Abstract
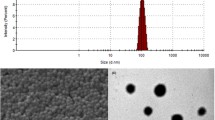
Curcumin, a widely used coloring agent and spice in food, has a potential in blocking brain tumor formation and curing Alzheimer’s disease. Due to the specific properties of blood–brain barrier (BBB), only traces of curcumin were transported across BBB. The aim of the present study was to design and characterize curcumin loaded polybutylcyanoacrylate nanoparticles (PBCN) coated with polysorbate 80, and to evaluate the effect of PBCN as a delivery system on carrying curcumin across BBB. Curcumin loaded nanoparticles were prepared by an anionic polymerization method, and they presented in a core–shell spherical shape under transmission electron microscopy, with an average diameter of 152.0 nm. The average drug loading was 21.1%. Physicochemical status of curcumin in the nanoparticles was confirmed with differential scanning colorimetry and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. The in vitro release behavior of drug from the nanoparticles was fitted to a double phase kinetics model. The studies of pharmacokinetic and bio-distribution to brain were conducted in mice after intravenous administration of the nanoparticle formulation at the dose of 5 mg/kg and curcumin solution at the dose of 10 mg/kg via the tail vein. The results showed that in plasma, the area under concentration–time curve (AUC0–∞) for curcumin loaded nanoparticles was greater than that for the control solution, moreover, the mean residence time of curcumin loaded nanoparticles was 14-fold that of the control solution. In brain, AUC0–∞ for curcumin loaded nanoparticles was 2.53-fold that for the control solution. In conclusion, the present study demonstrated that PBCN could enhance the transport of curcumin to brain and have a potential as a delivery system to cross the BBB.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aggarwal P, Hall JB, McLeland CB, Dobrovolskaia MA, McNeil SE (2009) Nanoparticle interaction with plasma proteins as it relates to particle biodistribution, biocompatibility and therapeutic efficacy. Int J Pharm 61:428–437. doi:10.1016/j.addr.2009.03.009
Agnihotri SA, Mallikarjuna NN, Aminabhavi TM (2004) Recent advances on chitosan-based micro-and nanoparticles in drug delivery. J Control Release 100:5–28. doi:10.#10.1016/j.jconrel.2004.08.010
Alyautdin RN, Petrov VE, Langer K, Berthold A, Kharkevich DA, Kreuter J (1997) Delivery of loperamide across the blood-brain barrier with polysorbate 80-coated polybutylcyanoacrylate nanoparticles. Pharm Res 14:325–328. doi:10.1023/A:1012098005098
Alyautdin RN, Tezikov EB, Ramge P, Kharkevich DA, Begley DJ, Kreuter J (1998) Significant entry of tubocurarine into the brain of rats by adsorption to polysorbate 80-coated poly (butylcyanoacrylate) nanoparticles: an in situ brain perfusion study. J Microencapsul 15:67–74. doi:10.3109/02652049809006836
Anand P, Kunnumakkara AB, Newman RA, Aggarwal BB (2007) Bioavailability of Curcumin: problems and promises. Mol Pharm 4:807–818. doi:10.1021/mp700113r
Batrakova EV, Li S, Li YL, Alakhovb VY, Elmquist WF, Kabanov AV (2004) Distribution kinetics of a micelle-forming block copolymer Pluronic P85. J Control Release 100:389–397. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2004.09.002
Behan N, Birkinshaw C, Clarke N (2001) Poly n-butyl cyanoacrylate nanoparticles: a mechanistic study of polymerisation and particle formation. Biomaterials 22:1335–1344. doi:10.1016/S0142-9612(00)00286-6
Duan JH, Zhang YD, Chen W, Shen CR, Liao MM, Pan YF, Wang JW, Deng XM, Zhao JF (2009) Cationic polybutyl cyanoacrylate nanoparticles for DNA delivery. J Biomed Biotechnol 2009:149254. doi:10.1155/2009/149254
