Summary
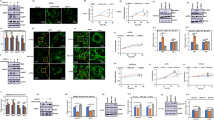
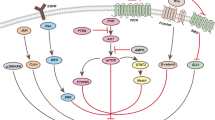
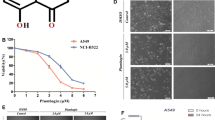
Smac/DIABLO is a mitochondrial protein released into cytosol during the progression of apoptosis. Smac/DIABLO promotes apoptosis by neutralizing the inhibitory effect of the inhibitor of apoptosis proteins (IAPs) on the processing and activity of the effecter of caspase. Here, we generated synthetic Smac peptide which possesses an IAP-binding domain and Drosophila antennapaedia penetration sequence, and examined whether it enhances the effect of the chemotherapeutic agent etoposide in the human glioblastoma cell line. Cellular uptake of Smac peptide in several glioma cell lines was most prominent at 6–12 h after addition. Caspase activity assay showed that our peptide successfully increased the activity of caspase-3 and caspase-9 in etoposide-induced apoptosis. In addition, Smac peptide increased the amount of cleaved PARP (poly ADP-ribose polymerase), but control peptides did not. Moreover, the addition of z-VAD-fmk, a caspase inhibitor, counterbalanced the effect of Smac peptide. Finally, we demonstrated that Smac peptide could enhance the growth inhibition effect of etoposide compared with control peptides. These results suggest that synthetic Smac peptide may be a new molecular targeting anti-tumor therapy for human glioblastoma.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
The Committee of Brain Tumor Registry of Japan, The Japanese Pathological Society: General Rules for Clinical and Pathological Studies on Brain Tumors. Kanehara & Co.,Ltd., Second Edition, 2002, p 54
Lowe SW, Lin AW, Apoptosis in cancer Carcinogenesis 21:485–495, 2000
Nicholson DW, From bench to clinic with apoptosis-based therapeutic agents Nature 407:810–816, 2000
Goyal L, Cell death inhibition: Keeping caspases in check Cell 104, 805–808, 2001
Deveraux QL, Reed JC, IAP family proteins-suppressors of apoptosis Genes Dev 13:239–252, 1999
Wagenknecht B, Glaser T, Naumann U, Kugler S, Isenmann S, Bahr M, Korneluk R, Liston P, Weller M, Expression and biological activity of X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis (XIAP) in human malignant glioma Cell Death Differ 6:370–376, 1999
Ashkenazi A, Dixit VM, Death receptors: signaling and modulation Science 281:1305–1308, 1998
Walczak H, Krammer PH, The CD95 (APO-1/Fas) and the TRAIL (APO-2L) apoptosis systems Exp Cell Res 256:58–66, 2000
Thornberry N, Lazebnik Y, Caspases: Enemies within Science 281:1312–1316, 1998
Scaffidi C, Fulda S, Srinivasan A, Friesen C, Li F, Tomaselli KJ, Debatin KM, Krammer PH, Peter ME, Two CD95 (APO-1/Fas) signaling pathways EMBO J 17:1675–1687, 1998
Kroemer G, Reed JC, Mitochondrial control of cell death Nature Med 6:513–519, 2000
Crook NE, Clem RJ, Miller LK, An apoptosis-inhibiting baculovirus gene with a zinc finger-like motif J Virol 67:2168–2174, 1993
Birnbaum MJ, Clem RJ, Miller LK, An apoptosis-inhibiting gene from a nuclear polyhedrosis virus encoding a polypeptide with Cys/His sequence motifs J Virol 68:2521–2528, 1994
Hay BA, Wassarman DA, Rubin GM, Drosophila homologs of baculovirus inhibitor of apoptosis proteins function to block cell death Cell 83:1253–1262, 1995
Rothe M, Pan MG, Henzel WJ, Ayres TM, Goeddel DV, The TNFR2-TRAF signaling complex contains two novel proteins related to baculoviral inhibitor of apoptosis proteins Cell 83:1243–1252, 1995
Roy N, Mahadevan MS, McLean M, Shutler G, Yaraghi Z, Farahani R, Baird S, Besner-Johnston A, Lefebvre C, Kang X, Salih M, Aubry H, Tamai K, Guan X, Ioannou P, Crawford TO, Jong PJ, Surh L, Ikeda JE, Korneluk RG, MacKenzie A, The gene for neuronal apoptosis inhibitory protein is partially deleted in individuals with spinal muscular atrophy Cell 80:167–178, 1995
