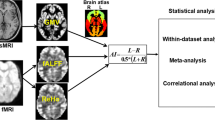
A total of 27 right-handed patients aged 7–30 years with diagnoses of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder were studied using standard MRI scans. Of these, 14 were aged below 13 years. The volumes of the lateral ventricles were measured using T1-weighted MRI images of sagittal sections of the brain to a precision of 3 mm3. External head sizes were also measured to allow ventricle volumes to be normalized. All patients underwent complex neuropsychological investigations. Memory was assessed, along with visual, auditory, tactile, and spatial recognition functions and the motor and speech spheres. Test data were assessed in terms of the severity of impairments associated with one brain structure or another on a tenpoint scale. Assessment points were summed for each hemisphere, for the “first area” (cortical structures), and all structures for statistical analysis. Neuropsychological testing revealed functional impairments predominantly of the frontal areas of the hemispheres, the hippocampus, and the reticular formation. Neuropsychological deficits were least linked with alterations in the postcentral and parietal areas of the cortex. Statistical analysis demonstrated a significant positive correlation between the normalized left lateral ventricle volume and the degree of neuropsychological impairments (r = 0.5127 at p = 0.0063) for the whole study group. The correlation was more marked on comparison of the normalized left ventricular volume and the severity of neuropsychological impairments related to the left hemisphere (r = 0.6303 at p = 0.0004). A relationship was seen between the volume of the intraventricular space and cortical functional impairments (r = 0.5071 at p = 0.0069) in patients less than 13 years old. A relationship between ventricular volume and linear head size was confirmed (r = 0.5759 at p = 0.0017), which was more marked in subjects less than 13 years old (r = 0.6833 at p = 0.01).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
V. M. Verkhlyutov,V. B. Strelets, M. V. Magomedova, and R. A. Magomedov, “Localization of sources of spontaneous EEG rhythms in patients with schizotypy and schizophrenia,” in: Dipole Sources of EEG Rhythms in Neurophysiology and Clinical Practice [in Russian], Working Report, 17–18 June 2002, Institute of Higher Nervous Activity and Neurophysiology, Russian Academy of Sciences, Moscow, pp. 31–32.
V. M. Verkhlyutov,Yu. V. Shchuchkin, V. L. Ushakov, V. B. Strelets, and Yu. A. Pirogov, “Assessment of the locations and dipole moments of the sources of alpha and theta rhythms using cluster analysis in health and schizophrenia,” Zh. Vyssh. Nerv. Deyat., 56, No. 1, 47–55 (2006).
A. R. Luriya, Higher Cortical Functions in Humans and Alterations in Local Brain Damage [in Russian], Moscow State University, Moscow (1962).
I. A. Skvortsov,Yu. A. Kholodov, É. G. Simernitskaya, A. M. Gorbach, T. N. Osipenko V. M. Verkhlyutov, G. E. Rudenskaya, V. A. Konyshev, G. E. Kharina, R. A. Maragey, A. Yu. Sagura, and A. I. Shalyapina, Neurological and Neuropsychological Assessment of Magnetoencephalographic Data in Epileptic Syndrome in Children. Questions in Neuropathology, Psychiatry, and Addiction Medicine [in Russian], Metsniereba, Tbilisi (1987), pp. 302–304.
E. D. Khomskaya, Neuropsychology [in Russian], Moscow State University, Moscow (1987).
F. Abell, M. Krams, J. Ashburner, R. Passingham, K. Friston, R. Frackowiak, F. Happe, C. Frith, and U. Frith, “The neuroanatomy of autism: a voxel-based whole brain analysis of structural scans,” Neuroreport, 10, 1647–1651 (1999).
H. Ananth, I. Popescu, H. D. Critchley, C. D. Good, R. S. Frackowiak, and R. J. Dolon, “Cortical and subcortical gray matter abnormalities in schizophrenia determined through structural magnetic resonance imaging with optimized volumetric voxel-based morphometry,” Am. J. Psychiatry, 159, 1497–1505 (2002).
M. S. Buchsbaum, S. Yang, E. Hazlett, B. V. Siegel, M. Germans, M. Haznedar, S. O’Flaithbheartaigh, T. Wei, J. Silverman, and L. J. Siever, “Ventricular volume and asymmetry in schizotypal personality disorder and schizophrenia assessed with magnetic resonance imaging,” Schizophr. Res., 27, 45–53 (1997).
T. D. Cannon, T. G. M. Erp, M. Huttunen, J. Lönnqvist, O. Salonen, L. Valanne, V. P. Putanen, C. G. Standertskjoeld-Nordenstrom, R. E. Gur, and M. Yan, “Regional grey matter, white matter, and cerebrospinal fluid distributions in schizophrenic patients, their siblings, and controls,” Arch. Gen. Psychiatry, 55, 1084–1091 (1998).
R. A. Carper, P. Moses, Z. D. Tigue, and E. Courchesne, “Cerebral lobes in autism: early hyperplasia and abnormal age effects,” NeuroImage, 16, 1038–1051 (2001).
S. A. Chance, M. M. Esiri, and T. J. Crow, “Ventricular enlargement in schizophrenia: a primary change in the temporal lobe,” Schizophr. Res., 62, 123–131 (2003).
M. K. Chung, K. M. Salton, A. L. Alexander, and R. J. Davidson, “Less white matter concentration in autism: 2D voxel-based morphometry,” NeuroImage, 23, 242–251 (2004).
