Abstract
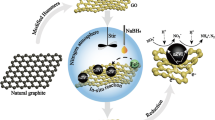
High specific surface area of graphene (GR) has gained special scientific attention in developing magnetic GR nanocomposite aiming to apply for the remediation of diverse environmental problems like point-of-use water purification and simultaneous separation of contaminants applying low external magnetic field (<1.0 T) from ground water. Fabrication of magnetic manganese-incorporated iron(III) oxide (Mn x 2+Fe2−x 3+O4 2−) (IMBO)–GR nanocomposite is reported by exfoliating the GR layers. Latest microscopic, spectroscopic, powder X-ray diffraction, BET surface area, and superconducting quantum interference device characterizations showed that the material is a magnetic nanocomposite with high specific surface area (280 m2 g−1) and pore volume (0.3362 cm3 g−1). Use of this composite for the immobilization of carcinogenic As(III) from water at 300 K and pH ~7.0 showed that the nanocomposite has higher binding efficiency with As(III) than the IMBO owing to its high specific surface area. The composite showed almost complete (>99.9 %) As(III) removal (≤10 μg L−1) from water. External magnetic field of 0.3 T efficiently separated the water dispersed composite (0.01 g/10 mL) at room temperature (300 K). Thus, this composite is a promising material which can be used effectively as a potent As(III) immobilizer from the contaminated groundwater (>10 μg L−1) to improve drinking water quality.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Avouris P, Dimitrakopoulos C (2012) Graphene: synthesis and applications. Mater Today 15:86–97
Babic BM, Milorjic SK, Polovina MJ, Koludieronic BV (1999) Point of zero charge and intrinsic equilibrium constants of activated carbon cloth. Carbon 37:477–480
Basu T, Gupta K, Ghosh UC (2010) Equilibrium and thermodynamics on arsenic(III) sorption reaction in the presence of background ions occurring in groundwater with nanoparticle agglomerates of hydrous iron(III) + chromium(III) mixed oxide. J Chem Eng Data 55:2039–2047
Chandra V, Kim KS (2011) Highly selective adsorption of Hg2+ by a polypyrrole-reduced graphene oxide composite. Chem Commun 47:3942–3944
Chandra V, Park J, Chun Y, Lee JW, Hwang I, Kim KS (2010) Water dispersible magnetite-reduced graphene oxide composites for arsenic removal. ACS Nano 4:3979–3986
Clesceri LS, Greenberg AE, Eaton AD (1998) Standard methods for the examination of water and waste water, 20th edn. APHA, AWWA & WEF, American Public Health Association, American Water Work Association, Water Environment Federation, Washington DC
Compton OC, Jain B, Dikin DA, Abouimrane A, Amine K, Nguyen ST (2011) Chemically active reduced graphene oxide with tunable C/O ratios. ACS Nano 5:4380–4391
Fan Z-J, Kai W, Yan Jun Y, Wei Tong W, Zhi L-J, Feng J, Ren YM, Song LP, Wei F (2011) Facile synthesis of graphene nanosheets via Fe reduction of exfoliated graphite oxide. ACS Nano 5:191–198
Ferrari AC, Meyer JC, Scardaci V, Casiraghi C, Lazzeri M, Mauri F, Piscanec S, Jiang D, Novoselov KS, Roth S, Geim AK (2006) Raman spectrum of grapheme and grapheme layers. Phys Rev Lett 97:187401–187404
Gao W, Majumdar M, Alemani LB, Narayanan TN, Ibarra MA, Pradhan BK, Ajayan PM (2011a) Graphene oxide also used for heavy metal adsorption; engineered graphite oxide materials for application in water purification. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 3:1821–1826
Gao Y, Li Y, Zhang L, Huang H, Hu J, Shah SM, Su X (2011b) Adsorption and removal of tetracycline antibiotics from aqueous solution by grapheme oxide. J Colloid Interface Sci 368:540–546
Geim AK, Novoselov KS (2007) The rise of graphene. Nat Mater 6:183–191
Gupta K, Biswas K, Ghosh UC (2008) Nanostructure iron(III)–zirconium(IV) binary mixed oxide: synthesis, characterization and physicochemical aspects of arsenic(III) sorption from the aqueous solution. Ind Eng Chem Res 47:9903–9912
Gupta A, Chen G, Joshi P, Tadigadapa S, Eklund PC (2009) Raman scattering from high frequency phonons in supported n-graphene layer films. Nano Lett 6:2667–2673
Gupta K, Maity A, Ghosh UC (2010) Manganese associated nanoparticles agglomerate of iron(III) oxide: synthesis, characterization and arsenic(III) sorption behavior with mechanism. J Hazard Mater 184:832–842
