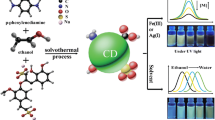
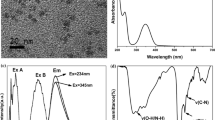
Abstract
A set of the highly fluorescent N, S co-doped carbon dots (NSCDs) were prepared through one-step hydrothermal synthesis at different temperature with citric acid as the carbon source and cysteamine as the N, S source. The NSCDs synthesized at 200 °C show significant quantum yield (81%) due to its optimal structure. The structure of the NSCDs changed with varying degrees of carbonization/aromatization and different content of multifunctional groups of C=O, −NH2, −OH, −SH, and N, S-aromatic heterocycte under different preparation temperatures, thus exhibiting tunable fluorescence. Especially, the obtained NSCDs exhibited a blue fluorescence in solution state and changed from strong blue to yellowish-green in its solid state under UV light as a result of the increase in preparation temperature. The as-prepared NSCDs can be used in selective detection of complex anions such as Cr2O7 2− and Fe(CN)6 3−, cell imaging, and preparation of fluorescent composite films.

ᅟ








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baker SN, Baker GA (2010) Luminescent carbon nanodots: emergent nanolights. Angew Chem Int Ed 49:6726–6744. doi:10.1002/anie.200906623
Bao L, Liu C, Zhang ZL, Pang DW et al (2015) Photoluminescence-tunable carbon nanodots: surface-state energy-gap tuning. Adv Mater 27:1663–1667. doi:10.1002/adma.201405070
Deng YH, Chen X, Wang F, Zhang XA, Zhao DX, Shen DZ (2014) Environment-dependent photon emission from solid state carbon dots and its mechanism. Nano 6:10388–10393. doi:10.1039/C4NR02544J
Ding H, Wei JS, Xiong HM (2014) Nitrogen and sulfur co-doped carbon dots with strong blue luminescence. Nano 6:13817–13823. doi:10.1039/C4NR04267K
Dong YQ, Shao JW, Chen CQ, Li H, Wang R, Chi YW et al (2012) Blue luminescent graphene quantum dots and graphene oxide prepared by tuning the carbonization degree of citric acid. Carbon 50:4738–4743. doi:10.1016/j.carbon.2012.06.002
Dong YQ, Pang HC, Yang HB, Guo CX, Shao JW, Chi YW et al (2013) Carbon-based dots co-doped with nitrogen and sulfur for high quantum yield and excitation-independent emission. Angew Chem Int Ed 52:7800–7804. doi:10.1002/anie.201301114
Hou J, Wang W, Zhou TY, Wang B, Li HY, Ding L (2016) Synthesis and formation mechanistic investigation of nitrogen-doped carbon dots with high quantum yields and yellowish-green fluorescence. Nano 8:11185–11193. doi:10.1039/C6NR02701F
Kasprzyk W, Bednarz S, Żmudzki P, Galica M, Bogdał D (2015) Novel efficient fluorophores synthesized from citric acid. RSC Adv 5:34795–34799. doi:10.1039/C5RA03226A
Krysmann MJ, Kelarakis A, Dallas P, Giannelis EP (2012) Formation mechanism of carbogenic nanoparticles with dual photoluminescence emission. J Am Chem Soc 134:747–750. doi:10.1021/ja204661r
Lee DW, Ma X, Jung JH, Jeong EJ, Hashemi H, Bregman A et al (2015) The effects of extended conjugation length of purely organic phosphors on their phosphorescence emission properties. Phys Chem Chem Phys 17:19096–19103. doi:10.1039/C5CP01003A
Li Y, Hu Y, Zhao Y, Shi GQ, Deng LE, Hou YB et al (2011) An electrochemical avenue to green-luminescent graphene quantum dots as potential electron-acceptors for photovoltaics. Adv Mater 23:776–780. doi:10.1002/adma.201003819
Li HT, Kang ZH, Liu Y, Lee ST (2012) Carbon nanodots: synthesis, properties and applications. J Mater Chem 22:24230–24253. doi:10.1039/C2JM34690G
Liang J, Jiao Y, Jaroniec M, Qiao SZ (2012) Sulfur and nitrogen dual-doped mesoporous graphene electrocatalyst for oxygen reduction with synergistically enhanced performance. Angew Chem Int Ed 51:11496–11500. doi:10.1002/anie.201206720
Liu HP, Ye T, Mao CD (2007) Fluorescent carbon nanoparticles derived from candle soot. Angew Chem Int Ed 46:6473–6475. doi:10.1002/anie.200701271
Lu WJ, Li Y, Li RJ, Shuang SM, Dong C, Cai ZW (2016) Facile synthesis of N-doped carbon dots as a new matrix for detection of hydroxy-polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by negative-ion matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8:12976–12984. doi:10.1021/acsami.6b01510
Mirtchev P, Henderson EJ, Soheilnia N, Yip CM, Ozin GA (2012) Solution phase synthesis of carbon quantum dots as sensitizers for nanocrystalline TiO2 solar cells. J Mater Chem 22:1265–1269. doi:10.1039/C1JM14112K
Qu D, Zheng M, Du P, Zhou Y, Zhang LG, Li D et al (2013) Highly luminescent S, N co-doped graphene quantum dots with broad visible absorption bands for visible light photocatalysts. Nano 5:12272–12277. doi:10.1039/C3NR04402E
Samantara AK, Sahu SC, Ghosh A, Jena BK (2015) Sandwiched graphene with nitrogen, sulphur co-doped CQDs: an efficient metal-free material for energy storage and conversionapplications. J Mater Chem A 3:16961–16970. doi:10.1039/C5TA03376D
Shen JH, Zhu YH, Yang XL, Li CZ (2012) Graphene quantum dots: emergent nanolights for bioimaging, sensors, catalysis and photovoltaic devices. Chem Commun 48:3686–3699. doi:10.1039/C2CC00110A
