Abstract
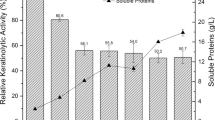
Coccidioides immitis is the causative agent of coccidioidomycosis, a systemic mycosis that attacks humans and a wide variety of animals. In the present study, we showed that the C. immitis mycelial form is able to release proteolytic enzyme into the extracellular environment. Under chemically defined growth conditions, mycelia secreted seven distinct polypeptides ranging from 15 to 65 kDa and an extracellular peptidase of 25 kDa. This enzyme had its activity fully inhibited by phenylmethylsulphonyl fluoride, a serine peptidase inhibitor. Conversely, metallo, cysteine, and aspartyl peptidase inhibitors did not alter the 25-kDa enzyme behavior. This extracellular serine peptidase was able to degrade keratin, a fibrous protein that composes human epidermis. Additionally, this peptidase cleaved different protein substrates, including gelatin, casein, hemoglobin, and albumin. Curiously, an 18-kDa serine peptidase activity was evidenced solely when casein was used as the co-polymerized protein substrate into the gel. The existence of different secreted peptidases could be advantageous for the adaptation of C. immitis to distinct environments during its complex lifecycle.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wanke B, Lazéra M, Monteiro PC, Lima FC, Leal MJ, Ferreira Filho PL, Kaufman L, Pinner RW, Ajello L. Investigation of an outbreak of endemic coccidioidomycosis in Brazil’s northeastern state of Piauí with a review of the occurrence and distribution of Coccidioides immitis in three other Brazilian states. Mycopathologia. 1999;148:57–67.
Cole GT, Xue JM, Okeke CN, Tarcha EJ, Basrur V, Schaller RA, Herr RA, Yu JJ, Hung CY. A vaccine against coccidioidomycosis is justified and attainable. Med Mycol. 2004;42:189–216.
DiCaudo DJ. Coccidioidomycosis: a review and update. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2006;55:929–42.
Anstead GM, Corcoran G, Lewis J, Berg D, Graybill JR. Refractory coccidioidomycosis treated with posaconazole. Clin Infect Dis. 2005;40:1770–6.
Fisher MC, Koenig GL, White TJ, Taylor JW. Molecular and phenotypic description of Coccidioides posadasii sp. nov., previously recognized as the non-California population of Coccidioides immitis. Mycologia. 2002;94:73–84.
Cole GT, Sun SH. Arthroconidium-spherule endospore transformation in Coccidioides immitis. In: Szaniszlo PJ, editor. Fungal dimorphism. New York: Plenum Publishing Corp.; 1985. p. 281–333.
Hung CY, Kalpathi SR, Yu JJ, Schaller RA, Xue J, Basrur V, Gardner MJ, Cole GT. A metalloproteinase of Coccidioides posadasii contributes to evasion of host detection. Infect Immun. 2005;73:6689–703.
Yuan L, Cole GT, Sun SH. Possible role of a proteinase in endosporulation of Coccidioides immitis. Infect Immun. 1988;56:1551–9.
Cole GT, Zhu SW, Hsu LL, Kruse D, Seshan KR, Wang F. Isolation and expression of a gene which encodes a wall-associated proteinase of Coccidioides immitis. Infect Immun. 1992;60:416–27.
Tarcha EJ, Basrur V, Hung CY, Gardner MJ, Cole GT. A recombinant aspartyl protease of Coccidioides posadasii induces protection against pulmonary coccidioidomycosis in mice. Infect Immun. 2006;74:516–27.
Nogueira de Melo AC, Dornelas-Ribeiro M, De Souza EP, Macrae A, Fracalanzza SE, Vermelho AB. Peptidase profiles from non-albicans Candida spp. isolated from the blood of a patient with chronic myeloid leukemia and another with sickle cell disease. FEMS Yeast Res. 2007;7:1004–12.
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951;193:264–75.
Laemmli UK. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970;227:680–5.
Santos ALS, Soares RMA. Candida guilliermondii isolated from HIV-infected human secretes a 50 kDa serine peptidase that cleaves a broad spectrum of proteinaceous substrates. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2005;43:13–20.
Ng TB. Peptides and proteins from fungi. Peptides. 2004;25:1055–73.
Lopez-Ribot JL, Casanova M, Murgui A, Martinez JP. Antibody response to Candida albicans cell wall antigens. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2004;41:187–96.
Hube B. Extracellular peptidases of human pathogenic fungi. Contrib Microbiol. 2000;5:126–37.
Monod M, Capoccia S, Lechenne B, Zaugg C, Holdom M, Jousson O. Secreted proteases from pathogenic fungi. Int J Med Microbiol. 2002;292:405–19.
Nziramasanga P, Lupan D. Elastase activity of Coccidioides immitis. J Med Microbiol. 1985;19:109–14.
Lupan DM, Nziramasanga P. Collagenolytic activity of Coccidioides immitis. Infect Immun. 1986;51:360–1.
Yuan L, Cole GT. Isolation and characterization of an extracellular proteinase of Coccidioides immitis. Infect Immun. 1987;55:1970–8.
Resnick S, Pappagianis D, McKerrow JH. Proteinase production by the parasitic cycle of the pathogenic fungus Coccidioides immitis. Infect Immun. 1987;55:2807–15.
Sun SH, Huppert M. A cytological study of morphogenesis in Coccidioides immitis. Sabouraudia. 1976;14:185–98.
Bloom JW, Camilli AE, Barbee RA. Disseminated coccidioidomycosis: a ten-year experience. In: Einstein HE, Catanzaro A, editors. Proceedings of the Fourth International Conference on Coccidioidomycosis. Washington, DC: The National Foundation for Infectious Disease; 1985. p. 369–78.
Griffin DH. Fungal physiology. New York: Wiley; 1981.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Brazilian agencies: MCT/CNPq (Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico), CEPG/UFRJ (Conselho de Ensino para Graduados e Pesquisas), FAPERJ (Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado do Rio de Janeiro), FUJB (Fundação Universitária José Bonifácio), and CAPES (Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lopes, B.G.B., Santos, A.L.S., Bezerra, C.C.F. et al. A 25-kDa Serine Peptidase with Keratinolytic Activity Secreted by Coccidioides immitis . Mycopathologia 166, 35–40 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11046-008-9116-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11046-008-9116-1