Summary
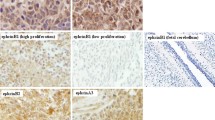
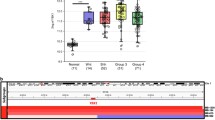
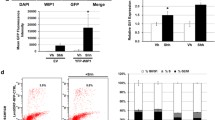
Hedgehog (Hh), Notch, and Wingless (Wnt) signaling control normal development of the cerebellum, and dysregulation of these signaling pathways are associated with medulloblastoma (MB). As an initial step in the study of the role of interacting signaling pathways in MB pathogenesis, we demonstrate the expression of several components of the Notch and Wnt signaling pathways, and activation of Notch signaling in MB from Ptch +/− mice that have elevated Hh signaling. We also show a marked downregulation in the expression of Notch2, Jagged1, Hes1, mSfrp1, and mFrz7 in cerebella of developing mice with reduced Hh signaling, suggesting that Hh signaling regulates the expression of these genes. Together with recent published data, these findings indicate that Hh signaling might synergize simultaneously with Notch and Wnt signaling in MB development by controlling Notch and Wnt pathway ligand, receptor and/or target gene expression.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kadin ME, Rubinstein LJ, Nelson JS, (1970) Neonatal cerebellar medulloblastoma originating from the fetal external granular layer J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 29: 583–600
Brault V, Moore R, Kutsch S, Ishibashi M, Rowitch DH, McMahon AP, Sommer L, Boussadia O, Kemler R, (2001) Inactivation of the beta-catenin gene by Wnt1-Cre-mediated deletion results in dramatic brain malformation and failure of craniofacial development Development 128: 1253–1264
Wallace VA, (1999) Purkinje-cell-derived Sonic hedgehog regulates granule neuron precursor cell proliferation in the developing mouse cerebellum Curr Biol 9: 445–448
Dahmane N, Ruiz-i-Altaba A, (1999) Sonic hedgehog regulates the growth and patterning of the cerebellum Development 126: 3089–3100
Wechsler-Reya RJ, Scott MP, (1999) Control of neuronal precursor proliferation in the cerebellum by Sonic Hedgehog Neuron 22: 103–114
Solecki DJ, Liu XL, Tomoda T, Fang Y, Hatten ME, (2001) Activated Notch2 signaling inhibits differentiation of cerebellar granule neuron precursors by maintaining proliferation Neuron 31: 557–568
Galderisi U, Cipollaro M, Giordano A: (2005) Stem cells and brain cancer. Cell Death Differ
Lee A, Kessler JD, Read TA, Kaiser C, Corbeil D, Huttner WB, Johnson JE, Wechsler-Reya RJ, (2005) Isolation of neural stem cells from the postnatal cerebellum Nat Neurosci 8: 723–729
Golestaneh N, Mishra B, (2005) TGF-beta, neuronal stem cells and glioblastoma Oncogene 24: 5722–5730
Xie J, Johnson RL, Zhang X, Bare JW, Waldman FM, Cogen PH, Menon AG, Warren RS, Chen LC, Scott MP, Epstein EH Jr, (1997) Mutations of the PATCHED gene in several types of sporadic extracutaneous tumors Cancer Res 57: 2369–2372
Wetmore C, Eberhart DE, Curran T, (2000) The normal patched allele is expressed in medulloblastomas from mice with heterozygous germ-line mutation of patched Cancer Res 60: 2239–2246
Kim JY, Nelson AL, Algon SA, Graves O, Sturla LM, Goumnerova LC, Rowitch DH, Segal RA, Pomeroy SL, (2003) Medulloblastoma tumorigenesis diverges from cerebellar granule cell differentiation in patched heterozygous mice Dev Biol 263: 50–66
Berman DM, Karhadkar SS, Hallahan AR, Pritchard JI, Eberhart CG, Watkins DN, Chen JK, Cooper MK, Taipale J, Olson JM, Beachy PA, (2002) Medulloblastoma growth inhibition by hedgehog pathway blockade Science 297: 1559–1561
Taylor MD, Liu L, Raffel C, Hui CC, Mainprize TG, Zhang X, Agatep R, Chiappa S, Gao L, Lowrance A, Hao A, Goldstein AM, Stavrou T, Scherer SW, Dura WT, Wainwright B, Squire JA, Rutka JT, Hogg D, (2002) Mutations in SUFU predispose to medulloblastoma Nat Genet 31: 306–310
Goodrich LV, Milenkovic L, Higgins KM, Scott MP, (1997) Altered neural cell fates and medulloblastoma in mouse patched mutants Science 277: 1109–1113
Machold R, Hayashi S, Rutlin M, Muzumdar MD, Nery S, Corbin JG, Gritli-Linde A, Dellovade T, Porter JA, Rubin LL, Dudek H, McMahon AP, Fishell G, (2003) Sonic hedgehog is required for progenitor cell maintenance in telencephalic stem cell niches Neuron 39: 937–950
Wallace VA, Raff MC, (1999) A role for Sonic hedgehog in axon-to-astrocyte signalling in the rodent optic nerve Development 126: 2901–2909
Jensen AM, Wallace VA, (1997) Expression of Sonic hedgehog and its putative role as a precursor cell mitogen in the developing mouse retina Development 124: 363–371
Weng AP, Aster JC, (2004) Multiple niches for Notch in cancer: context is everything Curr Opin Genet Dev 14: 48–54
