Abstract
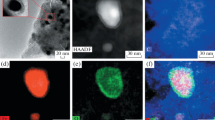
We report a new chemical approach toward air-stable nanoscale zero-valent iron (nZVI). The uniformly sized (approx. 80 nm) particles, formed by the reduction of Fe(II) salt by borohydride in the presence of glutamic acid, are coated by a thin inner shell of amorphous ferric oxide/hydroxide and a secondary shell consisting of glutamic acid. The as-prepared nanoparticles stabilized by the inorganic–organic double shell create 2D chain morphologies. They are storable for several months under ambient atmosphere without the loss of Fe(0) relative content. They show one order of magnitude higher rate constant for trichlorethene decomposition compared with the pristine particles possessing only the inorganic shell as a protective layer. This is the first example of the inorganic–organic (consisting of low-molecular weight species) double-shell stabilized nanoscale zero-valent iron material being safely transportable in solid-state, storable on long-term basis under ambient conditions, environmentally acceptable for in situ applications, and extraordinarily reactive if contacted with reducible pollutants, all in one.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Carpenter EE, Calvin S, Stroud RM, Harris VG (2003) Passivated iron as core-shell nanoparticles. Chem Mater 15:3245–3246
Comba S, Sethi R (2009) Stabilization of highly concentrated suspensions of iron nanoparticles using shear-thinning gels of xanthan gum. Water Res 43:3717–3726
Cornell RM, Schwertmann U (2003) The iron oxides: structure, properties, reactions, occurrence and uses, 2nd edn. Wiley-VCH Publishers, Weinheim
Dormann JL, Fiorani D, Tronc E (1997) Magnetic relaxation in fine-particle systems. In: Prigogine I, Rice SA (eds) Adv Chem Phys, vol 98. Wiley, New York, pp 283–494
Durmus Z, Kavas H, Toprak MS, Baykal A, Altincekic TG, Aslan A, Bozkurt A, Cosgun S (2009) l-lysine coated iron oxide nanoparticles: synthesis, structural and conductivity characterization. J Alloys Compd 484:371–376
Filip J, Zboril R, Schneeweiss O, Zeman J, Cernik M, Kvapil P, Otyepka M (2007) Environmental applications of chemically pure natural ferrihydrite. Environ Sci Technol 41:4367–4374
Geng G, Jin Z, Li T, Qi X (2009a) Preparation of chitosan-stabilized Fe0 nanoparticles for removal of hexavalent chromium in water. Sci Total Environ 407:4994–5000
Geng B, Jin Z, Li T, Qi X (2009b) Kinetics of hexavalent chromium removal from water by chitosan-Fe0 nanoparticles. Chemosphere 75:825–830
Ghauch A, Tuqan A, Assi HA (2009) Antibiotic removal from water: elimination of amoxicillin and ampicillin by microscale and nanoscale iron particles. Environ Pollut 157:1626–1635
Glavee GN, Klabunde KJ, Sorensen CM, Hadjipanayis GC (1995) Chemistry of borohydride reduction of iron(II) and iron(III) ions in aqueous and nonaqueous media. Formation of nanoscale Fe, FeB, and Fe2B powders. Inorg Chem 34:28–35
He F, Zhao D (2007) Manipulating the size and dispersibility of zerovalent iron nanoparticles by use of carboxymethyl cellulose stabilizers. Environ Sci Technol 41:6216–6221
Hoag GE, Collins JB, Holcomb JL, Hoag JR, Nadagouda MN, Varma RS (2009) Degradation of bromothymol blue by ‘greener’ nano-scale zero-valent iron synthesized using tea polyphenols. J Mater Chem 19:8671–8677
Kanel SR, Manning B, Charlet L, Choi H (2005) Removal of arsenic(III) from groundwater by nanoscale zero-valent iron. Environ Sci Technol 39:1291–1298
Kanel SR, Greneche JM, Choi H (2006) Arsenic(V) removal from groundwater using nano scale zero-valent iron as a colloidal reactive barrier material. Environ Sci Technol 40:2045–2050
Karabelli D, Uzum C, Shahwan T, Eroglu AE, Scott TB, Hallam KR, Lieberwirth I (2008) Batch removal of aqueous Cu2+ ions using nanoparticles of zero-valent iron: a study of the capacity and mechanism of uptake. Ind Eng Chem Res 47:4758–4764
