Abstract
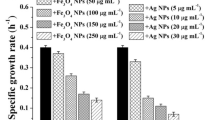
The antibacterial activities of magnesium oxide nanoparticles (MgO NP) alone or in combination with other antimicrobials (nisin and ZnO NP) against Escherichia coli O157:H7 and Salmonella Stanley were investigated. The results show that MgO NP have strong bactericidal activity against the pathogens, achieving more than 7 log reductions in bacterial counts. The antibacterial activity of MgO NP increased as the concentrations of MgO increased. A synergistic effect of MgO in combination with nisin was observed as well. However, the addition of ZnO NP to MgO NP did not enhance the antibacterial activity of MgO against both pathogens. Scanning electron microscopy was used to characterize the morphological changes of E. coli O157:H7 before and after antimicrobial treatments. It was revealed that MgO NP treatments distort and damage the cell membrane, resulting in a leakage of intracellular contents and eventually the death of bacterial cells. These results suggest that MgO NP alone or in combination with nisin could potentially be used as an effective antibacterial agent to enhance food safety.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Holy M, Al-Qadiri H, Lin M, Rasco B (2006) Inhibition of Listeria innocua in hummus by a combination of nisin and citric acid. J Food Protect 69(6):1322–1327
Boziaris IS, Adams MR (2001) Temperature shock, injury and transient sensitivity to nisin in Gram-negatives. J Appl Microbiol 91:715–724
Chandrapati S, O’Sullivan DJ (1998) Procedure for quantifiable assessment of nutritional parameters influencing Nisin production by Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis. J Biotechnol 63:229–233
Dawson PL, Carl GD, Acton JC, Han IY (2002) Effect of lauric acid and nisin-impregnated soy-based films on the growth of Listeria monocytogenes on turkey bologna. Poultry Sci 81:721–726
Fang TJ, Tsai HC (2003) Growth patterns of Escherichia coli O157:H7 in ground beef treated with nisin, chelators organic acids and their combinations immobilized in calcium alginate gels. Food Microbiol 20:243–253
Food and Drug Administration (FDA) (1988) Nisin preparation: affirmation of GRAS status as a direct human food ingredient. Federal Register 53:11247–11251
Food and Nutrition Board (1997) Dietary references intakes: calcium, phosphorus, magnesium, vitamin D and fluoride. In: Institute of Medicine (ed) Uses of dietary intakes, Food and Nutrition Board, vol 7. National Academy Press, Washington DC
Fu G, Vary PS, Lin CT (2005) Anatase TiO2 nanocomposites for antimicrobial coating. J Phys Chem B 109:8889–8898
Hauben KJA, Wuytack EY, Scootjens CCF, Michiels CW (1996) High pressure transient sensitization of E. coli to lysozyme and nisin by disruption of outer membrane permeability. J Food Prot 59:350–355
Henning S, Metz R, Hammes WP (1986) Studies on the mode of action of nisin. Int J Food Microbiol 3:121–134
Hewitt CJ, Bellara ST, Andreani A, Nebe-von-Caron G, Mcfarlane CM (2001) An evaluation of the antibacterial action of ceramic powder slurries using multiparameter flow cytometry. Biotechnol Lett 23:667–675
Huang Z, Maness PC, Blakee DM, Wolfrum EJ, Smoliski SL, Jacoby WA (2000) Bacterial mode of titanium dioxide photocatalysis. J Photochem Photobiol A: Chem 130:163–170
Huang L, Li D, Lin Y, Evans DG, Duan X (2005) Influence of nano-MgO particle size on bactericidal action against Bacillus subtilis var. niger. Chin Sci Bull 50(6):514–519
Jin T (2010) Inactivation of Listeria monocytogenes in skim milk and liquid egg white by antimicrobial bottle coating with polylactic acid and nisin. J Food Sci 75(2):M83–M88
