Abstract
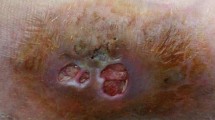
Exophiala spinifera is a rare fungus causing chromoblastomycosis or different types of phaeohyphomycosis (cutaneous, subcutaneous, disseminated and cyst phaeohyphomycosis). We report a case of a young male with phaeohyphomycosis due to E. spinifera, who had multiple itchy painful papular lesions disfiguring his face for 4 years. His diagnosis was delayed and had received antibacterial and antileishmanial therapy elsewhere without any improvement. While he reported to our hospital, the histopathology of the biopsy collected from the lesion demonstrated acute on chronic inflammation with granuloma formation and darkly pigmented fungal elements. The isolate grown on culture was identified as E. spinifera on the basis of morphological characters. The identification of the isolate was further confirmed by sequencing of the ITS region of ribosomal DNA. After treatment with oral itraconazole, he had marked clinical improvement.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ajello L. Hyalohyphomycosis and phaeohyphomycosis: two global disease entities of public health importance. Eur J Epidemiol. 1986;2:243–51.
Padhye AA, Ajello L, Chandler FW, Banos JE, Hernandez-Perez E, Llerena J, et al. Phaeohyphomycosis in El Salvador caused by Exophiala spinifera. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1983;32:799–803.
Padhye AA, Kaplan W, Neuman MA, Case P, Radcliffe GN. Subcutaneous phaeohyphomycosis caused by Exophiala spinifera. Sabouraudia. 1984;22:493–500.
Kotylo PK, Israel KS, Cohen JS, Bartlett MS. Subcutaneous phaeohyphomycosis of the finger caused by Exophiala spinifera. Am J Clin Pathol. 1989;91:624–7.
Mirza SH, Hannan A, Ahmad A, Ahmad M. Subcutaneous phaeohyphomycosis. J Infect. 1993;27:75–8.
Campos-Takaki GM, Jardim ML. Report of chronic subcutaneous abscesses caused by Exophiala spinifera. Mycopathologia. 1994;127:73–6.
Shivaprakash MR, Appannanavar SB, Dhaliwal M, Gupta A, Gupta S, Gupta A, et al. Colletotrichum truncatum: an unusual pathogen causing mycotic keratitis and endophthalmitis. J Clin Microbiol. 2011;49:2894–8.
Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Reference method for broth dilution antifungal susceptibility testing of filamentous fungi; Approved standard—M38-A2. Wayne: CLSI; 2008.
Ajello L. Phaeohyphomycosis: definition and etiology. PAHO Sci Pub. 1975;304:126–30.
de Hoog GS, Poonwan N. Gerrits van den Ende AHG. Taxonomy of Exophiala spinifera and its relationship to E. jeanselmei. Stud Mycol. 1999;43:133–42.
de Hoog GS, Vicente V, Caligiorne RB, Kantarcioglu S, Tintelnot K, Gerrits van den Ende AHG, et al. Species diversity and polymorphism in the Exophiala spinifera clade containing opportunistic black yeast-like fungi. J Clin Microbiol. 2003;41:4767–78.
Vitale RG, de Hoog GS. Molecular diversity, new species and antifungal susceptibilities in the Exophiala spinifera clade. Med Mycol. 2002;40:545–56.
Zeng JS, Sutton DA, Fothergill AW, Rinaldi MG, Harrak MJ, de Hoog GS. Spectrum of clinically relevant Exophiala species in the United States. J Clin Microbiol. 2007;45:3713–20.
Dai WL, Ren ZF, Wen JZ, Lnj HY, Chen RE, Wang DL, et al. First case of systemic phaeohyphomycosis caused by Exophiala spinifera in China. Chin J Dermatol. 1987;20:13–5.
Lacaz CD, Porto E, Andrade JG, Tellhes FDJ. Feohifomicose disseminada por Exophiala spinifera. Ann Bras DermatoI. 1984;59:238–43.
Negroni R, Helou SH, Petri N, Robles AM, Arechavala A, Bianchi MH. Case study: posaconazole treatment of disseminated phaeohyphomycosis due to Exophiala spinifera. Clin Infect Dis. 2004;38:e15–20.
Sharkey PK, Graybill JR, Rinaldi MG, Stevens DA, Tucker RM, Peterie JD, et al. Itraconazole treatment of phaeohyphomycosis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1990;23:577–86.