Duckett CS, Nava VE, Gedrich RW, Clem RJ, Van Dongen JL, Gilfillan MC, Shiels H, Hardwick JM, Thompson CB, A conserved family of cellular genes related to the baculovirus iap gene and encoding apoptosis inhibitors EMBO J. 15:2685–2694, 1996
Liston P, Roy N, Tamai K, Lefebvre C, Baird S, Cherton-Horvat G, Farahani R, McLean M, Ikeda JE, MacKenzie A, Korneluk RG, Suppression of apoptosis in mammalian cells by NAIP and a related family of IAP genes Nature 379:349–353, 1996
Uren AG, Pakusch M, Hawkins CJ, Puls KL, Vaux DL, Cloning and expression of apoptosis inhibitory protein homologs that function to inhibit apoptosis and/or bind tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factors Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:4974–4978, 1996
Fraser AG, James C, Evan GI, Hengartner MO, Caenorhabditis elegans inhibitor of apoptosis protein (IAP) homologue BIR-1 plays a conserved role in cytokinesis Curr Biol 9:292–301, 1996
Uren AG, Beilharz T, O’Connell MJ, Bugg SJ, van Driel R, Vaux DL, Lithgow T, Role for yeast inhibitor of apoptosis (IAP)-like proteins in cell division Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:10170–10175, 1999
Miller LK, An exegesis of IAPs: salvation and surprises from BIR motifs Trends Cell Biol 9:323–328, 1999
Hinds MG, Norton RS, Vaux DL, Day CL, Solution structure of a baculoviral inhibitor of apoptosis (IAP) repeat Nat Struct Biol 6:648–651, 1999
Sun C, Cai M, Gunasekera AH, Meadows RP, Wang H, Chen J, Zhang H, Wu W, Xu N, Ng SC, Fesik SW, NMR structure and mutagenesis of the inhibitor-of-apoptosis protein XIAP Nature 401:818–822, 1999
Salvesen GS, Duckett CS, IAP proteins: blocking the road to death’s door Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 3:401–410, 2002
Deveraux QL, Takahashi R, Salvesen GS, Reed JC, IAP family proteinssuppressors of apoptosis Nature 388:300–304, 1997
Roy N, Deveraux QL, Takahashi R, Salvesen GS, Reed JC, The c-IAP-1 and c-IAP-2 proteins are direct inhibitors of specific caspases EMBO J 16:6914–6925, 1997
Deveraux QL, Roy N, Stennicke HR, Van Arsdale T, Zhou Q, Srinivasula SM, Alnemri ES, Salvesen GS, Reed JC, IAPs block apoptotic events induced by caspase−8 and cytochrome c by direct inhibition of distinct caspases EMBO J 17:2215–2223, 1998
Du C, Fang M, Li Y, Li L, Wang X, Smac, a mitochondrial protein that promotes cytochrome c-dependent caspase activation during apoptosis Cell 102:33–42, 2000
Verhagen AM, Ekert PG, Pakusch M, Silke J, Connolly LM, Reid GE, Moritz RL, Simpson RJ, Vaux DL, Identification of DIABLO, a mammalian protein that promotes apoptosis by binding to and antagonizing IAP proteins Cell 102:43–53, 2000
Verhagen AM, Vaux DL, Cell death regulation by the mammalian IAP antagonist Diablo/Smac Apoptosis 7:163–166, 2002
Shi Y, A conserved tetrapeptide motif: potentiating apoptosis through IAP-binding Cell Death Differ 9:93–95, 2002
Wu G, Chai J, Suber TL, Wu JW, Du C, Wang X, Shi Y, Structural basis of IAP recognition by Smac/DIABLO Nature 408:1008–1012, 2000
Liu Z, Sun C, Olejniczak ET, Meadows RP, Betz SF, Oost T, Herrmann J, Wu JC, Fesik SW, Structural basis for binding of Smac/DIABLO to the XIAP BIR3 domain Nature 408:1004–1008, 2000
Fulda S, Wick W, Weller M, Debatin KM, Smac agonists sensitize for Apo2L/TRAIL- or anticancer drug-induced apoptosis and induce regression of malignant glioma in vivo Nat Med 8:808–815, 2002
Arnt CR, Chiorean MV, Heldebrant MP, Gores GJ, Kaufmann SH, Synthetic Smac/DIABLO peptides enhance the effects of chemotherapeutic agents by binding XIAP and cIAP1 in situ J Biol Chem 277:44236–4243, 2002
