Summary
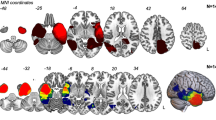
Visual evoked cortical magnetic field (VEF) waveforms were recorded from both hemifields in 21 patients with temporo-parieto-occipital mass lesions to identify preserved visual pathways. Fifteen patients had visual symptoms pre-operatively. Magnetoencephalographic (MEG) VEF responses were detected, using single equivalent current dipole (ECD), in 17/21 patients studied. Displaced or abnormal responses were seen in 15 patients with disruption of pathway in one patient. Three of 21 patients had alterations in the surgical approach or the planned resection based on the MEG findings. The surgical outcome for these three patients suggests that the MEG study may have played a useful role in pre-surgical planning.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rezai AR, Mogliner AY, Cappell J, Hund M, Llinas RR, Kelly PJ, (1997) Integration of functional brain mapping in image guided neurosurgery Acta Neurochir Suppl (Wien) 68:85–89
Roberts TP, Zusman E, McDermott M, Barbaro N, Rowley HA,(1995) Correlation of functional magnetic source imaging with intraoperative cortical stimulation in neurosurgical patients J Image Guided Surg 16:339–347
Penfield W, Boldrey E, (1937) Somatic motor and sensory representation in the cerebral cortex of many as studies by electrical stimulation Brain 60:389–443
Ojemann G, Ojemann J, Lettich E, Berger M, (1989) Cortical language localization in left, dominant hemisphere. An electrical stimulation mapping investigation in 117 patients J Neurosurg 71: 316–326
Wheless JW, Castillo E, Maggio V, Kim HL, Breier JI, Simos PG, Papanicolaou AC, (2004) Magnetoencephalography (MEG) and magnetic source imaging (MSI) Neurologist 10:138–153
Ganslandt O, Buchfelder M, Hastreiter P, Grummich P, Fahlbusch R, Nimsky C, (2004) Magnetic source imaging supports clinical decision making in glioma patients Clin Neurol Neurosurg107:20–26
Gallen CC, Schwartz BJ, Bucholz RD, Malik G, Barkley GL, Smith J, Tung H, Copeland B, Bruno L, Assam S, Hirschkoff E, Bloom F, (1995) Presurgical localization of functional cortex using magnetic source imaging J Neurosurg 82:988–994
Hämäläinen M, Hari R, Ilmoniemi J, Knuutila J, Lounasmaa OV, (1993) Magnetoencephalography-theory, instrumentation, and applications to noninvasive studies of the working human brain Rev Modern Phy65(2): 413–497
Sato S, (editor): Magnetoencephalography, Raven, New York, 1990
Ganslandt O, Fahlbusch R, Nimsky C, et al, (1999) Functional neuronavigation with magnetoencephalography: outcome in 50 patients with lesions around the motor cortex J Neurosurg 91:73–79
SchiffbauerH, Berger MS, Ferrari P, Freudenstein D, Rowley HA, Roberts TP, (2003) Preoperative magnetic source imaging for brain tumor surgery: a quantitative comparion with intraopertive sensory and motor mpping Neurosurg Focus 15:E7
Harding GF, Armstrong RA, Janday B, (1992) Visual evoked electrical and magnetic response to half-field stimulation using pattern reversal stimulation Ophthalmic Physiol Opt 12:171–174
Papanicolaou AC, Simos PG, Breier JI, Zouridakis G, Willmore LJ, Wheless JW, Constantinou JE, Maggio WW, Gormley WB, (1999) Magnetoencephalographic mapping of the language specific cortex J Neurosurg 90:85–93
Fischer MJ, Scheler G, Stefan H. (2005) Utilization of magnetoencephalography results to obtain favourable outcomes in epilepsy surgery Brain128:153–157
Assaf BA, Karkar KM, Laxer KD, Garcia PA, Austin EJ, Barbaro NM, Aminoff MJ, (2004) Magnetoencephalography source localization and surgical outcome in temporal lobe epilepsy Clin Neurophysiol 115:2066–2076
Knowlton RC, Laxer KD, Aminoff MJ, Roberts TP, Wong ST, Rowley HA (1997) Magnetoencephalography in partial epilepsy: clinical yield and localization accuracy Ann Neurol 42:622–631
Nakamura A, Kakigi R, Hoshiyama M, Koyama S, Kitamura Y, Shimojo M, (1997) Visual Evoked Cortical Magnetic Fields to Pattern reversal stimulation Cognitive Brain Res 6:9–22
Bowyer SM, Mason K, Tepley N, Smith BJ, Barkley GL, (2003) MEG validation parameters for clinical evaluation of interictal epileptic activity J Clin Neurophysiol 20:87–93
Johnston PR, Gulrajani RM, (2000) Selecting the corner in the L-curve approach to Tikhonov regularization IEEE T Bio-Med Eng 47:1293–1296
Barbati G, Porcaro C, Zappasodi F, Rossini PM, Tecchio F, (2004) Optimization of an independent component analysis approach for artifact identification and removal in magnetoencephalographic signals Clin Neurophysiol 115:1220–1232
Acknowledgement
Research supported by NIH/NINDS Grant RO1-NS30914, Hermelin Brain Tumor Center and The Henry Ford Neuroscience Institute.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Grover, K., Bowyer, S., Rock, J. et al. Retrospective review of MEG visual evoked hemifield responses prior to resection of temporo-parieto-occipital lesions. J Neurooncol 77, 161–166 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-005-9014-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-005-9014-z