Whittle DI, Kominos S. Use of itraconazole for treating subcutaneous phaeohyphomycosis caused by Exophiala jeanselmei. Clin Infect Dis. 1995;21:1068.
Vitale RG, Afeltra J, de Hoog GS, Rijs AJ, Verweij PE. In vitro activity of amphotericin B and itraconazole in combination with flucytosine, sulfadiazine and quinolones against Exophiala spinifera. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2003;51:1297–300.
Vitale RG, De Hoog GS, Verweij PE. In vitro activity of amphotericin B, itraconazole, terbinafine and 5-fluocytosine against Exophiala spinifera and evaluation of post-antifungal effects. Med Mycol. 2003;41:301–7.
Meletiadis J, Meis JF, de Hoog GS, Verweij PE. In vitro susceptibilities of 11 clinical isolates of Exophiala species to six antifungal drugs. Mycoses. 2000;43:309–12.
Rivard RG, McCall S, Griffith ME, Hawley JS, Ressner RA, Borra H, et al. Efficacy of caspofungin and posaconazole in a murine model of disseminated Exophiala infection. Med Mycol. 2007;45:685–9.
Rajam RV, Kandhari KC, Thirumalachar MJ. Chromoblastomycosis caused by a rare yeast like dematiaceous fungus. Mycopathol Mycol Appl. 1958;9:5–19.
Nielsen HS Jr, Conant NF. A new human pathogenic Phialophora. Sabouraudia. 1968;6:228–31.
Wang DL, Li RY, Wang XH, Dai WL. Studies on three strains of Exophiala spinifera. Acta Mycol Sin. 1987;62:29–32.
Barba-Gomez JF, Mayorga J, McGinnis MR, Gonzalez-Mendoza A. Chromoblastomycosis caused by Exophiala spinifera. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1992;26:367–70.
Padhye AA, Hampton AA, Hampton MT, Hutton NW, Prevost-Smith E, Davis MS. Chromoblastomycosis caused by Exophiala spinifera. Clin Infect Dis. 1996;22:331–5.
Rajendran C, Khaitan BK, Mittal R, Ramam M, Bhardwaj M, Datta KK. Phaeohyphomycosis caused by Exophiala spinifera in India. Med Mycol. 2003;41:437–41.
Takahara M, Imafuku S, Matsuda T, Uenotsuchi T, Matsumoto T, Padhye AA, et al. Concurrent double infections of the skin: phaeohyphomycosis and nocardiosis in a patient with idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2005;53:S277–80.
Dutriaux C, Saint-Cyr I, Desbois N, Cales-Quist D, Diedhou A, Boisseau-Garsaud AM. Subcutaneous phaeohyphomycosis due to Exophiala spinifera in a renal transplant recipient. Ann Dermatol Venereol. 2005;132:259–62.
Tomson N, Abdullah A, Maheshwari MB. Chromomycosis caused by Exophiala spinifera. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2006;31:239–41.
Singal A, Pandhi D, Bhattacharya SN, Das S, Aggarwal S, Mishra K. Pheohyphomycosis caused by Exophiala spinifera: a rare occurrence. Int J Dermatol. 2008;47:44–7.
Harris JE, Sutton DA, Rubin A, Wickes B, De Hoog GS, Kovarik C. Exophiala spinifera as a cause of cutaneous phaeohyphomycosis: case study and review of the literature. Med Mycol. 2009;47:87–93.
Radhakrishnan D, Jayalakshmi G, Madhumathy A, Banu ST, Geethalakshmi S, Sumathi G. Subcutaneous phaeohyphomycosis due to Exophiala spinifera in an immunocompromised host. Ind J Med Microbiol. 2010;28:396–9.
Badali H, Chander J, Bayat M, Seyedmousavi S, Sidhu S, Rani H, et al. Multiple subcutaneous cysts due to Exophiala spinifera in an immunocompetent patient. Med Mycol. 2012;50:207–13.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the Indian Council of Medical Research, New Delhi, India, for providing financial aid for National Culture Collection of Pathogenic Fungi (NCCPF).
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, G., Shivaprakash, M.R., De, D. et al. Chronic Disfiguring Facial Lesions in an Immunocompetent Patient Due to Exophiala spinifera: A Case Report and Review of Literature. Mycopathologia 174, 293–299 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11046-012-9548-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11046-012-9548-5