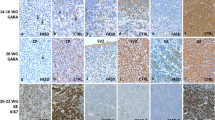
The aim of the present work was to study the relationship between the development of synaptic contacts and benzodiazepine receptors (functionally associated with the brain GABAergic system) in the brains of embryos and fetuses aged 8–15 weeks obtained from alcoholic female patients. Materials from 33 women with grade II alcoholism (ICD-10 F10.201 and F10.202) and 30 control women were studied. In contrast to controls, brain cells developing in conditions of prenatal alcoholization showed slowed formation of synaptic benzodiazepine receptors and increases in their density. These are interpreted as compensatory reactions promoting adaptation of the fetal nervous system to the effects of alcohol and functional deficiency of the GABAergic system.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Z. Ivanshina, “Development of synaptic contacts in the human brain at different stages of embryogenesis,” Zh. Nevrol. Psikhiat., No. 7, 983–989 (1976).
N. S. Kovetskii, A. V. Solonskii, and T. L. Moiseeva, “Impairments to brain development in fetuses from mothers abusing alcohol during pregnancy,” Zh. Nevrol. Psikhiat., No. 3, 58–63 (1995).
Yu. I. Savulev and Zh. V. Soloviev, “Cell contacts in the human brain at the early stages of embryonic development,” in: Convergence and Synapses [in Russian], Moscow (1973), pp. 149–151.
A. V. Solonskii, “Effects of alcoholization of mothers during pregnancy on the development of cortical synapses in human embryos,” Sib. Vestn. Psikhiat. Narkol., No. 4, 25–29 (2002).
A. V. Solonskii, S. V. Logvinov, N. A. Kutenova, and A. V. Danilets, “Quantitative dynamics of synaptogenesis and vasculogenesis of the brain in human embryos and fetuses in conditions of prenatal exposure to ethanol,” Sib. Vestn. Psikhiat. Narkol., No. 1, 79–83 (2008).
A. V. Solonskii and S. V. Logvinov, “Ultrastructural and morphometric characteristics of synaptogenesis in the brains of human embryos and fetuses in conditions of prenatal exposure to ethanol,” Byull. Sib. Med., No. 1, 45 (2008).
T. V. Shushpanova and V. Ya. Semke, “Properties of benzodiazepine receptors of the central and peripheral types in various human brain structures in alcoholism,” Byull. Eksperim. Biol. Med., 127, Suppl. 1, 40–42 (1999).
T. V. Shushpanova and V. Ya. Semke, “Peripheral benzodiazepine receptors on platelets in alcoholism,” Zh. Nevrol. Psikhiat., 106, No. 11, 53–56 (2006).
A. Abi-Dargham, J. H. Krystal, S. Anjilvel, et al., “Alterations of benzodiazepine receptors in type II alcoholic subjects measured with SPECT and [123I]iomazenil,” Am. J. Psychiatry, 155, 1550–1555 (1998).
T. N. Behar, A. E. Schaffner, C. A. Stott, et al., “Differential response of cortical plate and ventricular zone cells to GABA as a migration stimulus,” J. Neurosci., 18, 6378–6387 (1998).
Y. Ben-Ari, J. L. Gaiarsa, R. Tyzio, et al., “GABA: a pioneering transmitter that excites immature neurons and generates primitive oscillations,” Physiol. Rev., 87, 1215–1284 (2007).
F. L. Bookstein, A. P. Streissguth, P. D. Connor, et al., “Damage to the human cerebellum from prenatal alcohol exposure: the anatomy of a single biometrical explanation,” Anat. Record New Anat., 289, 195–209 (2006).
K. J. Buck, and R. A. Harris, “Benzodiazepine agonist and inverse agonist actions on GABAA receptor-operated chloride channels. II. Chronic effects of ethanol,” J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther., 253, No. 2, 713–719 (1990).
M. Davies, “The role of GABAA receptors in mediating the effects of alcohol in the central nervous system,” Rev. Psychiat. Neurosci., 28, No. 4, 263–274 (2003).
T. L. Dellovade, A. M. Davis, C. Ferguson, et al., “GABA influences the development of the ventromedial nucleus of the hypothalamus,” J. Neurobiol., 49, No. 4, 264–276 (2001).
M. Emerit, M. Raid, and M. Hamon, “Trophic effects of neurotransmitters during brain maturation,” Biol. Neonate, 62, 193–201 (1992).
E. A. Frost, R. S. Gist, and F. Adriano, “Drugs, alcohol, pregnancy, and the fetal alcohol syndrome,” Int. Anesthesiol. Clin., 49, No. 1, 119–133 (2011).