Katsenovich YP, Miralles-Wilhelm FR (2009) Evaluation of nanoscale zerovalent iron particles for trichloroethene degradation in clayey soils. Sci Total Environ 407:4986–4993
Kim HJ, Phenrat T, Tilton RD, Lowry GV (2009) Fe0 nanoparticles remain mobile in porous media after aging due to slow desorption of polymeric surface modifiers. Environ Sci Technol 43:3824–3830
Kim HS, Ahn JY, Hwang KY, Kim IK, Hwang I (2010) Atmospherically stable nanoscale zero-valent iron particles formed under controlled air contact: characteristics and reactivity. Environ Sci Technol 44:1760–1766
Li XQ, Zhang WX (2007) Sequestration of metal cations with zerovalent iron nanoparticles: a study with high resolution X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (HR-XPS). J Phys Chem C 111:6939–6946
Li L, Fan M, Brown RC, Van Leeuwen JH, Wang J, Wang W, Song Y, Zhang P (2006) Synthesis, properties, and environmental applications of nanoscale iron-based materials: a review. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 36:405–431
Liang F, Fan J, Guo Y, Fan M, Wang J, Yang H (2008) Reduction of nitrite by ultrasound-dispersed nanoscale zero-valent iron particles. Ind Eng Chem Res 47:8550–8554
Lien HL, Zhang W (2001) Nanoscale iron particles for complete reduction of chlorinated ethenes. Colloid Surf A 191:97–105
Liou YH, Lo SL, Kuan WH, Lin CJ, Weng SC (2006) Effect of precursor concentration on the characteristics of nanoscale zerovalent iron and its reactivity of nitrate. Water Res 40:2485–2492
Liu Y, Majetich SA, Tilton RD, Sholl DS, Lowry GV (2005) TCE dechlorination rates, pathways, and efficiency of nanoscale iron particles with different properties. Environ Sci Technol 39:1338–1345
Machala L, Zboril R, Gedanken A (2007) Amorphous iron(III) oxide: a review. J Phys Chem B 111:4003–4018
Mantion A, Gozzo F, Schmitt B, Stern WB, Gerber Y, Robin AY, Fromm KM, Painsi M, Taubert A (2008) Amino acids in iron oxide mineralization: (incomplete) crystal phase selection is achieved even with single amino acids. J Phys Chem C 112:12104–12110
Marinescu G, Patron L, Culita DC, Neagoe C, Lepadatu CI, Balint I, Bessais L, Cizmas CB (2006) Synthesis of magnetite nanoparticles in the presence of aminoacids. J Nanopart Res 8:1045–1051
Martin JE, Herzing AA, Yan W, Li XQ, Koel BE, Kiely C, Zhang WX (2008) Determination of the oxide layer thickness in core-shell zerovalent iron nanoparticles. Langmuir 24:4329–4334
Nakamoto K (2009a) Infrared and Raman spectra of inorganic and coordination compounds, Part A: Theory and applications in inorganic chemistry. Wiley Inc., Hoboken, pp 82–84, 254–258
Nakamoto K (2009b) Infrared and Raman spectra of inorganic and coordination compounds, Part B: Applications in coordination, organometallic, and bioinorganic chemistry. Wiley Inc., Hoboken, pp 12–21, 58, 62, 69, 177
Nurmi JT, Sarathy V, Tratnyek PG, Baer DR, Amonette JE, Karkamkar A (2011) Recovery of iron/iron oxide nanoparticles from solution: comparison of methods and their effects. J Nanopart Res 13:1937–1952
Papefthymiou GC (2009) Nanoparticle magnetism. NanoToday 4:438–447
Phenrat T, Long TC, Lowry GV, Veronesi B (2009) Partial oxidation («aging») and surface modification decrease the toxicity of nanosized zerovalent iron. Environ Sci Technol 43:195–200
Ponder SM, Darab JG, Bucher J, Caulder D, Craig I, Davis L, Edelstein N, Lukens W, Nitsche H, Rao L, Shuh DH, Mallouk TE (2001) Surface chemistry and electrochemistry of supported zerovalent iron nanoparticles in the remediation of aqueous metal contaminants. Chem Mater 13:479–486
Ramos MAV, Yan W, Li XQ, Koel BE, Zhang WX (2009) Simultaneous oxidation and reduction of arsenic by zero-valent iron nanoparticles: understanding the significance of the core-shell structure. J Phys Chem C 113:14591–14594
Saleh N, Phenrat T, Sirk K, Dufour B, Ok J, Sarbu T, Mayjaszewski K, Tilton RD, Lowry GV (2005) Adsorbed triblock copolymers deliver reactive iron nanoparticles to the oil/water interface. Nano Lett 5:2489–2494