Gupta K, Bhattacharya S, Chattopadhyay D, Mukhopadhyay A, Biswas H, Dutta J, Ray NR, Ghoah UC (2011) Ceria associated manganese oxide nanoparticles: synthesis, characterization and arsenic(V) sorption behavior. Chem Eng J 172:219–229
Gupta K, Bhattacharya S, Nandi D, Dhar A, Maity A, Mukhopadhyay A, Chattopadhyay D, Ray NR, Sen P, Ghosh UC (2012) Arsenic(III) sorption on nanostructured cerium incorporated manganese oxide (NCMO): a physical insight into the mechanistic pathway. J Colloid Interface Sci 377:269–276
Harvey CF, Swartz CH, Bhaduzzaman ABM, Keon-Blute N, Yu W, Ali MA, Ray J, Beckie R, Niedon V, Brabander D (2002) Arsenic mobility and groundwater extraction in Bangladesh. Science 298:1602–1606
He HK, Gao C (2010) Supraparamagnetic conductive and processable multifunctional grapheme nanosheets coated with high density Fe3O4 nanoparticles. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2:3201–3210
Hu J, Irena MCL, Chen G (2007) Comparative study of various magnetic nanoparticles for Cr(VI) removal. Sep Purif Technol 56:249–256
Kim WY, Kim KS (2008) Prediction of very large values of magnetoresistance in a graphene nanoribbon device. Nat Nanotechnol 3:408–412
Kim KS, Zhao Y, Jang H, Lee SY, Kim JM, Kim KS, Ahn JH, Kim P, Choi JY, Hong BH (2009) Large-scale pattern growth of graphene films for stretchable transparent electrodes. Nature 457:706–710
Kuo SL, Lee JF, Wu NL (2007) Study on pseudocapacitance mechanism of aqueous MnFe2O4 supercapitor. J Electrochem Soc 154:A34–A38
Lai J, Shafi KVPM, Ulman A, Loos K, Yang N, Cui MH, Estournès TVC, Locke DC (2004) Mixed iron–manganese oxide nanoparticles. J Phys Chem B 108:14876–14883
Lakshmipathiraj P, Narasimhan BRV, Prabhakar S, Raju BB (2006) Adsorption studies of arsenic on Mn-substituted iron oxyhydroxide. J Colloid Interface Sci 304:317–322
Lee M-T (1988) Catalytic behaviors of Fe–Mn mixed oxides, National Science Council, Republic of Chaina. PB 90140971, 1–52
Lian P, Zhu X, Liang S, Li Z, Wang W, Wang H (2010) Large reversible capacity of high quality grapheme sheets as an anode material for lithium ion batteries. Electrochem Acta 55:3909–3914
Lin TF, Wu JK (2001) Adsorption of arsenite and arsenate within activated alumina grains: equilibrium and kinetics. Water Res 35:2049–2057
Luoa X, Wanga C, Luoa S, Donga R, Tua X, Zenga G (2012) Adsorption of As(III) and As(V) from water using magnetite Fe3O4-reduced graphite oxide–MnO2 nanocomposites. Chem Eng J 187:45–52
Marcano DC, Kosynkin DV, Berlin JM, Sinitskii A, Sun Z, Slesarev A, Alemany LB, Lu W, Tour JM (2010) Improved synthesis of graphene oxide. ACS Nano 4:4806–4814
Matsuo Y, Nishino Y, Fukutsuka T, Sugie Y (2008) Removal of formaldehyde from gas phase by silylated graphite oxide containing amino groups. Carbon 46:1162–1163
Mauter MS, Elimelech M (2008) Environmental applications of carbon-based nanomaterials. Environ Sci Technol 42:5843–5859
McArthur JM, Ravenscroft P, Saifiullah S, Thirwall MF (2001) Arsenic in groundwater: testing pollution mechanisms for sedimentary aquifers in Bangladesh. Water Res 37:109–117
Meyer JC, Geim AK, Katsnelson MI, Novoselov KS, Booth TJ, Roth S (2007) The structure of suspended grapheme sheets. Nature 446:60–63
Miyamoto J, Kanoh H, Kaneko K (2005) The addition of mesoporosity to activated carbon fibers by a simple reactivation process. Carbon 43:855–857
Mohan D, Pittman CU Jr (2007) Arsenic removal from water/wastewater using adsorbents—a critical review. J Hazard Mater 147:1–53
Mondal P, Majumder CB, Mohanty B (2006) Laboratory based approaches for arsenic remediation from contaminated water: recent developments. J Hazard Mater B137:464–479
Moon G, Park Y, Kim W, Choi W (2011) Photochemical loading of metal nanoparticles on reduced graphene oxide sheets using phosphotungstate. Carbon 49:3454–3462
Nakamoto K (1986) Infrared and Raman spectra of inorganic and coordination compounds, 4th edn. Wiley, New York, p 74
Nandi D, Ghosh AK, Gupta K, De A, Sen P, Duttachowdhury A, Ghosh UC (2012) Polypyrrole–titanium(IV) doped iron(III) oxide nanocomposites: synthesis, characterization with tunable electrical and electrochemical properties. Mater Res Bull 47:2095–2103
Nesbitt HW, Canning GW, Bancroft GM (1998) XPS study of reductive dissolution of 7 Å-birnessite by H3AsO3, with constraints on reaction mechanism. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 62:2097–2110
