Abstract
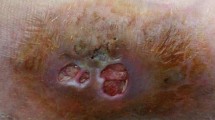
Pyrenochaeta romeroi is a rare fungal agent of chronic, suppurative subcutaneous infections leading to mycetoma. It is an unusual cause of deep, non-mycetomatous infections. We herein present review of the literature along with a case of 61-year-old Indian female with rheumatoid arthritis who developed subcutaneous phaeohyphomycosis caused by Pyrenochaeta romeroi. It posed a diagnostic challenge, as the culture from fine-needle aspirate revealed a non-sporulating dematiaceous mould, which was the only supportive tool for its diagnosis and initiation of the therapy. However, it was the molecular sequencing which played the pivotal role in clinching the final aetiological diagnosis. To the best of our knowledge, this is the 20th case of Pyrenochaeta species infection occurring worldwide and first case report of subcutaneous phaeohyphomycosis caused by Pyrenochaeta romeroi in a rheumatoid arthritis patient.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Badali H, Chander J, Gulati N, Attri A, Chopra R, Najafzadeh MJ, et al. Subcutaneous phaeohyphomycotic cyst caused by Pyrenochaeta romeroi. Med Mycol. 2010;48:763–8.
van de Sande WW, Maghoub el S, Fahal AH, Goodfellow M, Welsh O, Zijlstra E. The mycetoma knowledge gap: identification of research priorities. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2014;8(3):e2667. doi:10.1371/journal.pntd.0002667.
Borelli D. Opportunistic fungi as producers of gray colonies and mycetomata. Dermatologica. 1979;159:168–74.
Girard C, Dereure O, Rispail P, Durand L, Guilhou JJ. Subcutaneous phaeohyphomycosis due to Pyrenochaeta romeroi in a patient with leprosy. Acta Derm Venereol. 2004;84:154–5.
Sutton DA, Rinaldi MG, Sanche SE. Demetiaceous fungi. In: Anaissie EJ, McGinnis MR, Pfaller MA, editors. Clinical mycology. 2nd ed. London: Churchill Livingstone Elsevier; 2009. p. 329–54.
Andre M, Brumpt V, Destombes P, Segretain G. Fungal mycetoma with black grains due to Pyrenochaeta romeroi in Cambodia. Bull Soc Pathol Exot Filiales. 1968;61:108–12.
Baylet R, Camain R, Chabal J, Izarn R. Recent contribution to the study of mycetoma in Senegal. Neotestudina rosatii, Pyrenochaeta romeroi, Aspergillus nidulans. Bull Soc Med Afr Noire Lang Fr. 1968;13:311–3.
David-Chausse J, Texier L, Darrasse H, Moulinier C. Autochthonous mycetoma of the foot due to Pyrenochaeta romeroi. Bull Soc Fr Dermatol Syphiligr. 1968;75:452–3.
Thammayya A, Sanyal M, Basu N. Pyrenochaeta romeroi causing mycetoma pedis in India. J Indian Med Assoc. 1979;73:66–7.
English MP. Infection of the finger-nail by Pyrenochaeta unguis—hominis. Br J Dermatol. 1980;103:91–3.
Serrano JA, Pisano ID, Lopez FA. Black grain minimycetoma caused by Pyrenochaeta mackinnonii, the first clinical case of eumycetoma reported in Barinas state, Venezuela. J Mycol Med. 1998;8:34–9.
Mohanty JC, Mohanty SK, Sahoo A, Ghosh SK, Pattnaik KL. Eumycetoma caused by Pyrenochaeta romeroi: a case report. Indian J Dermatol. 2000;45:76–7.
Ferrer C, Perez-Santonja JJ, Rodriguez AE, Colom MF, Gene J, Alio JL, et al. New Pyrenochaeta species causing keratitis. J Clin Microbiol. 2009;47:1596–8.
Cerar D, Malallah YM, Howard SJ, Bowyer P, Denning DW. Isolation, identification and susceptibility of Pyrenochaeta romeroi in a case of eumycetoma of the foot in the UK. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2009;34:617–8.
Verkley GJ, Gene J, Guarro J, Perez-Santonja JJ, Rodriguez AE, Colom MF, et al. Pyrenochaeta keratinophila sp. nov., isolated from an ocular infection in Spain. Rev Iberoam Micol. 2010;27:22–4.
Khan Z, Ahmad S, Kapila K, Ramaswamy NV, Alath P, Joseph L, et al. Pyrenochaeta romeroi: a causative agent of phaeohyphomycotic cyst. J Med Microbiol. 2011;60:842–6.
Thiyagarajan UM, Bagul A, Nicholson M. A nodulo-cystic eumycetoma caused by Pyrenochaeta romeroi in a renal transplant recipient: a case report. J Med Case Rep. 2011;5:460.
Ocampo MA, Kanitakis J, Bienvenu AL, Chauvet C, Euvrard S. Phaeohyphomycosis caused by Pyrenochaeta romeroi mimicking a plantar wart in a kidney transplant recipient. Transpl Infect Dis. 2012;14:E173–4.
Hsiao YW, Chia JH, Lu CF, Chung WH. Molecular diagnosis and therapeutic experience of subcutaneous Pyrenochaeta romeroi infection: a case report and review of the literature. Int J Dermatol. 2013;52:1237–40.
Chan YY, Tan AL, Tan BH. Subcutaneous abscess due to Pyrenochaeta romeroi in a renal transplant recipient. Singapore Med J. 2014;55:e64–6.
Yadav S, Agarwal R, Singh S, Goel S. Pyrenochaeta romeroi causing subcutaneous phaeohyphomycotic cyst in a diabetic female. Med Mycol Case Rep. 2015;8:47–9.
Rinaldi MG. Phaeohyphomycosis. Dermatol Clin. 1996;14:147–53.
Badali H, Najafzadeh MJ, Van Esbroeck M, Van den Enden E, Tarazooie B, Meis JFGM, et al. The clinical spectrum of Exophiala jeanselmei, with a case report and in vitro antifungal susceptibility of the species. Med Mycol. 2010;48:318–27.
Chowdhary A, Meis JF, Guarro J, de Hoog GS, Kathuria S, Arendrup MC, et al. ESCMID and ECMM joint clinical guidelines for the diagnosis and management of systemic phaeohyphomycosis: diseases caused by black fungi. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2014;20 (Suppl 3):47–75. doi:10.1111/1469-0691.12515.
Sharkey PK, Graybill JR, Rinaldi MC, Stevens DA, Tucker RM, Peterie JD, et al. Itraconazole treatment of phaeohyphomycosis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1990;23:577–86.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sharma, S., Capoor, M.R., Singh, M. et al. Subcutaneous Phaeohyphomycosis Caused by Pyrenochaeta romeroi in a Rheumatoid Arthritis Patient: A Case Report with Review of the Literature. Mycopathologia 181, 735–743 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11046-016-0022-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11046-016-0022-7