Weng AP, Ferrando AA, Lee W, Morris JPt, Silverman LB, Sanchez-Irizarry C, Blacklow SC, Look AT, Aster JC, (2004) Activating mutations of NOTCH1 in human T cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia Science 306: 269–271
Nicolas M, Wolfer A, Raj K, Kummer JA, Mill P, van Noort M, Hui CC, Clevers H, Dotto GP, Radtke F, (2003) Notch1 functions as a tumor suppressor in mouse skin Nat Genet 33: 416–421
Hovanes K, Li TW, Munguia JE, Truong T, Milovanovic T, Lawrence Marsh J, Holcombe RF, Waterman ML, (2001) Beta-catenin-sensitive isoforms of lymphoid enhancer factor-1 are selectively expressed in colon cancer Nat Genet 28: 53–57
Utsuki S, Oka H, Sato Y, Tsutiya B, Kondo K, Tanizaki Y, Tanaka S, Fujii K, (2004) E, N-cadherins and beta-catenin expression in medulloblastoma and atypical teratoid/rhabdoid tumor Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 44: 402–406discussion 407
Ellison DW, Onilude OE, Lindsey JC, Lusher ME, Weston CL, Taylor RE, Pearson AD, Clifford SC, (2005) Beta-Catenin status predicts a favorable outcome in childhood medulloblastoma: the United Kingdom Children’s Cancer Study Group Brain Tumour Committee J Clin Oncol 23: 7951–7957
Lee Y, Miller HL, Jensen P, Hernan R, Connelly M, Wetmore C, Zindy F, Roussel MF, Curran T, Gilbertson RJ, McKinnon PJ, (2003) A molecular fingerprint for medulloblastoma Cancer Res 63: 5428–5437
Lewis PM, Gritli-Linde A, Smeyne R, Kottmann A, McMahon AP, (2004) Sonic hedgehog signaling is required for expansion of granule neuron precursors and patterning of the mouse cerebellum Dev Biol 270: 393–410
Meng X, Poon R, Zhang X, Cheah A, Ding Q, Hui CC, Alman B, (2001) Suppressor of fused negatively regulates beta-catenin signaling J Biol Chem 276: 40113–40119
Wetmore C, Eberhart DE, Curran T, (2001) Loss of p53 but not ARF accelerates medulloblastoma in mice heterozygous for patched Cancer Res 61: 513–516
Tong WM, Ohgaki H, Huang H, Granier C, Kleihues P, Wang ZQ, (2003) Null mutation of DNA strand break-binding molecule poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase causes medulloblastomas in p53(−/−) mice Am J Pathol 162: 343–352
Rao G, Pedone CA, Valle LD, Reiss K, Holland EC, Fults DW, (2004) Sonic hedgehog and insulin-like growth factor signaling synergize to induce medulloblastoma formation from nestin-expressing neural progenitors in mice Oncogene 23: 6156–6162
Hartmann W, Koch A, Brune H, Waha A, Schuller U, Dani I, Denkhaus D, Langmann W, Bode U, Wiestler OD, Schilling K, Pietsch T, (2005) Insulin-like growth factor II is involved in the proliferation control of medulloblastoma and its cerebellar precursor cells Am J Pathol 166: 1153–1162
Hallahan AR, Pritchard JI, Hansen S, Benson M, Stoeck J, Hatton BA, Russell TL, Ellenbogen RG, Bernstein ID, Beachy PA, Olson JM, (2004) The SmoA1 mouse model reveals that notch signaling is critical for the growth and survival of sonic hedgehog-induced medulloblastomas Cancer Res 64: 7794–7800
Fan X, Mikolaenko I, Elhassan I, Ni X, Wang Y, Ball D, Brat DJ, Perry A, Eberhart CG, (2004) Notch1 and notch2 have opposite effects on embryonal brain tumor growth Cancer Res 64: 7787–7793
Dahmen RP, Koch A, Denkhaus D, Tonn JC, Sorensen N, Berthold F, Behrens J, Birchmeier W, Wiestler OD, Pietsch T, (2001) Deletions of AXIN1, a component of the WNT/wingless pathway, in sporadic medulloblastomas Cancer Res 61: 7039–7043
Yokota N, Nishizawa S, Ohta S, Date H, Sugimura H, Namba H, Maekawa M, (2002) Role of Wnt pathway in medulloblastoma oncogenesis Int J Cancer 101: 198–201
Koch A, Waha A, Tonn JC, Sorensen N, Berthold F, Wolter M, Reifenberger J, Hartmann W, Friedl W, Reifenberger G, Wiestler OD, Pietsch T, (2001) Somatic mutations of WNT/wingless signaling pathway components in primitive neuroectodermal tumors Int J Cancer 93: 445–449
Acknowledgements
We thank A. P. McMahon for kindly providing us with Nestin Cre;Smo n/c mice. This work was supported by funding from the National Cancer Institute of Canada and the Canadian Institutes of Health Research to VAW who is also the recipient of a CIHR New Investigator Award. G. D. Dakubo was a recipient of an M. S. Society Postdoctoral Fellowship at the time that these experiments were performed.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dakubo, G.D., Mazerolle, C.J. & Wallace, V.A. Expression of Notch and Wnt pathway components and activation of Notch signaling in medulloblastomas from heterozygous patched mice. J Neurooncol 79, 221–227 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-006-9132-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-006-9132-2