Jin T, Gurtler J (2011) Inactivation of Salmonella in liquid egg albumen by antimicrobial bottle coatings infused with allyl isothiocyanate, nisin and zinc oxide nanoparticles. J Appl Microbiol 110:704–712
Jin T, Zhang H (2008) Biodegradable polylactic acid polymer with nisin for use in antimicrobial food packaging. J Food Sci 73(3):M127–M134
Jin T, Liu L, Sommers C, Zhang H, Boyd G (2009a) Radiation resistance and postirradiation proliferation of Listeria monocytogenes on ready-to-eat deli meat in the presence of pectin/nisin films. J Food Protect 72(3):644–649
Jin T, Liu LS, Zhang H, Hicks K (2009b) Antimicrobial activity of nisin incorporated in pectin and polylactic acid composite films against Listeria monocytogenes. Int J Food Sci Technol 44:322–329
Jin T, Sun D, Su Y, Zhang H, Sue HJ (2009c) Antimicrobial efficacy of zinc oxide quantum dots against Listeria monocytogenes, Salmonella Enteritidis, and Escherichia coli O157:H7. J Food Sci 74:M46–M52
Jin T, Sun D, Zhang H, Sue HJ (2009d) Application of zinc oxide quantum dots in food safety. In: Sahu SC, Casciano DA (eds) Nanotoxicity: from in vivo and in vitro models to health risk. Wiley Publisher, Hoboken, pp 81–95
Jin T, Zhang H, Boyd G (2010) Incorporation of preservatives in polylactic acid films for inactivating Escherichia coli O157:H7 and extending microbiological shelf-life of strawberry puree. J Food Protect 73(5):812–818
Koper OB, Klabunde JS, Marchin GL, Klabunde KJ, Stoimenov PK, Babra L (2002) Nanoscale powders and formulations with biocidal activity toward spores and vegetative cells of Bacillus species, viruses, and toxins. Curr Microbiol 44:49–55
Kourai H (1993) Immobilized microbiocide. J Antibact antifungal agents 21:331–337 (in Japanese)
Liu Y, He L, Mustapha A, Li H, Hu ZQ, Lin M (2009) Antibacterial activities of zinc oxide nanoparticles against Escherichia coli O157:H7. J Appl Microbiol 107:1193–1201
Liu LS, Jin T, Coffin DR, Liu CK, Hick KB (2010) Poly(lactic acid) membranes containing bacteriocins and EDTA for inhibition of the surface growth of gram-negative bacteria. J Appl Polym Sci 117(1):486–492
Makhluf S, Dror R, Nitzan Y, Abramovich Y, Jelinek R, Gedanken A (2005) Microwave-assisted synthesis of nanocrystalline MgO and its use as Bacteriocide. Adv Funct Mater 15:1708–1715
McCormick KE, Han IY, Acton JC, Sheldon BW, Dawson PL (2005) In-package pasteurization combined with biocide impregnated films to inhibit Listeria monocytogenes and Salmonella Typhimurium in turkey bologna. Food Sci 70(1):M52–M57
Millette M, Le Tien C, Smoragiewicz W, Lacroix M (2007) Inhibition of Staphylococcus aureus on beef by nisin-containing modified alginate films and beads. Food Control 18:878–884
Moll GN, Clark J, Chan WC, Bycroft BW, Roberts GCK, Konings WM, Driessen AJM (1997) Role of transmembrane pH gradient and membrane binding in nisin pore formation. J Bacteriol 179:135–140
Morones JR, Elechiguerra JL, Camacho A, Holt K, Kouri JB, Ramirez JT, Yacaman MJ (2005) The bactericidal effect of silver nanoparticles. Nanotechnology 16:2346–2353
Morris JG (2011) How safe is our food? Emerg Infect Dis 17(1):126–128
Nel A, Xia T, Ma¨dler L, Li N (2006) Toxic potential of materials at the nanolevel. Science 311:622–627
Okouchi S, Murata R, Sugita H, Moriyoshi Y, Maeda N (1995) Calorimetric evaluation of the antimicrobial activities of calcined dolomite. J Antibact Antifungal Agents 26:109–114 (in Japanese)
Pal S, Tak YK, Song JM (2007) Does the antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles depend on the shape of the nanoparticle? A study of the gram-negative bacterium Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol 73(6):1712–1720
Sawai J (2003) Quantitative evaluation of antibacterial activities of metallic oxide powders (ZnO, MgO and CaO) by conductimetric assay. J Microbiol Methods 54:177–182