E. Courchesne, C. M. Karns, H. R. Davis, R. Ziccardi, R. A. Carper, Z. D. Tigue, H. J. Chisum, P. Moses, K. Pierce, C. Lord, A. J. Lincoln, S. Pizzo, L. Schreibman, R. H. Hass, N. A. Akshoomoff, and R. Y. Courchesne, “Unusual brain growth patterns in early life in patients with autistic disorder: an MRI study,” Neurology, 57, 245–254 (2001).
C. Davatzikos, D. Shen, R. C. Gur, Z. Wu, D. Liu,Y. Fan, P. Hughett, B. I. Turetsky, and R. E. Gur, “Whole-brain morphometric study of schizophrenia revealing a spatially complex set of focal abnormalities,” Arch. Gen. Psychiatry, 62, No. 11, 1218–1227 (2005).
C. C. Dickey, M. E. Shenton, Y. Hirayasu, I. Fischer, M. M. Vogelmaier, M. A. Niznikiewicz, L. J. Seidman, S. Fraone, and R. W. McCarley, “Large CSF volume not attributable to ventricular volume in schizotypal personality disorder,” Am. J. Psychiatry, 157, No. 1, 48–54 (2000).
C. Gaser, I. Nenadic, B. R. Buchsbaum, E. A. Hazlett, and M. S. Buchsbaum, “Ventricular enlargement in schizophrenia related to volume reduction of the thalamus, striatum, and superior temporal cortex,” Am. J. Psychiatry, 161, No. 1, 154–156 (2004).
R. E. Gur, B. I. Turetsky,W. B. Bilker, and R. C. Gur, “Reduced gray matter volume in schizophrenia,” Arch. Gen. Psychiatry, 56, 905–911 (1999).
M. S. M. Izac, “Basic anatomy and physiology of sleep,” Am. J. E. N. D. Technol., 46, No. 1, 18–38 (2006).
L. Krabbendam and J. Jolles, “The neuropsychology of schizophrenia,” Biol. Psychiatry, 52, No. 7, 631–647 (2002).
C. McDonald, N. Marshall, P. C. Sham, E. T. Bullmore, K. Schulze, B. Chapple, F. Bramon, F. Filbey, S. Quraishi, M. Walshe, and R. M. Murray, “Regional brain morphometry in patients with schizophrenia or bipolar disorder and their unaffected relatives,” Am. J. Psychiatry, 163, No. 3, 478–487 (2006).
C. J. Mummery, K. Patterson, C. J. Price, J. Ashburner, R. S. Frackowiak, and J. R. Hodges, “A voxel-based morphometry study of semantic dementia: relationship between temporal lobe atrophy and semantic memory,” Ann. Neurol., 47, 36–45 (2000).
R. M. Murray, “Auditory hallucinations and the temporal cortical response to speech in schizophrenia: A functional magnetic resonance imaging study,” Am. J. Psychiatry, 15, 1676–1682 (1997).
K. L. Narr, R M. Bilder, A. W. Toga, R. P. Woods, D. E. Rex, P. R. Szeszko, D. Robinson, S. Sevy, H. Gunduz-Bruce, Y. P. Wang, H. DeLuca, and P. M. Thompson, “Mapping cortical thickness and gray matter concentration in first episode schizophrenia,” Cereb. Cortex, 15, No. 6, 708–719 (2005).
K. L. Narr, P. M. Thompson, P. Szeszko, D. Robinson, S. Jang, R. P. Woods, S. Kim, M. Kiralee, K. M. Hayashi, D. Asunction, A.W. Toga, and R. M. Bilder, “Regional specificity of hippocampal volume reductions in first-episode schizophrenia,” NeuroImage, 21, 1563–1575 (2004).
G. Neckelmann, K. Specht, A. Lund, L. Ersland, A. I. Smievoll, D. Neckelmann, and K. Hugdahl, “MR morphometry analysis of grey matter volume reduction in schizophrenia: association with hallucination,” Int. J. Neurosci., 116, 9–23 (2006).
G. Nellhaus, “Head circumference from birth to eighteen years,” Pediatrics, 41, No. 1, 106–114 (1968).
S. A. Rombouts, F. Barkhof, M. P. Witter, and P. Scheltens, “Unbiased whole brain analysis of grey matter loss in Alzheimer’s disease,” Neurosci. Lett., 285, 231–233 (2000).
H. J. Rosen, J. H. Kramer, M. L. Gorno-Tempini, N. Schuff, M.Weiner, and B. L. Miller, “Patterns of cerebral atrophy in primary progressive aphasia,” Am. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry, 10, 89–97 (2002).
T. Sigmundsson, J. Suckling, M. Maier, S. Williams, E. Bullmore, K. Greenwood, R. Fukuda, M. Ron, and B. Toone, “Structural abnormalities in frontal, temporal, and limbic regions and interconnecting white matter tracts in schizophrenic patients with prominent negative symptoms,” Am. J. Psychiatry, 158, 234–243 (2001).
C. Testa, M. P. Laakso, F. Sabattoli, R. Fossi, A. Beltramello, H. Soininen, and G. B. Frisoni, “A comparison between the accuracy of voxel-based morphometry and hippocampal volumetry in Alzheimer’s disease,” J. Agn. Reson. Imaging, 19, 274–0282 (2004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Zhurnal Vysshei Nervnoi Deyatel’nosti imeni I. P. Pavlova, Vol. 59, No. 1, pp. 34–44, January–February, 2009.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Verkhlyutov, V.M., Gapienko, G.V., Ushakov, V.L. et al. MRI Morphometry of the Cerebral Ventricles in Patients with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder. Neurosci Behav Physi 40, 295–303 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11055-010-9256-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11055-010-9256-x