Duro R, Alvarez C, Martínez-Pacheco R, Gómez-Amoza JL, Concheiro A, Souto C (1998) The adsorption of cellulose ethers in aqueous suspensions of pyrantel pamoate: effects on zeta potential and stability. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 45:181–188. doi:10.1016/S0939-6411(97)00103-3
Fawaz F, Guyot M, Lagueny AM, Devissaguet JP (1997) Ciprofloxacin-loaded poly(isobutylcyanoacrylate) nanoparticles: preparation and characterization. Int J Pharm 154:191–203 Cote INIST: 16510, 35400006884077.0080
Gao KP, Jiang XG (2006) Influence of particle size on transport of methotrexate across blood brain barrier by polysorbate 80-coated polybutylcyanoacrylate nanoparticles. Int J Pharm 310:213–219. doi:10.1016/j.ijpharm.2005.11.040
Gelperina SE, Khalansky AS, Skidan IN, Smirnova ZS, Bobruskin AI, Severin SE, Turowski B, Zanella FE, Kreuter J (2002) Toxicological studies of doxorubicin bound to polysorbate 80-coated poly (butyl cyanoacrylate) nanoparticles in healthy rats and rats with intracranial glioblastoma. Toxicol Lett 126:131–141. doi:10.1016/S0378-4274(01)00456-8
Gessner A, Olbrich C, Schroder W, Kayser O, Muller RH (2001) The role of plasma proteins in brain targeting: species dependent protein adsorption patterns on brain-specific lipid drug conjugate (LDC) nanoparticles. Int J Pharm 214:87–91. doi:10.1016/S0378-5173(00)00639-6
Gulyaev AE, Gelperina SE, Skidan IN, Antropov AS, Kivman GY, Kreuter J (1999) Significant transport of doxorubicin into the brain with polysorbate 80 coated nanoparticles. Pharm Res 16:1564–1570. doi:10.1023/A:1018983904537
Huang CY, Lee YD (2006) Core-shell type of nanoparticles composed of poly [(n-butyl cyanoacrylate)-co-(2-octylcyanoacrylate)] copolymers for drug delivery application: synthesis, characterization and in vitro degradation. Int J Pharm 325:132–139. doi:10.1016/j.ijpharm.2006.06.008
Huang CY, Chen CM, Lee YD (2007) Synthesis of high loading and encapsulation efficient paclitaxel-loaded poly (n-butyl cyanoacrylate) nanoparticles via miniemulsion. Int J Pharm 338:267–275. doi:10.1016/j.ijpharm.2007.01.052
Huo DJ, Deng SH, Li LB, Ji JB (2005) Studies on the poly(lactic-co-glycolic) acid microspheres of cisplatin for lung-targeting. Int J Pharm 289:63–67. doi:10.1016/j.ijpharm.2004.10.017
Ishrat T, Hoda MN, Khan MB, Yousuf S, Ahmad M, Khan MM, Ahmad A, Islama F (2009) Amelioration of cognitive deficits and neurodegeneration by curcumin in rat model of sporadic dementia of Alzheimer’s type (SDAT). Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 19:636–647. doi:10.1016/j.euroneuro.2009.02.002
Kreuter J, Alyautdin RN, Kharkevich DA, Ivanov AA (1995) Passage of peptides through the blood-brain barrier with colloidal polymer particles (nanoparticles). Brain Res 674:171–174. doi:10.1016/0006-8993(95)00023-J
Kreuter J, Shamenkov D, Petrov V, Ramage P, Cychutek K, Koch BC, Alyautdin R (2002) Apolipoprotein-mediated transport of nanoparticle-bound drugs across the blood–brain barrier. J Drug Target 10:317–325. doi:10.1080/10611860290031877
Kuo YC, Chen HH (2006) Effect of nanoparticulate poly (butyl) cyanoacrylate and methylmethacrylate-sulfopropylmethacrylate on the permeability of zidovudine and lamivudine across the in vitro blood–brain barrier. Int J Pharm 327:160–169. doi:10.1016/j.ijpharm.2006.07.044
Kuo YC, Su FL (2007) Transport of stavudine, delavirdine, and saquinavir across the blood–brain barrier by polybutylcyanoacrylate, methylmethacrylate-sulfopropylmethacrylate, and solid lipid nanoparticles. Int J Pharm 340:143–152. doi:10.1016/j.ijpharm.2007.03.012
Li J, Jiang YY, Fan GR, Wu YT, Zhang C (2009) A rapid and simple HLPC method for the determination of curcumin in rat plasma: assay development, validation, and application to a pharmacokinetic study of curcumin liposome. J Biomed Chromatogr 23:1201–1207. doi:10.1002/.bmc1244
Liu J, Zhu J, Du Z, Qin B (2005) Preparation and pharmacokinetic evaluation of Tashinone IIA solid lipid nanoparticles. Drug Dev Ind Pharm 31:551–556. doi:10.1080/03639040500214761