Sawai J, Yoshikawa T (2004) Quantitative evaluation of antifungal activity of metallic oxide powders (MgO, CaO and ZnO) by an indirect conductimetric assay. J Appl Microbiol 96:803–809
Sawai J, Igarashi H, Hashimoto A, Kokugan T, Shimizu M (1995) Evaluation of growth inhibitory effect of ceramic powder slurry on bacteria by conductance method. J Chem Eng Jpn 28:288–293
Sawai J, Shoji S, Igarashi H, Hashimoto A, Kokugan T, Shimizu M, Kojima H (1998) Hydrogen peroxide as an antibacterial factor in zinc oxide powder slurry. J Ferment Bioeng 86:521–522
Sawai J, Kojima H, Igarashi H, Hashimoto A, Shoji S, Shimizu M (1999) Bactericidal action of calcium oxide powder. Trans Mater Res Soc Jpn 24:667–670
Sawai J, Kojima H, Igarashi H, Hashimoto A, Shoji S, Sawaki T, Hakoda A, Kawada E, Kokugan T, Shimizu M (2000) Antibacterial characteristics of magnesium oxide powder. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 16:187–194
Sheldon BW (2001) Development of an inhibitory absorbent cellulose gum tray pads for reducing spoilage microorganisms and the risk of cross contamination. Poult Sci 80(Suppl 1):17
Shi LE, Xing L, Hou B, Ge H, Guo X, Tang Z (2010) Inorganic nano mental oxides used as anti-microorganism agents for pathogen control. In: Mendez-Vilas A (ed) Current research education technology topics in applied microbiology, microbial biotechnology. Formatex Research Center, Badajoz
Shirashi F, Toyoda K, Fukinbara S (1999) Photolytic smf photocatalytic treatment of an aqueous solution containing microbial cells and organic compounds in an annular-flow reactor. Chem Eng Sci 54:1547–1552
Steels H, James SA, Roberts IN, Stratford M (2000) Sorbic acid resistance: the inoculum effect. Yeast 16:1173–1183
Stoimenov PK, Klinger RL, Marchin GL, Klabunde KJ (2002) Metal oxide nanoparticles as bactericidal agents. Langmuir 18:6679–6686
Ukuku DO, Fett W (2004) Effect of nisin in combination with EDTA, sodium lactate, and potassium sorbate for reducing Salmonella on whole and fresh-cut cantaloupe. J Food Prot 67(10):2143–2150
Wang YL, Wan YZ, Dong XH, Cheng GX, Tao HM, Wen TY (1995) Preparation and characterization of antibacterial viscose-based activated carbon fiber supporting silver. Carbon 36:1567–1571
Wang YL, Wan YZ, Dong H, Cheng GX, Tao HM, Wen TY (1998) Preparation and characterization of antibacterial viscose-based activated carbon fibre supporting silver. Carbon 36:1567–1571
Wilczynski M (2000) Anti-microbial porcelain enamels. Ceram Eng Sci Proc 21:81–83
Xie Y, He Y, Irwin P, Jin T, Shi X (2011) Antibacterial activity and mechanism of zinc oxide nanoparticles against Campylobacter jejuni. Appl Environ Microbiol 77(7):2325–2331
Yamamoto O (2001) Influence of particle size on the antibacterial activity of zinc oxide. Int J Inorgan Mater 3:643–646
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank Anita Parameswaran and Gaoping Bao for technical support. We would also like to thank our reviewers, Drs. Joshua Gurtler and Dike Ukuku for careful critiques.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Mention of trade names or commercial products in this article is solely for the purpose of providing specific information and does not imply recommendation or endorsement by the U.S. Department of Agriculture. USDA is an equal opportunity provider and employer.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jin, T., He, Y. Antibacterial activities of magnesium oxide (MgO) nanoparticles against foodborne pathogens. J Nanopart Res 13, 6877–6885 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-011-0595-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-011-0595-5