Summary
Introduction:
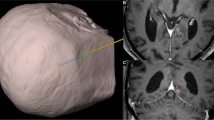
The use of image-guided systems (IGS) for brain biopsy has increased in neurosurgical practice. We sought to evaluate the accuracy of a plastic, disposable burr hole mounted guide for stereotactic biopsy using an IGS and compare the results of different targeting methods with those of frame based localization.
Methods:
MRIs were performed on a skull model with mounted fiducials with a stereotactic frame in place and data was loaded onto the Stealth IGS. The model was placed in a Mayfield head holder and fixed to the OR table. Registration of imaging to physical space was carried out. Using three different targeting methods on the Stealth IGS, the distance between the target and the predicted position of the target, the offset error, was measured in three dimensions and confirmed by 2 observers. A sum of squares for the 3 offset errors in all planes was used to calculate the summed vector error. The same MRI dataset used with the Cosman–Roberts–Wells (CRW) stereotactic frame for comparison. The summed vector error was calculated in the same manner to compare the accuracy of targeting with these guides to the frame-based CRW system.
Results:
For frameless stereotaxy using the “Straight- guide 4 2D” targeting method the mean error was 2.58 ± 0.51 mm (n=12). The vector error was 5.23 ± 0.54 (n=4). For the registration set and target using the “Offset- guide 4 2D” targeting method the mean error was 1.66 ± 0.36 mm (n=12). The vector error was 3.32 ± 0.72 (n=4). The best localization was obtained with the “probe’s eye” planning and targeting. The mean error was 0.33 ± 0.16 mm (n=12). The vector error was 1.0 ± 0.28 (n=4). We found a statistical difference between the different techniques (P<0.001) (Kruskal–Wallis One Way Analysis of Variance on Ranks). An all pairwise multiple comparison procedure (Holm–Sidak method) found an overall significance level = 0.05. For the frame-based CRW the mean error from the target was 1.03 ± 0.19 mm (n=18) and the mean target localization error vector was 2.23 ± 0.14 (n=6). We found a statistically significant difference between NDT guide “Probes Eye” vs. the MR-CRW (P=0.003, Mann–Whitney Rank Sum Test).
Conclusions:
These results indicate that using MR imaging, surgical planning software and the skull mounted Navigus-DT with the probe’s eye view option for targeting, localization accuracy appears to fall within acceptable ranges compared with frame-based methods which have been the standards for stereotactic brain biopsy and functional neurosurgery. Furthermore, there may be considerable differences in accuracy between different targeting methods.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
GH Barnett DW Miller J Weisenberger (1999) ArticleTitleFrameless stereotaxy with scalp-applied fiducial markers for brain biopsy procedures: experience in 218 cases J Neurosurg 91 569–576 Occurrence Handle10507376 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1MvjsFaisg%3D%3D
NL Dorward TS Paleologos O Alberti DG Thomas (2002) ArticleTitleThe advantages of frameless stereotactic biopsy over frame-based biopsy Br J Neurosurg 16 110–118 Occurrence Handle12046728 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD38zgsFOjtQ%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1080/02688690220131705
Paleologos TS, Dorward NL, Wadley JP, Thomas DG: Clinical validation of true frameless stereotactic biopsy: analysis of the first 125 consecutive cases. Neurosurgery 49: 830–835; discussion 835–837, 2001.
Smith JS, Quinones-Hinojosa A, Barbaro NM, McDermott MW: Frame-based stereotactic biopsy remains an important diagnostic tool with distinct advantages over frameless stereotactic biopsy. J Neurooncol, 2004.
MJ Fritsch MJ Leber L Gossett BA Lulu AJ Hamilton (1998) ArticleTitleStereotactic biopsy of intracranial brain lesions. High diagnostic yield without increased complications: 65 consecutive biopsies with early postoperative CT scans Stereotact Funct Neurosurg 71 36–42 Occurrence Handle10072672 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1M7nt1altw%3D%3D
Quinones-Hinojosa A, Sanai N, McDermott MW: Assessment of image guided accuracy using two types of disposable biopsy guides as compared to frame-based localization, in, American Association of Neurological Surgeons Abstract Archive (http://www.aans.org/Library/Article.aspx?ArticleId=12387), 2002.
Fontaine D, Dormont D, Hasboun D, Clemenceau S, Valery C, Oppenheim C, Sahel M, Marsault C, Philippon J, Cornu P: Magnetic resonance-guided stereotactic biopsies: results in 100 consecutive cases. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 142: 249–255; discussion 255–246, 2000.
J McInerney DW Roberts (2000) ArticleTitleFrameless stereotaxy of the brain Mt Sinai J Med 67 300–310 Occurrence Handle11021780 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3cvmsFymtA%3D%3D
Moriarty TM, Quinones-Hinojosa A, Larson PS, Alexander E 3rd, Gleason PL, Schwartz RB, Jolesz FA, Black PM: Frameless stereotactic neurosurgery using intraoperative magnetic resonance imaging: stereotactic brain biopsy. Neurosurgery 47: 1138–1145; discussion 1145–1136, 2000.
Wen DY, Hall WA, Miller DA, Seljeskog EL, Maxwell RE: Targeted brain biopsy: a comparison of freehand computed tomography-guided and stereotactic techniques. Neurosurgery 32: 407–412; discussion 412–403, 1993.
IM Germano JV Queenan (1998) ArticleTitleClinical experience with intracranial brain needle biopsy using frameless surgical navigation Comput Aided Surg 3 33–39 Occurrence Handle9699077 Occurrence Handle10.1002/(SICI)1097-0150(1998)3:1<33::AID-IGS5>3.0.CO;2-M Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1czmsVagsQ%3D%3D
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Quiñones-Hinojosa, A., Ware, M.L., Sanai, N. et al. Assessment of Image Guided Accuracy in a Skull Model: Comparison of Frameless Stereotaxy Techniques vs. Frame-Based Localization. J Neurooncol 76, 65–70 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-005-2915-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-005-2915-z