Y. Ikeda, N. Nishiyama, H. Saito, and H. Katsuki, “GABAA receptor stimulation promotes survival of embryonic rat striatal neurons in culture,” Dev. Brain. Res., 98, 253–258 (1997).
C. Ikonomiou, P. Bittigau, M. J. Ishimaru, et al., “Ethanol-induced apoptotic neurodegeneration and fetal alcohol syndrome,” Science, 287, No. 5455, 1056–1060 (2000).
R. A. Harris, “Ethanol actions on multiple ion channels: which are important?” Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res., 23, 1563–1570 (1999).
J. He, K. Nixon, A. K. Shetty, et al., “Chronic alcohol exposure reduces hippocampal neurogenesis and dendritic growth of newborn neurons,” Eur. J. Neurosci., 21, 2711–2720 (2005).
K. L. Jones and D. W. Smith, “Recognition of the fetal alcohol syndrome in early infancy,” Lancet, No. 7836, part 2, 999–1001 (1973).
M. Katsura, “Functional involvement of cerebral diazepam binding inhibitor (DBI) in the establishment of drug dependence,” Folia Pharmacol. Japon., 117, No. 3, 159–168 (2001).
A. Y. Klintsova, J. L. Helfer, L. H. Calizo, et al., “Persistent impairment of hippocampal neurogenesis in young adult rats following early postnatal alcohol exposure,” Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res., 31, 2073–2082 (2007).
A. R. Kriegstein and D. F. Owens, “GABA may act as a self-limiting trophic factor at developing synapses,” Sci. STKE, 95 (2001).
A. S. LaMantia, “The usual suspects: GABA and glutamate may regulate proliferation in the neocortex,” Neuron, 15, 1223–1225 (1995).
G. H. Levine, J. J. Maglio, and J. Horwitz, “Differentiation effects of ethanol on signal transduction,” Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res., 24, 93–101 (2000).
I. A. Lobo and R. A. Harris, “GABAA receptors and alcohol,” Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav., 90, No. 1, 90–94 (2008).
D. Maric, Q. Y. Liu, I. Maric, et al., “GABA expression dominates neuronal lineage progression in embryonic rat neocortex and facilitates neurite outgrowth via GABA(A) autoreceptor/Cl-channels,” J. Neurosci., 21, No. 7, 2343–2360 (2001).
T. Narahashi, K. Kuriyama, P. Illes, et al., “Neuroreceptors and ion channels as targets of alcohol,” Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res., 25, No. 5, Supplement, 182–188 (2001).
J. L. Olney, D. F. Wozniak, V. Jevtovic-Todorovic, et al., “Glutamate and GABA receptor dysfunction in the fetal alcohol syndrome,” Neurotox. Res., 4, No. 4, 315–325 (2002).
H. C. Olson, B. A. Morse, and C. Huffine, “Development and psychopathology: fetal alcohol syndrome and related conditions,” Semin. Clin. Neuropsychiatry, 3, No. 4, 62–84 (1998).
R. Reichelt, D. Hofmann, H. J. Födisch, et al., “Ontogeny of the benzodiazepine receptor in human brain: fluorographic, immunochemical and reversible binding studies,” J. Neurochem., 57, No. 4, 1128–1135 (1991).
E. Sigel and A. Buhr, “The benzodiazepine binding site of GABAA receptors,” Trends Pharmacol. Sci., 18, No. 11, 425–429 (1997).
A. K. Singh, S. Gupta, M. Younus, and M. Ramzam, “In vitro neurogenesis from neural progenitor cells isolated from hippocampus region of the brain of adult rats exposed to ethanol during early development through their alcohol-drinking mothers,” Alcohol and Alcoholism, 44, 185–198 (2009).
C. Taylor, J. Nash, A. Rich, et al., “Assessment of GABA A benzodiazepine receptor (GBzR) sensitivity in patients with alcohol dependence,” Alcohol and Alcoholism, 43, No. 6, 614–618 (2008).
K. R. Warren, F. J. Calhoun, P. A. May, et al., “GABA A receptors and alcohol.” J. Psychiatry Neurosci., 28, No. 4, 270–271 (2003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Zhurnal Nevrologii i Psikhiatrii imeni S. S. Korsakova, Vol. 112, No. 1, pp. 60–67, January, 2012.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shushpanova, T.V., Solonskii, A.V. Synaptogenesis and the Formation of Benzodiazepine Receptors in the Human Brain in Conditions of Prenatal Alcoholization. Neurosci Behav Physi 43, 423–430 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11055-013-9749-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11055-013-9749-5