Summary
Purpose
In order to improve the survival of patients with a glioblastoma multiforme tumor (GBM), new therapeutic strategies must be developed. The use of a death inducing ligand such as TRAIL (TNF Related Apoptosis Inducing Ligand) seems a promising innovative therapy. The aim of this study was to quantify the expression of the death regulating receptors TRAIL-R1, TRAIL-R2 and TRAIL on primary GBM specimens and to correlate this expression with survival.
Experimental design
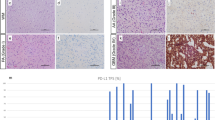
Expression of TRAIL and TRAIL-receptors was assessed by immunohistochemistry, both quantitatively (% of positive tumor cells) and semi-quantitatively (staining intensity) within both the perinecrotic and intermediate tumor zones of primary GBM specimens. RT-PCR of GBM tissue was performed to show expression of TRAIL receptor mRNA.
Results
Immunohistochemistry showed a slight diffuse intracytoplasmic and a stronger membranous staining for TRAIL and TRAIL receptors in tumor cells. Semi-quantitative expression of TRAIL showed a significantly higher expression of TRAIL in the perinecrotic zone than in the intermediate zone of the tumor (P=0.0001). TRAIL-R2 expression was significantly higher expressed than TRAIL-R1 (P=0.005). The antigenic load of TRAIL-R2 was positively correlated with survival (P=0.02). Multivariate analysis of TRAIL-R1 within the study group (n=62) showed that age, gender, staining intensity, antigenic load, % of TRAIL-R1 expression, were not statistically correlated with survival however radiotherapy was significantly correlated (multivariate analysis: age: P=0.15; gender: P=0.64; staining intensity: P=0.17; antigenic load: P=0.056; % of TRAIL-R1 expression: P=0.058; radiotherapy: P=0.0001). Subgroup analysis of patients who had received radiotherapy (n=47) showed a significant association of % of TRAIL-R1 expression and the antigenic load of TRAIL-R1 with survival (multivariate analysis: P=0.036, respectively, P=0.023).
Multivariate analysis of TRAIL-R2 staining intensity and antigenic load, within the study group (P=0.004, respectively, P=0.03) and the subgroup (P=0.002, respectively, P=0.004), showed a significant association with survival. RT-PCR analysis detected a negative relation between the amount of TRAIL-R1 mRNA and the WHO grade of astrocytic tumors (P=0.03).
Conclusions
TRAIL-R1 and TRAIL-R2 expression on tumor cells are independent prognostic factors for survival in patients with a glioblastoma multiforme. Both receptors could be targets for TRAIL therapy. As TRAIL-R2 is more expressed, in comparison with TRAIL-R1, on GBM tumor cells, TRAIL-R2 seems to be of more importance as a target for future TRAIL therapy than TRAIL-R1.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
DeAngelis LM. (2001) Brain tumorsN Engl J Med 344:114–123
Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, Weller M, Fisher B, Taphoorn MJ, Belanger K, Brandes AA, Marosi C, Bogdahn U, Curschmann J, Janzer RC, Ludwin SK, Gorlia T, Allgeier A, Lacombe D, Cairncross JG, Eisenhauer E, Mirimanoff RO. (2005) Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastomaN Engl J Med 352:987–996
Ashkenazi A, Pai RC, Fong S, Leung S, Lawrence DA, Marsters SA, Blackie C, Chang L, McMurtrey AE, Hebert A, DeForge L, Koumenis IL, Lewis D, Harris L, Bussiere J, Koeppen H, Shahrokh Z, Schwall RH. (1999) Safety and antitumor activity of recombinant soluble Apo2 ligandJ Clin Invest 104:155–162
Wiley SR, Schooley K, Smolak PJ, Din WS, Huang CP, Nicholl JK, Sutherland GR, Smith TD, Rauch C, Smith CA, (1995) Identification and characterization of a new member of the TNF family that induces apoptosisImmunity 3: 673–682
Nitsch R, Bechmann I, Deisz RA, Haas D, Lehmann TN, Wendling U, Zipp F. (2000) Human brain-cell death induced by tumour-necrosis-factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL)Lancet 356: 827–828
Jo M, Kim TH, Seol DW, Esplen JE, Dorko K, Billiar TR, Strom SC. (2000) Apoptosis induced in normal human hepatocytes by tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligandNat Med 6: 564–567
de Vries EG, van der Graaf WT, Heijenbrok FJ, Hoekstra HJ, de Jong S: Don’t blaze the trailblazer TRAIL too early. Lancet 356: 2014, 2000
Knight MJ, Riffkin CD, Muscat AM, Ashley DM, Hawkins CJ: Analysis of FasL and TRAIL induced apoptosis pathways in glioma cells. Oncogene 13: 5789–5798, 2001