Lv QZ, Yu AH, Xi YW, Li HL, Song ZM, Cui J, Cao FL, Zhai GX (2009) Development and evaluation of penciclovir-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles for topical delivery. Int J Pharm 372:191–198. doi:10.1016/j.ijpharm.2009.01.014
Ma ZS, Shayeganpour A, Brocks DR, Lavasanifar A, Samuel J (2007) High-performance liquid chromatography analysis of curcumin in rat plasma: application to pharmacokinetics of polymeric micellar formation of curcumin. Biomed Chromatogr 21:546–552. doi:10.1002/bmc.795
Mulik R, Mahadika K, Paradkarb A (2009) Development of curcuminoids loaded poly (butyl) cyanoacrylate nanoparticles: Physicochemical characterization and stability study. Eur Pharm Sci 37:395–404. doi:10.1016/j.ejps.2009.03.009
Müller RH, Jacobs C, Kayser O (2001) Nanosuspensions as particulate drug formulations in therapy. Rationale for development and what we can expect for the future. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 47:3–19. doi:10.1016/S0169-409X(00)00118-6
Nerurkar MM, Bueto PS, Borchardt RT (1996) The use of surfactants to enhance the permeability of peptides through Caco-2 cells by inhibition of an apically polarized efflux system. Pharm Res 13:528–534. doi:10.1023/A:1016033702220
Olivier JC (2005) Drug transport to brain with targeted nanoparticles. Am Soc Exp Neuro Ther 2:108–119 PMCID: PMC539329
Pak Y, Patek R, Mayersohn M (2003) Sensitive and rapid isocratic liquid chromatography method for the quantitation of curcumin in plasma. J Chromatogr B 796:339–346. doi:10.1016/j.jchromb.2003.08.018
Pan MH, Huang TM, Lin JK (1998) Biotransformation of curcumin through reduction and glucuronidation in mice. Drug Metab Dispos 27:486–494. doi:0090-9556/99/2704-0486-0494
Pardridge WM (2002) Drug and gene delivery to the brain: the vascular route. Neuron 36:555–558. doi:10.1016/S0896-6273(02)01054-1
Petri B, Bootz A, Khalansky A, Hekmatara T, Müller R, Uhl R, Kreuter J, Gelperina S (2007) Chemotherapy of brain tumour using doxorubicin bound to surfactant-coated poly(butyl cyanoacrylate) nanoparticles: revisiting the role of surfactants. J Control Release 117:51–58. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2006.10.015
Purkayasthaa S, Berliner A, Fernando SS, Ranasinghe B, Ray I, Tariq H, Banerjee P (2009) Curcumin blocks brain tumor formation. Brain Res 1266:130–138. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2009.01.066
Ramge P, Unger RE, Oltrogge JB, Zenker D, Begley DJ, Kreuter J, VonBriesen H (2000) Polysorbate 80 coating enhances uptake of polybutylcyanoacrylate (PBCA) nanoparticles by human and bovine primary brain capillary endothelial cells. Eur J Neurosci 12:1931–1940. doi:10.1046/j.1460-9568.2000.00078.x
Reddy LH, Murthy RR (2004) Influence of polymerization technique and experimental variables on the particle properties and release kinetics of methotrexate from poly (butylcyanoacrylate) nanoparticles. Acta Pharm 54:103–118. http://scholar.google.cn/scholar
Ringman JM, Frautschy SA, Cole GM, Masterman DL, Cummings JL (2005) A potential role of the curry spice curcumin in Alzheimer’s disease. Curr Alzheimer Res 2:131–136 PMCID: PMC1702408
Schroeder U, Sommerfeld P, Ulrich S, Sabel BA (1998) Nanoparticle technology for delivery of drugs across the blood–brain barrier. J Pharm Sci 87:1305–1307. doi:10.1021/js980084y
Simeonova M, Ivanova G, Enchev V, Markov N, Kamburov M, Petkov C, Devery A, Connor R, Brougham D (2009) Physicochemical characterization and in vitro behavior of daunorubicin-loaded poly(butylcyanoacrylate) nanoparticles. Acta Biomater 5:2109–2121. doi:10.1016/j.actbio.2009.01.026
Steiniger SC, Kreuter J, Khalansky AS, Skidan IN, Bobruskin AI, Smirnova ZS, Severin SE, Uhl R, Kock M, Geiger KD, Gelperina SE (2004) Chemotherapy of glioblastoma in rats using doxorubicin-loaded nanoparticles. Int J Cancer 109:759–767. doi:10.1002/ijc.20048
