Abstract
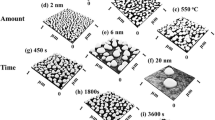
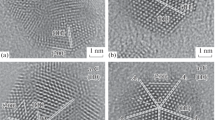
The tetraoctylammonium bromide-stabilized gold nanoparticles have been successfully fabricated. The shape evolution of these nanoparticles under different annealing temperatures has been investigated using high-resolution transmission electron microscopy. After an annealing at 100 °C for 30 min, the average diameters of the gold nanoparticles change a little. However, the shapes of gold nanoparticles change drastically, and facets appear in most nanoparticles. After an annealing at 200 °C for 30 min, not only the size but also the shape changes a lot. After an annealing at 300 °C for 30 min, two or more gold nanoparticles coalesce into bigger ones. In addition, because of the presence of Cu grid during the annealing, some gold particles become the nucleation sites of Cu2O nanocubes, which possess a microstructure of gold-particle core/Cu2O shell. These Au/Cu2O heterostructure nanocubes can only be formed at a relatively high temperature (≥300 °C). The results can provide some insights on controlling the shapes of gold nanoparticles.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ascencio JA, Gutiérrez-Wing C, Espinosa ME, Marin M, Tehuacanero S, Zorrilla C, José-Yacamán M (1998) Structure determination of small particles by HREM imaging: theory and experiment. Surf Sci 396:349–368. doi:10.1016/S0039-6028(97)00689-4
Ascencio JA, Pérez M, José-Yacamán M (2000) A truncated icosahedral structure observed in gold nanoparticles. Surf Sci 447:73–80. doi:10.1016/S0039-6028(99)01112-7
Brust M, Walker M, Berthell D, Schiffrin DJ, Whyman R (1994) Synthesis of thiol derivatised gold nanoparticles in a two phase liquid/liquid system. J Chem Soc Chem Commun 1994:801–802. doi:10.1039/c39940000801
Buffat P, Borel JP (1976) Size effect on the melting temperature of gold nanoparticles. Phys Rev A 13:2287–2298. doi:10.1103/PhysRevA.13.2287
Buffat P-A, Flüeli M, Spycher R, Stadelmann P, Borel J-P (1991) Crystallographic structure of small gold particles studied by high-resolution electron microscopy. Faraday Discuss 92:173–187. doi:10.1039/fd9919200173
El-Sayed MA (2001) Some interesting properties of metals confined in time and nanometer space of different shapes. Acc Chem Res 34:257–264. doi:10.1021/ar960016n
Gittins DI, Caruso F (2001) Spontaneous phase transfer of nanopaticulate metals from organic to aqueous media. Angew Chem Int Ed 40:3001–3004. doi:10.1002/1521-3773(20010817)40:16<3001::AID-ANIE3001>3.0.CO;2-5
Liu XG, Wu NQ, Wunsch BH, Barsotti RJ, Stellacci F (2006) Shape-controlled growth of micrometer sized gold crystals by a slow reduction method. Small 2:1046–1050. doi:10.1002/smll.200600219
Marks LD (1994) Experimental studies of small particle structures. Rep Prog Phys 57:603–649. doi:10.1088/0034-4885/57/6/002
Martin TP (1996) Shells of atoms. Phys Rep 273:199–241. doi:10.1016/0370-1573(95)00083-6
Pauwels B, Van Tendeloo C, Bouwen W, Kuhn LT, Lievens P, Lei H, Hou M (2000) Low energy deposited gold clusters investigated by high resolution electron microscopy and molecular dynamics simulations. Phys Rev B 62:10383–10393. doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.62.10383
Pinto A, Pennisi AR, Faraci G, D’Agostino G, Mobilio S, Boscherini F (1995) Evidence for truncated octahedral structures in supported gold clusters. Phys Rev B 51:5315–5321. doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.51.5315
Teranishi T, Hasegawa S, Shimizu T, Miyake M (2001) Heat-induced size evolution of gold nanoparticles in the solid state. Adv Mater 13:1699–1701. doi:10.1002/1521-4095(200111)13:22<1699::AID-ADMA1699>3.0.CO;2-3
Wang ZL (2000) Transmission electron microscopy of shape-controlled nanocrystals and their assemblies. J Phys Chem B 104:1153–1175. doi:10.1021/jp993593c
Wang YQ, Smirani R, Ross GG (2004) Nanotwinning in silicon nanocrystals produced by ion implantation. Nano Lett 4:2041–2045. doi:10.1021/nl048764q
Wang YQ, Smirani R, Ross GG, Schiettekatte F (2005) Ordered coalescence of Si nanocrystals in SiO2. Phys Rev B 71:161310. doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.71.161310
Wang YQ, Nikitin K, McComb DW (2008) Fabrication of Au-Cu2O core-shell nanocube heterostructures. Chem Phys Lett 456:202–205. doi:10.1016/j.cplett.2008.03.027
Zhou GW, Wang L, Birtcher RC, Baldo PM, Pearson JE, Yang JC, Eastman JA (2006) Cu2O island shape transition during Cu-Au alloy oxidation. Phys Rev Lett 96:226108. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.96.226108
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the financial support from Qingdao University (Project No. 06300701).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y.Q., Liang, W.S. & Geng, C.Y. Shape evolution of gold nanoparticles. J Nanopart Res 12, 655–661 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-009-9612-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-009-9612-3