Abstract
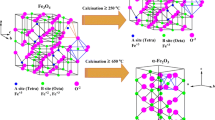
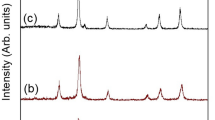
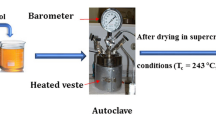
Magnetite synthesized via three different synthesis routes (coprecipitation process in aqueous media, electrochemical synthesis in presence of complexing agents and solid state reaction at high temperature) has been characterized by X-Ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy, thermal analysis (TGA), FT-IR and Mössbauer spectroscopies. Although each procedure gave homogeneous magnetite powders, many differences could be seen in the physico-chemical properties of the samples mostly depending on the synthesis conditions. For instance, at least two factors seem to have a huge impact onto the Fe3O4 behaviour: the presence of hydration water molecules and the particle size of the powders since a superparamagnetic behaviour was observed with the thinnest particles, at room temperature, on the Mössbauer spectra via the appearance of line broadening and a pronounced central doublet.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bean C.P., Livingston J.D. (1959) J. Appl. Phys. 30:120S
Brousse T., Bélanger D. (2003) Electrochem. Solid State Lett. 6:A244
Chen D., Xu R. (1998) Mater. Res. Bull. 33:1015
Couling S.B. & S. Mann, 1985. J. Chem. Soc. 23, 1713
Darken L.S., Gurry R.W. (1946) J. Am. Chem. Soc. 68:798
Diandra L.L., Reuben D.R. (1996) Chem. Mater. 8:1770
Elmore W.C. (1938) Phys. Rev. 54:309
Franger S., Bach S., Pereira-Ramos J-P., Baffier N. (2000) J. Electrochem. Soc. 147:3226
Franger S., Bach S., Farcy J., Pereira-Ramos J-P., Baffier N. (2002) J. Power Sources 109:262
Franger S., Berthet P., Berthon J., (2004) J. Solid State Electrochem. 8:218
Hsu J.H., Chen S.Y., Chang C.R. (2002) J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 242–245:479
Jolivet J-P., Massart R., Fruchart J-M. (1983) Nouv. J. Chim. 7:325
Jolivet J-P., Belleville P., Tronc E., Livage J. (1992) Clays Clay Miner. 40:531
Khollam Y.B., Dhage S.R., Potdar H.S., Deshpande S.B., Bakare P.P., Kulkarni S.D., Date S.K. (2002) Mater. Lett. 56:571
Kiyama M. (1974) Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 47:1646
Klug H.P. & L.E. Alexander, 1974. X-Ray diffraction procedures for polycrystalline and amorphous materials. 2nd edn. Wiley Interscience.
Koltsov D., Perry M. (2004) Physicians World 7:31
Liu Z., Zhang D., Han S., Li C., Lei B., Lu W., Fang J., Zhou C. (2005) J. Am. Chem. Soc. 127:6
Livage J. (1996) Solid State Ionics 86–88:935
Livage J., Beteille F., Roux C., Chatry M., Davidson P. (1998) Acta Mater. 46:743
Massart R., (1980) C. R. Acad. Sci. Paris 291C:1
Morup S., Topsoe H., Lipka J. (1976) J. Physique 37:C6-287
Nedkov I., Merodiiska T., Kolev S., Krezhov K., Niarchos D., Moraitakis E., Kusano Y., Takada J. (2002) Monatshefte für Chemie 133:823
Olowe A.A., Génin J.M.R. (1991) Corros. Sci. 2:965
Olowe A.A., Pauron B., Génin J.M.R. (1991) Corrosion Sci. 2:985
Palosz B., Stel’makh S., Grzanka E., Gierlotha S., Pielaszek R., Bismayer U., Werner S., Palosz W. (2004) J. Phys. Condens. Matter 16(5):S353
Petzold W., Petzold A. (1958) Z. Anal. Chem. 161:241
Riegel E.R., Schwartz R.D. (1952) Anal. Chem. 14:1803
Siles-Dotor M.G., Morales A., Benaissa M., Cabral-Prieto A. (1997) Nanostruct. Mater. 8:657
Tronc E., Jolivet J-P., Massart R., (1982) Mater. Res. Bull. 17:1365
Tronc E., Belleville P., Jolivet J-P., Livage J., (1992) Langmuir 8:313
Tsouris C., Depaoli D.W., Shor J.T., Hu M.Z.-C., Ying T.-Y. (2001) Colloids Surf. A 177:233
Visalakshi G., Venkateswaran G., Kulshreshtha S.K., Moorty P.N. (1993) Mater. Res. Bull. 28:829
Wan S., Huang J., Yan H., Liu K. (2006) J. Mater. Chem. 16:298
Wang L., Li J., Ding W., Zhou T., Liu B., Zhong W., Wu J., Du Y. (1999) J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 207:111
Wang J., Sun J., Sun Q., Chen Q. (2003) Mater. Res. Bull. 38:1113
Yamamoto A., Honmyo T., Hosoito N., Kiyama M., Shinjo T. (1993) Nucl. Instrum. Methods B 76:202
Zaïtsev V.S., Filimonov D.S., Presnyakov I.A., Gambino R.J., Chu B. (1999) J. Colloid Interface Sci. 212:49
Ziese M., Höhne R., Hong N.H., Dienelt J., Zimmer K., Esquinazi P. (2002) J Magn Magn Mater 242–245:450
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Mr. Christian Haut (ICMMO, Université Paris Sud – XI) who provided the electronic micrographs of our magnetite samples and would like to acknowledge Pr. Ph. Barboux (ENSCP/Paris) for fruitful discussions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Franger, S., Berthet, P., Dragos, O. et al. Large influence of the synthesis conditions on the physico-chemical properties of nanostructured Fe3O4 . J Nanopart Res 9, 389–402 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-006-9105-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-006-9105-6