Sullivan CO, Birkinshaw C (2004) In vitro degradation of insulin-loaded poly (n-butylcyanoacrylate) nanoparticles. Biomaterials 25:4375–4382. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2003.11.001
Sun WQ, Xie CS, Wang HF, Hu Y (2004) Specific role of polysorbate 80 coating on the targeting of nanoparticles to the brain. Biomaterials 25:3065–3071. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2003.09.087
Sun WT, Zhang N, Li AG, Zou WW, Xu WF (2008) Preparation and evaluation of N3-O-toluyl-fluorouracil-loaded liposomes. Int J Pharm 353:243–250. doi:10.1016/j.ijpharm.2007.11.017
Tonnesen HH, Masson M, Loftsson T (2002) Studies of curcumin and curcuminoids. XXVII. Cyclodextrin complexation: solubility, chemical and photochemical stability. Int J Pharm 244:127–135. doi:10.1016/S0378-5173(02)00323-X
Vinogradov SV, Bronich TK, Kabanov AV (2002) Nanosized cationic hydrogels for drug delivery: preparation, properties and interactions with cells. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 54:135–147. doi:10.1016/S0169-409X(01)00245-9
Wang YJ, Pan MH, Cheng AL, Lin LI, Ho YS, Hsieh CY, Lin JK (1997) Stability of curcumin in buffer solutions and characterization of its degradation products. J Pharm Biomed 15:1867–1876. doi:10.1016/S0731-7085(96)02024-9
Wang CX, Huang LS, Hou LB, Jiang L, Yan ZT, Wang LY, Liang Z (2008) Antitumor effects of polysorbate-80 coated gemcitabine polybutylcyanoacrylate nanoparticles in vitro and its pharmacodynamics in vivo on C6 glioma cells of a brain tumor model. Brain Res 1200:159–168. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2009.01.011
Wang JL, Wang R, Li LB (2009) Preparation and properties of hydroxycamptothecin-loaded nanoparticles made of amphiphilic copolymer and normal polymer. J Colloid Interface Sci 336:808–813. doi:10.1016/j.jcis.2009.04.080
Wilson B, Samanta MK, Santhi K, Kumar KPS, Paramakrishnan N, Suresh B (2008a) Poly(n-butylcyanoacrylate) nanoparticles coated with polysorbate 80 for the targeted delivery of rivastigmine into the brain to treat Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Res 1200:159–168. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2008.01.039
Wilson B, Sampath KP, Santhi K, Kumar KPS, Paramakrishnan N, Suresh B (2008b) Targeted delivery of tacrine into the brain with polysorbate 80-coated poly(n-butylcyanoacrylate) nanoparticles. Eur Pharm Biopharm 70:75–84. doi:10.1016/j.ejpb.2008.03.009
Wolberg H, Lippoldt A (2002) Tight junctions of the blood–brain barrier: development, composition and regulation. Vasc Pharmacol 38:323–337. doi:10.1016/S1537-1891(02)00200-8
Woodcock DM, Linsenmeyer ME, Chojnowski G, Kriegler AB, Nink V, Sawyer WH, Webster LK (1992) Reversal of multidrug resistance by surfactants. Br J Cancer 66:62–68 PMCID: PMC1977900
Xiao YY, Song YM, Chen ZP, Ping QN (2006) Preparation of silymarin proliposome: a new way to increase oral bioavailability of silymarin in beagle dogs. Int J Pharm 352:273–279. doi:10.1016/j.ijpharm.2006.03.037
Ye JS, Wang Q, Zhou XF, Na Z (2008) Injectable actarit-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles as passive targeting therapeutic agents for rheumatoid arthritis. Int J Pharm 319:162–168. doi:10.1016/j.ijpharm.2007.10.014
Zhu WW, Yu AH, Wang WH, Dong RQ, Wu J, Zhai GX (2008) Formulation design of microemulsion for dermal delivery of penciclovir. Int J Pharm 360:184–190. doi:10.1016/j.ijpharm.2008.04.008
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, M., Gao, Y., Guo, C. et al. Enhancement of transport of curcumin to brain in mice by poly(n-butylcyanoacrylate) nanoparticle. J Nanopart Res 12, 3111–3122 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-010-9907-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-010-9907-4