Shi JY, Chan CY, Pang YT, Ye WW, Tian F, Lyu J et al (2015) A fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) biosensor based on graphene quantum dots (GQDs) and gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) for the detection of mecA gene sequence of Staphylococcus aureus. Biosens Bioelectron 67:595–600. doi:10.1016/j.bios.2014.09.059
Song ZQ, Quan FY, Xu YH, Liu ML, Cui L, Liu JQ (2016) Multifunctional N, S co-doped carbon quantum dots with pH- and thermo-dependent switchable fluorescent properties and highly selective detection of glutathione. Carbon 104:169–178. doi:10.1016/j.carbon.2016.04.003
Wang BB, Cheng QJ, Wang LH, Zheng K, Ostrikov K (2012) The effect of temperature on the mechanism of photoluminescence from plasma-nucleated, nitrogenated carbon nanotips. Carbon 50:3561–3571. doi:10.1016/j.carbon.2012.03.028
Wang Y, Kalytchuk S, Zhang Y, Shi HC, Kershaw SV, Rogach AL (2014a) Thickness-dependent full-color emission tunability in a flexible carbon dot ionogel. J Phys Chem Lett 5:1412–1420. doi:10.1021/jz5005335
Wang WP, Lu YC, Huang H, Wang AJ, Chen JR, Feng JJ (2014b) Solvent-free synthesis of sulfur- and nitrogen-co-doped fluorescent carbon nanoparticles from glutathione for highly selective and sensitive detection of mercury (II) ions. Sensors Actuators B Chem 202:741–747. doi:10.1016/j.snb.2014.06.010
Wu P, Li Y, Yan XP (2009) CdTe quantum dots (QDs) based kinetic discrimination of Fe2+ and Fe3+, and CdTe QDs-fenton hybrid system for sensitive photoluminescent detection of Fe2+. Anal Chem 81:6252–6257. doi:10.1021/ac900788w
Xu MH, He GL, Li ZH, He FJ, Gao F, Su YJ et al (2014) A green heterogeneous synthesis of N-doped carbon dots and their photoluminescence applications in solid and aqueous states. Nano 6:10307–10315. doi:10.1039/C4NR02792B
Xu Q, Pu P, Zhao JG, Dong CB, Gao C, Chen YS et al (2015a) Preparation of highly photoluminescent sulfur-doped carbon dots for Fe (III) detection. J Mater Chem A 3:542–546. doi:10.1039/C4TA05483K
Xu MH, Xu SS, Yang Z, Shu MJ, He GL, Huang D et al (2015b) Hydrophilic and blue fluorescent N-doped carbon dots from tartaric acid and various alkylol amines under microwave irradiation. Nano 7:15915–15923. doi:10.1039/C5NR04209G
Xue MY, Zhang LL, Zou MB, Lan CQ, Zhan ZH, Zhao SL (2015) Nitrogen and sulfur co-doped carbon dots: a facile and green fluorescence probe for free chlorine. Sensors Actuators B Chem 219:50–56. doi:10.1016/j.snb.2015.05.021
Yang ZC, Li X, Wang J (2011) Intrinsically fluorescent nitrogen-containing carbon nanoparticles synthesized by a hydrothermal process. Carbon 49:5207–5212. doi:10.1016/j.carbon.2011.07.038
Yang Z, Yao Z, Li GF, Fang GY, Nie HG, Liu Z et al (2012) Sulfur-doped graphene as an efficient metal-free cathode catalyst for oxygen reduction. ACS Nano 6:205–211. doi:10.1021/nn203393d
Zhang WX, Dai DJ, Chen XF, Guo XX, Fan JY et al (2014) Red shift in the photoluminescence of colloidal carbon quantum dots induced by photon reabsorption. Appl Phys Lett 104:091902. doi:10.1063/1.4867487
Zhao AD, Zhao CQ, Li M, Ren JS, Qu XG (2014) Ionic liquids as precursors for highly luminescent, surface-different nitrogen-doped carbon dots used for label-free detection of Cu2+/Fe3+ and cell imaging. Anal Chim Acta 809:128–133. doi:10.1016/j.aca.2013.10.046
Zheng M, Xie ZG, Qu D, Li D, Du P, Jing XB et al (2013) On−off−on fluorescent carbon dot nanosensor for recognition of chromium (VI) and ascorbic acid based on the inner filter effect. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 5:13242–13247. doi:10.1021/am4042355
Zhou J, Wang C, Qian ZS, Chen CC, Ma JJ, Du GH et al (2012) Highly efficient fluorescent multi-walled carbon nanotubes functionalized with diamines and amides. J Mater Chem 22:11912–11914. doi:10.1039/C2JM31192E
Zhou J, Yang Y, Zhang CY (2013) A low-temperature solid-phase method to synthesize highly fluorescent carbon nitride dots with tunable emission. Chem Commun 49:8605–8607. doi:10.1039/C3CC42266F
Zhu SJ, Meng QN, Wang L, Zhang JH, Song YB, Jin H et al (2013) Highly photoluminescent carbon dots for multicolor patterning, sensors, and bioimaging. Angew Chem Int Ed 52:3953–3957. doi:10.1002/anie.201300519
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Funding
This work was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21374046), Program for Changjiang Scholars and Innovative Research Team in University, Open Project of State Key Laboratory of Supramolecular Structure and Materials (SKLSSM201718) and the Testing Foundation of Nanjing University.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOC 1164 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, M., Meng, X., Li, B. et al. N, S co-doped carbon dots with high quantum yield: tunable fluorescence in liquid/solid and extensible applications. J Nanopart Res 19, 217 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-017-3914-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-017-3914-7