Abstract
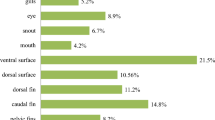
Phoma herbarum has been associated with two outbreaks of systemic mycosis in hatchery-reared chinook salmon (Oncorhynchus tshawytscha) fingerlings. Affected fish exhibited abnormal swimming behavior, exophthalmia, multiple rounded areas of muscle softening, protruded hemorrhagic vents, and abdominal swelling. In all affected fish, swimbladders were filled with whitish creamy viscous fungal mass, surrounded by dark red areas in swimbladder walls, kidneys, and musculature. Clinical and histopathological examinations suggest that the infection may have started primarily in the swimbladder and then spread to the kidneys, gastrointestinal tract, and surrounding musculature. Consistent microscopical findings included broad septate branched fungal hyaline hyphae, 5–12 µm in diameter within the swimbladder, stomach, and often within and adjacent to blood vessels. Profuse growths of woolly brown fungal colonies were obtained from swimbladders and kidneys on Sabouraud medium. On corn meal agar the formation of pycnidia, characteristic of Phoma spp., was detected within 10 days of incubation. Morphological and molecular analyses identified this fungus as Phoma herbarum. This report underscores systemic fungal infections as a threat to raceway-raised salmon.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dexter JL, O’Neal P. Michigan Fish Stocking Guidelines II: With Periodic Updates. State of Michigan, Department of Natural Resources, Fisheries Division Special Report, 2004; number 32:67
AJ Ross WT Yasutake S Leek (1975) ArticleTitle Phoma herbarum, a fungal plant saprophyte, as a fish pathogen J Fish Res Board Can 32 1648–1652
J Sambrook EF Fritsch T Maniatis (1989) Molecular cloning. A laboratory manual EditionNumber2 Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press Cold Spring Harbor, NY
V Silva CN Pereira L Ajello L Mendoza (2005) ArticleTitleMolecular evidence for multiple hosts specific strains in the genus Rhinosporidium J Clin Microbiol 43 1865–1868 10.1128/JCM.43.4.1865-1868.2005 Occurrence Handle10.1128/JCM.43.4.1865-1868.2005 Occurrence Handle15815010 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2MXjvF2ks7g%3D
L Luna (1968) Manual of Histologic Staining Methods of the Armed Forces Institute of Pathology Washington, D.C 258
EB Prophet B Mills JB Arrington LH Sobin (1992) Laboratory methods in histotechnology. Armed Forces Institute of Pathology Washington, D.C 279
GH Boerema (1964) ArticleTitle Phoma herbarum westend, the type-species of the Phoma-genus Persoonia 3 9–16
J Baker IF Salkin P Forgacs JH Haines ME Kemma (1987) ArticleTitleFirst report of subcutaneous phaeohyphomycosis of the foot caused by Phoma minutella J Clin Microbiol 25 2395–2397 Occurrence Handle3429630 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaL1c7hsFyqug%3D%3D
JV Moran PA Greenberger R Patterson (2002) ArticleTitleLong-term evaluation of hypersensitivity pneumonitis: A case study follow-up and literature review Allergy Asthma Proc 23 265–270 Occurrence Handle12221897
T Taskinen T Meklin M Nousiainen T Husman A Nevalainen M Korppi (1997) ArticleTitleMoisture and mold problems in schools and respiratory manifestations in school children: Clinical and skin test findings Acta Paediatr 86 1181–1187 Occurrence Handle10.1111/j.1651-2227.1997.tb14841.x Occurrence Handle9401510 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1c%2FmsFSgsA%3D%3D
Z Hubalek B Rosicky M Otcenasek (1980) ArticleTitleFungi from interior organs of free-living small mammals in Czechoslovakia and Yugoslavia Folia Parasitol (Praha) 27 269–279 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaL3M%2FisFWntA%3D%3D
JF Rivero-Cruz M Macias CM Cerda-Garcia-Rojas R Mata (2003) ArticleTitleA new phytotoxic nonenolide from Phoma herbarum J Nat Prod 66 511–514 10.1021/np020501t Occurrence Handle10.1021/np020501t Occurrence Handle12713403 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXis1Kgurw%3D
Y Fujimaki S Egusa Y Jo (1986) ArticleTitleA visceral mycosis in ayu fry, Plecoglossus altivelis Temminck & Schlegel, caused by a species of Phoma J Fish Dis 9 111–116 10.1111/j.1365-2761.1986.tb00989.x Occurrence Handle10.1111/j.1365-2761.1986.tb00989.x
GH Boerema J Gruyter Particlede HA Kesteren Particlevan (1994) ArticleTitleContributions towards a monograph of Phoma (Coelomycetes)-III, 1. Section Plenodomus: Taxa often with a Leptosphaeria telemorph Persoonia 15 431–487
J DeGruyter ME Noordeloos GE Boerema (1993) ArticleTitleContributions towards a monograph of Phoma (Coelomycetes)-I. 2. Section Phoma: Additional taxa with very small conidia and taxa with conidia up to 7 µm long Persoonia 15 369–400
L Ajello MR McGinnis J Camper (1977) ArticleTitleAn outbreak of phaeohyphomycosis in rainbow trout caused by Scolecobasidium humicola Mycopathologia 62 15–22 10.1007/BF00491991 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00491991 Occurrence Handle563511 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaE1c%2FntFKhtA%3D%3D
Blazer VS, Wolke RE. An Exophiala-like fungus as the cause of a systemic mycosis of marine fish. J Fish Dis 1979; 2:145
TC Kirilenko MA Al-Achmed (1977) ArticleTitle Ochroconis tshawytschae (Doty et Slater) comb, nov Mikrobiol Zh 39 303–306 Occurrence Handle561295 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaE2s3lsVersQ%3D%3D
JW Carmichael (1966) ArticleTitleCerebral mycetoma of trout due to a Phialophora-like fungus Sabouraudia 5 120–123 Occurrence Handle6010250 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaF2s3ls1Sqsw%3D%3D
N Fijan (1969) ArticleTitleSystemic mycosis in channel catfish Bull Wild Dis Assoc 5 109–110 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaF1M3kt1WnsA%3D%3D
MR McGinnis L Ajello (1974a) ArticleTitleA new species of Exophiala isolated from channel catfish Mycologia 66 518–520 Occurrence Handle10.2307/3758495 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaE2c3ntlamtg%3D%3D
EJ Otis RE Wolke (1985) ArticleTitleInfection of Exophiala salmonis in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) J Wildlife Dis 21 61–64 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaL2M7mtFSrtg%3D%3D
RH Richards A Holliman S Helgason (1978) ArticleTitle Exophiala salmonis infection in Atlantic salmon, Salmo salar L J Fish Dis 1 357–368 10.1111/j.1365-2761.1978.tb00040.x Occurrence Handle10.1111/j.1365-2761.1978.tb00040.x
JC Wolf SA Smith (1999) ArticleTitleSystemic zygomycosis in farmed tilapia fish J Comp Path 121 301–306 10.1053/jcpa.1999.0323 Occurrence Handle10.1053/jcpa.1999.0323 Occurrence Handle10486168 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1MvhslOitQ%3D%3D
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Faisal, M., Elsayed, E., Fitzgerald, S.D. et al. Outbreaks of phaeohyphomycosis in the chinook salmon (Oncorhynchus tshawytscha) caused by Phoma herbarum . Mycopathologia 163, 41–48 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11046-006-0084-z
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11046-006-0084-z