Nethravathi C, Rajamathi M (2008) Chemically modified graphene sheets produced by the solvothermal reduction of colloidal dispersions of graphite oxide. Carbon 46:1994–1998
Nickson RT, McArthur JM, Burgess WG, Ravenscroft P, Ahmed KM, Rahaman M (1998) Arsenic poisoning in Bangladesh groundwater. Nature 395:338
Novoselov KS, Geim AK, Morozov SV, Jiang D, Zhang Y, Dubonos SV, Grigorieva IV, Firsov AA (2004) Electric field effect in atomically thin carbon films. Science 306:666–669
Osmokrovi P, Jovaleki C, Manojlovi D, Pavlovi MB (2006) Synthesis of MnFe2O4 nanoparticles by mechanochemical reaction. J Optoelectron Adv Mater 8:312–314
Pan D, Wang S, Zhao B, Wu M, Zhang H, Wang Y, Jiao Z (2009) Storage properties of disordered graphene nanosheets. Chem Mater 21:3136
Ramanathan T, Abdala AA, Stankovich S, Dikin DA, Alonso MH, Piner RD, Adamson DH, Schniepp HC, Chen X, Ruoff RS et al (2008) Functionalized graphene sheets for polymer nanocomposites. Nat Nanotechnol 3:327–331
Roberts LC, Hug SJ, Ruettimann T, Billah M, Khan AW, Rahman MT (2004) Arsenic removal with iron(II) and iron(III) in waters with high silicate and phosphate concentrations. Environ Sci Technol 38:307–315
Schedin F, Geim AK, Morozov SV, Hill EW, Blake P, Katsnelson MI, Novoselov KS (2007) Detection of individual gas molecules adsorbed on graphene. Nat Mater 6:652–655
Seredych M, Bandosz TJ (2007) Removal of ammonia by graphite oxide via its intercalation and reactive adsorption. Carbon 45:2130–2132
Si Y, Samulski ET (2008) Synthesis of water soluble graphene. Nano Lett 8:1679–1682
Silva GC, Almeida FS, Ferreira AM, Ciminelli VST (2012). Preparation and application of a magnetic composite (Mn3O4/Fe3O4) for removal of As(III) from aqueous solutions. Mater Res 15(3):403–408
Smedley PL, Kinniburgh G (2002) A review of the source, behaviour and distribution of arsenic in natural waters. Appl Geochem 17:517–568
Sreeprasad TS, Maliyekkal SM, Lisha KP, Pradeep T (2011) Reduced graphene oxide–metal/metal oxide composites: facile synthesis and application in water purification. J Hazard Mater 186:921–931
Tuinstra F, Koenig JL (1970) Raman spectrum of graphite. J Chem Phys 53:1126–1130
Wang X, Zhi L, Mullen K (2008) Transparent, conductive graphene electrodes for dye-sensitized solar cells. Nano Lett 8:323–327
Yang X, Zhang X, Ma Y, Huang Y, Chen Y, Wang Y (2009) Superparamagnetic graphene oxide Fe3O4 nanoparticles hybrid for controlled targeted drug carriers. J Mater Chem 19:2710–2714
Yang S-T, Chang Y, Wang H, Liu G, Chen S, Wang Y, Liu Y, Cao A (2010) Folding/aggregation of graphene oxide and its application in Cu2+ removal. J Colloid Interface Sci 351:122–127
Yang S-T, Chen S, Zhang L, Huang J, Chen F, Yang Z, Yao J, Zhang Z (2011) Controlled assembly of Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles on graphene oxide. Nanoscale 3:1446–1450
Yu YJ, Zhao Y, Ryu S, Brus L, Kim KS, Kim P (2009) Charge transfer chemical doping of few layer graphenes: charge distribution and band gap formation. Nano Lett 9:3430–3434
Zhang S, Li X, Chen JP (2010a) Preparation and evaluation of a magnetite-doped activated carbon fiber for enhanced arsenic removal. Carbon 48:60–67
Zhang K, Dwivedi V, Chi CY, Wu JS (2010b) Graphene oxide/ferric hydroxide composites for efficient arsenate removal from drinking water. J Hazard Mater 182:162–168
Acknowledgments
Authors sincerely acknowledge the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), New Delhi (INDIA) for providing financial support of this work, and also the Head, Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry and the Vice-Chancellor of Presidency University, Kolkata for laboratory facilities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Special Issue Editors: Mamadou Diallo, Neil Fromer, Myung S. Jhon
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Nanotechnology for Sustainable Development
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nandi, D., Gupta, K., Ghosh, A.K. et al. Manganese-incorporated iron(III) oxide–graphene magnetic nanocomposite: synthesis, characterization, and application for the arsenic(III)-sorption from aqueous solution. J Nanopart Res 14, 1272 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-012-1272-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-012-1272-z