Grotzer MA, Eggert A, Zuzak TJ, Janss AJ, Marwaha S, Wiewrodt BR, Ikegaki N, Brodeur GM, Phillips PC. (2000) Resistance to TRAIL-induced apoptosis in primitive neuroectodermal brain tumor cells correlates with a loss of caspase-8 expressionOncogene 19: 4604–4610
Dorr J, Waiczies S, Wendling U, Seeger B, Zipp F. (2002) Induction of TRAIL-mediated glioma cell death by human T cellsJ Neuroimmunol 122: 117–124
Rohn TA, Wagenknecht B, Roth W, Naumann U, Gulbins E, Krammer PH, Walczak H, Weller M. (2001) CCNU-dependent potentiation of TRAIL/Apo2L-induced apoptosis in human glioma cells is p53-independent but may involve enhanced cytochrome c releaseOncogene 20: 4128–4137
Frank S, Kohler U, Schackert G, Schackert HK. (1999) Expression of TRAIL and its receptors in human brain tumorsBiochem Biophys Res Commun 257: 454–459
Kleihues P, Cavenee WK: Pathology & Genetics of Tumours of the Nervous System, 2000
Sondergaard KL, Hilton DA, Penney M, Ollerenshaw M, Demaine AG (2002) Expression of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha in tumours of patients with glioblastomaNeuropathol Appl Neurobiol 28: 210–217
Plate KH, Breier G, Weich HA, Risau W (1992) Vascular endothelial growth factor is a potential tumour angiogenesis factor in human gliomas in vivoNature 359: 845–848
Shweiki D, Itin A, Soffer D, Keshet E. (1992) Vascular endothelial growth factor induced by hypoxia may mediate hypoxia-initiated angiogenesisNature 359: 843–845
Strater J, Hinz U, Walczak H, Mechtersheimer G, Koretz K, Herfarth C, Moller P, Lehnert T (2002) Expression of TRAIL and TRAIL receptors in colon carcinoma: TRAIL-R1 is an independent prognostic parameterClin Cancer Res 8: 3734–3740
Spierings DC, de Vries EG, Vellenga E, van den Heuvel FA, Koornstra JJ, Wesseling J, Hollema H, de Jong S (2004) Tissue distribution of the death ligand TRAIL and its receptorsJ Histochem Cytochem 52: 821–831
Golstein P, (1997) Cell death: TRAIL and its receptorsCurr Biol 7:R750–R753
Wajant H, Moosmayer D, Wuest T, Bartke T, Gerlach E, Schonherr U, Peters N, Scheurich P, Pfizenmaier K (2001) Differential activation of TRAIL-R1 and -2 by soluble and membrane TRAIL allows selective surface antigen-directed activation of TRAIL-R2 by a soluble TRAIL derivativeOncogene 20: 4101–4106
Nakamura M, Rieger J, Weller M, Kim J, Kleihues P, Ohgaki H (2000) APO2L/TRAIL expression in human brain tumorsActa Neuropathol (Berl) 99: 1–6
Dorr J, Bechmann I, Waiczies S, Aktas O, Walczak H, Krammer PH, Nitsch R, Zipp F: Lack of tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand but presence of its receptors in the human brain. J Neurosci 22: RC209, 2002
Rieger J, Ohgaki H, Kleihues P, Weller M. (1999) Human astrocytic brain tumors express AP02L/TRAILActa Neuropathol (Berl) 97: 1–4
Gratas C, Tohma Y, Van Meir EG, Klein M, Tenan M, Ishii N, Tachibana O, Kleihues P, Ohgaki H (1997) Fas ligand expression in glioblastoma cell lines and primary astrocytic brain tumorsBrain Pathol 7: 863–869
Tartaglia LA, Goeddel DV (1992) Two TNF receptorsImmunol Today 13: 151–153
Nagata S, (1997) Apoptosis by death factorCell 88: 355–365
Bremer E, Kuijlen J, Samplonius D, Walczak H, de Leij L, Helfrich W (2004) Target cell-restricted and -enhanced apoptosis induction by a scFv:sTRAIL fusion protein with specificity for the pancarcinoma-associated antigen EGP2Int J Cancer 109: 281–290
Bremer E, Samplonius DF, van Genne L, Dijkstra MH, Kroesen BJ, de Leij LF, Helfrich W (2005) Simultaneous inhibition of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) signaling and enhanced activation of tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) receptor-mediated apoptosis induction by an scFv:sTRAIL fusion protein with specificity for human EGFRJ Biol Chem 280: 10025–10033
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by KWF research grant for clinical residents.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kuijlen, J., Mooij, J.J.A., Platteel, I. et al. TRAIL-receptor expression is an independent prognostic factor for survival in patients with a primary glioblastoma multiforme. J Neurooncol 78, 161–171 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-005-9081-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-005-9081-1