Yang L, Mashima T, Sato S, Mochizuki M, Sakamoto H, Yamori T, Oh-Hara T, Tsuruo T, Predominant suppression of apoptosome by inhibitor of apoptosis protein in non-small cell lung cancer H460 cells: therapeutic effect of a novel polyarginine-conjugated Smac peptide Cancer Res 63:831–837, 2003
Bartling B, Lewensohn R, Zhivotovsky B, Endogenously released Smac is insufficient to mediate cell death of human lung carcinoma in response to etoposide Exp Cell Res 298:83–95, 2004
Guo F, Nimmanapalli R, Paranawithana S, Wittman S, Griffin D, Bali P, O’Bryan E, Fumero C, Wang HG, Bhalla K, Ectopic overexpression of second mitochondria-derived activator of caspases (Smac/DIABLO) or cotreatment with N-terminus of Smac/DIABLO peptide potentiates epothilone B derivative-(BMS247550) and Apo-2L/TRAIL-induced apoptosis Blood 99:3419–3426, 2002
Yin D, Tamaki N, Kokunai T, Wild-type p53-dependent etoposide-induced apoptosis mediated by caspase−3 activation in human glioma cells J Neurosurg 93:289–297, 2000
Slee EA, Zhu H, Chow SC, MacFarlane M, Nicholson DW, Cohen GM, Benzyloxycarbonyl-Val-Ala-Asp (OMe) fluoromethylketone (Z-VAD.FMK) inhibits apoptosis by blocking the processing of CPP32 Biochem J 315:21–24, 1996
Thoren PE, Persson D, Karlsson M, Norden B, The antennapedia peptide penetratin translocates across lipid bilayers – the first direct observation FEBS Lett 482:265–268, 2000
Satoh MS, Lindahl T, Role of poly(ADP-ribose) formation in DNA repair Nature 356:356–358, 1992
Lazebnik YA, Kaufmann SH, Desnoyers S, Poirier GG, Earnshaw WC, Cleavage of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase by a proteinase with properties like ICE. Nature 371:346–347, 1994
Nicholson DW, Ali A, Thornberry NA, Vaillancourt JP, Ding CK, Gallant M, Gareau Y, Griffin PR, Labelle M, Lazebnik YA, Munday NA, Raju SM, Smulson ME, Yamin TT, Yu VL, Douglas K, Identification and inhibition of the ICE/CED-3 protease necessary for mammalian apoptosis Nature 376:37–43. 1995
Oliver FJ, de la Rubia G, Rolli V, Ruiz-Ruiz MC, de Murcia G, Murcia JM, Importance of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase and its cleavage in apoptosis. Lesson from an uncleavable mutant J Biol Chem 273:33533–33539, 1998
Tikoo A, O’Reilly L, Day CL, Verhagen AM, Pakusch M, Vaux DL, Tissue distribution of Diablo/Smac revealed by monoclonal antibodies Cell Death Differ 9:710–716, 2002
MacFarlane M, Merrison W, Bratton SB, Cohen GM, Proteasome-mediated degradation of Smac during apoptosis: XIAP promotes Smac ubiquitination in vitro J Biol Chem 277:36611–36616, 2002
Nagane M, Pan G, Weddle JJ, Dixit VM, Cavenee WK, Huang HJ, Increased death receptor 5 expression by chemotherapeutic agents in human gliomas causes synergistic cytotoxity with tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand in vitro and in vivo Cancer Res 60:847–853, 2000
Gomi A, Shinoda S, Masuzawa T, Ishikawa T, Kuo MT, Transient induction of the MRP/GS-X pump and gamma-glutamylcysteine synthetase by 1-(4-amino-2-methyl-5-pyrimidinyl)methyl-3-(2-chloroethyl)-3- nitrosourea in human glioma cells Cancer Res 57:5292–5299, 1997
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research from the Japanese Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (Grant No.15659337).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mizukawa, K., Kawamura, A., Sasayama, T. et al. Synthetic Smac peptide enhances the effect of etoposide-induced apoptosis in human glioblastoma cell lines. J Neurooncol 77, 247–255 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-005-9045-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-005-9045-5