Schneeweiss O, Zboril R, Mashlan M, Petrovsky E, Tucek J (2006) Novel solid-state synthesis of α-Fe and Fe3O4 nanoparticles embedded in a MgO matrix. Nanotechnology 17:607–616
Schrick B, Blough JL, Jones AD, Mallouk TE (2002) Hydrodechlorination of trichloroethylene to hydrocarbons using bimetallic nickel-iron nanoparticles. Chem Mater 14:5140–5147
Schrick B, Hydutsky BW, Blough JL, Mallouk TE (2004) Delivery vehicles for zerovalent metal nanoparticles in soil and groundwater. Chem Mater 16:2187–2193
Slunsky J (2010) Production and application of nanoscale zero-valent iron (nZVI) for groundwater remediation and other utilization. VEGAS-Kolloquium:101–105
Sohn K, Kang SW, Ahn S, Woo M, Yang SK (2006) Fe(0) nanoparticles for nitrate reduction: stability, reactivity, and transformation. Environ Sci Technol 440:5514–5519
Sousa MH, Tourinho FA, Rubim JC (2000) Use of Raman micro-spectroscopy in the characterization of MIIFe2O4 (M = Fe, Zn) electric double layer ferrofluids. J Raman Spectrosc 31:185–191
Sun YP, Li XQ, Cao J, Zhang WX, Wang HP (2006) Characterization of zero-valent iron nanoparticles. Adv Colloid Interface Sci 120:47–56
Sun YP, Li XQ, Zhang WX, Wang HP (2007) A method for the preparation of stable dispersion of zero-valent iron nanoparticles. Colloids Surf A 308:60–66
Tiehm A, Krassnitzer S, Koltypin Y, Gedanken A (2009) Chloroethene dehalogenation with ultrasonically produced air-stable nano iron. Ultrason Sonochem 16:617–621
Tiraferri A, Chen KL, Sethi R, Elimelech M (2008) Reduced aggregation and sedimentation of zero-valent iron nanoparticles in the presence of guar gum. J Colloid Interface Sci 324:71–79
Tratnyek PG, Johnson RL (2006) Nanotechnologies for environmental cleanup. NanoToday 1:44–48
Wang Z, Zhu H, Wang X, Yang F, Yang X (2009) One-pot green synthesis of biocompatible arginine-stabilized magnetic nanoparticles. Nanotechnology 20(46): 465606 (10 pp). doi: 10.1088/0957-4484/20/46/465606
Wang Q, Lee S, Choi H (2010a) Aging study on the structure of Fe0-nanoparticles: stabilization, characterization, and reactivity. J Phys Chem C 114:2027–2033
Wang W, Thou M, Jin Z, Li T (2010b) Reactivity characteristics of poly(methyl methacrylate) coated nanoscale iron particles for trichloroethylene remediation. J Hazard Mater 173:724–730
Zhang WX (2003) Nanoscale iron particles for environmental remediation: an overview. J Nanopart Res 5:323–332
Zhang L, Fang M (2010) Nanomaterials in pollution trace detection and environmental improvement. NanoToday 5:128–142
Zhang X, Deng B, Guo J, Wang Y, Lan Y (2011) Ligand-assisted degradation of carbon tetrachloride by microscale zero-valent iron. J Environ Manag 92:1328–1333
Acknowledgments
Dr. Dalibor Jančík is thanked for the analysis of SAED data, Bc. Jan Kolařík for AAS measurements, and Dr. Giorgio Zoppellaro for his valuable comments and encouragement. Financial support by P108/11/P657 Grant awarded by GACR, the project of the Ministry of Industry and Business of the Czech Republic (project ID: FR-TI3/196), the Operational Program Research and Development for Innovations - European Regional Development Fund (project CZ.1.05/2.1.00/03.0058 of the Ministry of Education, Youth and Sports of the Czech Republic), the projects of the Ministry of Education of the Czech Republic (1M6198959201 and MSM6198959218), and the project of the Academy of Sciences of the Czech Republic (KAN115600801) is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Siskova, K., Tucek, J., Machala, L. et al. Air-stable nZVI formation mediated by glutamic acid: solid-state storable material exhibiting 2D chain morphology and high reactivity in aqueous environment. J Nanopart Res 14, 805 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-012-0805-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-012-0805-9