quantitative single-strand conformation polymorphism analysis. Clin Chem 52:370–378
Sizemore N, Lerner N, Dombrowski N, Sakurai H, Stark GR (2002) Distinct roles of the Ikappa B kinase alpha and beta subunits in liberating nuclear factor kappa B (NF-kappa B) from Ikappa B and in phosphorylating the p65 subunit of NF-kappa B. J Biol Chem 277:3863–3869
Wolf S, Chen Z, Dong G, Sunwoo JB, Bancroft CC, Capo DE, Yeh NT, Mukaida N, Van Waes C (2001) IL (interleukin)-lalpha promotes nuclear factor-kappaB and AP-1-induced IL-8 expression, cell survival, and proliferation in head and neck squamous cell carcinomas. Clin Cancer Res 7(6):1812–1820
Arlt A, Vorndamm J, Muerkoster S, Yu H, Schmidt WE, Folsch UR, Schafer H (2002) Autocrine production of interleukin 1beta confers constitutive nuclear factor kappaB activity and chemoresistance in pancreatic carcinoma cell lines. Cancer Res 62:910–916
Coward WR, Okayama Y, Sagara H, Wilson SJ, Holgate ST, Church MK (2002) NF-kappa B and TNF-alpha: a positive autocrine loop in human lung mast cells? J Immunol 169:5287–5293
Lu T, Strak G (2004) Cytokine overexpression and constitutive NF-kappa B in cancer. Cell Cycle 3:1114–1117
Wakabayashi K, Kambe F, Cao X, Murakami R, Mitsuyama H, Nagaya T, Saito K, Yoshida J, Seo H (2004) Inhibitory effects of cyclosporin A on calcium mobilization-dependent interleukin-8 expression and invasive potential of human glioblastoma U251MG cells. Oncogene 23:6924–6932
Mahe Y, Mukaida N, Kuno K, Akiyama M, Ikeda N, Matsushima K, Murakami S (1991) Hepatitis B virus X protein transactivates human interleukin-8 gene through acting on nuclear factor kB and CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein-like cis-elements. J Biol Chem 266:13759–13763
Matsusaka T, Fujikawa K, Nishio Y, Mukaida N, Matsushima K, Kishimoto T, Akira S (1993) Transcription factors NF-IL6 and NF-kappa B synergistically activate transcription of the inflammatory cytokines, interleukin 6 and interleukin 8. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:10193–10197
Lefranc F, Brotchi J, Kiss R (2005) Possible future issues in the treatment of glioblastomas: special emphasis on cell migration and the resistance of migrating glioblastoma cells to apoptosis. J Clin Oncol 23:2411–2422
Rao JS (2003) Molecular mechanisms of glioma invasiveness: the role of proteases. Nat Rev Cancer 3:489–501
Brat DJ, Bellail AC, Van Meir EG (2005) The role of interleukin-8 and its receptors in gliomagenesis and tumoral angiogenesis. Neuro-oncol 7:122–133
Huang S, Pettaway CA, Uehara H, Bucana CD, Fidler IJ (2001) Blockade of NF-kappaB activity in human prostate cancer cells is associated with suppression of angiogenesis, invasion, and metastasis. Oncogene 20:4188–4197
Fujioka S, Sclabas GM, Schmidt C, Frederick WA, Dong QG, Abbruzzese JL, Evans DB, Baker C, Chiao PJ (2003) Function of nuclear factor kappaB in pancreatic cancer metastasis. Clin Cancer Res 9:346–354
Watanabe H, Iwase M, Ohashi M, Nagumo M (2002) Role of interleukin-8 secreted from human oral squamous cell carcinoma cell lines. Oral Oncol 38:670–679
Lin Y, Huang R, Chen L, Li S, Shi Q, Jordan C, Huang RP (2004) Identification of interleukin-8 as estrogen receptor-regulated factor involved in breast cancer invasion and angiogenesis by protein arrays. Int J Cancer 109:507–515
Robe PA, Bentires-Alj M, Bonif M, Rogister B, Deprez M, Haddada H, Khac MT, Jolois O, Erkmen K, Merville MP, Black PM, Bours V (2004) In vitro and in vivo activity of the nuclear factor-kappaB inhibitor sulfasalazine in human glioblastomas. Clin Cancer Res 10:5595–5603
Lamszus K, Brockmann MA, Eckerich C, Bohlen P, May C, Mangold U, Fillbrandt R, Westphal M (2005) Inhibition of glioblastoma angiogenesis and invasion by combined treatments directed against vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2, epidermal growth factor receptor, and vascular endothelial-cadherin. Clin Cancer Res 11(13):4934–4940
Hu B, Jarzynka MJ, Guo P, Imanishi Y, Schlaepfer DD, Cheng SY (2006) Angiopoietin 2 induces glioma cell invasion by stimulating matrix metalloprotease 2 expression through the alphavbeta1 integrin and focal adhesion kinase signaling pathway. Cancer Res 66(2):775–783
Mayes DA, Hu Y, Teng Y, Siegel E, Wu X, Panda K, Tan F, Yung WK, Zhou YH (2006) PAX6 suppresses the invasiveness of glioblastoma cells and the expression of the matrix metalloproteinase-2 gene. Cancer Res 66(20):9809–9817
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Raychaudhuri, B., Han, Y., Lu, T. et al. Aberrant constitutive activation of nuclear factor κB in glioblastoma multiforme drives invasive phenotype. J Neurooncol 85, 39–47 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-007-9390-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-007-9390-7