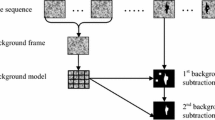
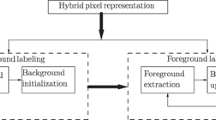
Abstract
Background modeling is a well accepted foreground detection technique for many visual surveillance applications like remote sensing, medical imaging, traffic monitoring, crime detection, machine/robot vision etc. Regardless of simplicity of foreground detection concept, no conventional algorithms till date seem to be able to concurrently address the key challenges like illumination variation, dynamic background, low contrast and noisy sequences. To mitigate this issue, this paper proposes an improved scheme for foreground detection particularly addresses all the aforementioned key challenges. The suggested scheme operates as follows: First, a spatio-temporal local binary pattern (STLBP) technique is employed to extract both spatial texture feature and temporal motion feature from a video frame. The present scheme modifies the change detection rule of traditional STLBP method to make the features robust under challenging situations. The improvisation in change description rule reflects that to extract STLBP features, the mean of the surrounding pixels is chosen instead of a fixed center pixel across a local region. Further, in many foreground detection algorithms a constant learning rate and constant threshold value is considered during background modeling which in turn fails to detect a proper foreground under multimodal background conditions. So to address this problem, an adaptive formulation in background modeling is proposed to compute the learning rate (αb) and threshold value (Tp) to detect the foreground accurately without any false labeling of pixels under challenging environments. The performance of the proposed scheme is evaluated through extensive simulations using different challenging video sequences and compared with that of the benchmark schemes. The experimental results demonstrate that the proposed scheme outperforms significant improvements in terms of both qualitative as well as quantitative measures than that of the benchmark schemes.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ashraphijuo M, Aggarwal V, Wang X (2017) On deterministic sampling patterns for robust low-rank matrix completion. IEEE Signal Process Lett 25(3):343–347
Azizpour H, Laptev I (2012) Object detection using strongly-supervised deformable part models. In: European conference on computer vision. Springer, pp 836–849
Bilodeau GA, Jodoin JP, Saunier N (2013) Change detection in feature space using local binary similarity patterns. In: 2013 International conference on computer and robot vision (CRV). IEEE, pp 106–112
Bouwmans T (2011) Recent advanced statistical background modeling for foreground detection-a systematic survey. Recent Pat Comput Sci 4(3):147–176
Bouwmans T (2014) Traditional and recent approaches in background modeling for foreground detection: an overview. Comput Sci Rev 11:31–66
Bouwmans T, Garcia-Garcia B (2019) Background subtraction in real applications: challenges, current models and future directions. arXiv preprint arXiv:190103577
Bouwmans T, Zahzah EH (2014) Robust pca via principal component pursuit: a review for a comparative evaluation in video surveillance. Comput Vis Image Underst 122:22–34
Bouwmans T, El Baf F, Vachon B (2008) Background modeling using mixture of gaussians for foreground detection-a survey. Recent Pat Comput Sci 1 (3):219–237
Bouwmans T, Porikli F, Höferlin B, Vacavant A (2014), Handbook on “background modeling and foreground detection for video surveillance”
Bouwmans T, Sobral A, Javed S, Jung SK, Zahzah EH (2017) Decomposition into low-rank plus additive matrices for background/foreground separation: a review for a comparative evaluation with a large-scale dataset. Comput Sci Rev 23:1–71
Chakraborty S, Paul M, Murshed M, Ali M (2017) Adaptive weighted non-parametric background model for efficient video coding. Neurocomputing 226:35–45
Chen BH, Huang SC (2014) An advanced moving object detection algorithm for automatic traffic monitoring in real-world limited bandwidth networks. IEEE Trans Multimed 16(3):837–847
Chiranjeevi P, Sengupta S (2012) Spatially correlated background subtraction, based on adaptive background maintenance. J Vis Commun Image Represent 23(6):948–957
Dalal N, Triggs B (2005) Histograms of oriented gradients for human detection. In: 2005 IEEE computer society conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR’05), IEEE vol 1, 886–893
Davis JW, Sharma V (2007) Background-subtraction using contour-based fusion of thermal and visible imagery. Comput Vis Image Underst 106(2–3):162–182
Elgammal A, Harwood D, Davis L (2000) Non-parametric model for background subtraction. In: European conference on computer vision. Springer, pp 751–767
Ershadi NY, Menéndez J M, Jimenez D (2018) Robust vehicle detection in different weather conditions: using mipm. PloS One 13(3) pp:1–30
Feng J, Xu H, Yan S (2013) Online robust pca via stochastic optimization. In: Advances in neural information processing systems, pp 404–412
Goehner K, Desell T, Eckroad R, Mohsenian L, Burr P, Caswell N, Andes A, Ellis-Felege S (2015) A comparison of background subtraction algorithms for detecting avian nesting events in uncontrolled outdoor video. In: 2015 IEEE 11th international conference on e-science. IEEE, pp 187–195
Goyal K, Singhai J (2018) Texture-based self-adaptive moving object detection technique for complex scenes. Comput Electr Eng 70:275–283
Goyette N, Jodoin PM, Porikli F, Konrad J, Ishwar P (2012) Changedetection. net: a new change detection benchmark dataset. In: 2012 IEEE computer society conference on computer vision and pattern recognition workshops. IEEE, pp 1–8
Hadi RA, George LE, Mohammed MJ (2017) A computationally economic novel approach for real-time moving multi-vehicle detection and tracking toward efficient traffic surveillance. Arab J Sci Eng 42(2):817–831
Hadiuzzaman M, Haque N, Rahman F, Hossain S, Siam MRK, Qiu TZ (2017) Pixel-based heterogeneous traffic measurement considering shadow and illumination variation. Signal Image Video Process 11(7):1245–1252
Han G, Wang J, Cai X (2017) Background subtraction based on modified online robust principal component analysis. Int J Mach Learn Cybern 8 (6):1839–1852
Haritaoglu I, Harwood D, Davis LS (2000) W/sup 4: real-time surveillance of people and their activities. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 22 (8):809–830
Heikkila M, Pietikainen M (2006) A texture-based method for modeling the background and detecting moving objects. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 28(4):657–662
Hofmann M, Tiefenbacher P, Rigoll G (2012) Background segmentation with feedback: the pixel-based adaptive segmenter. In: 2012 IEEE computer society conference on computer vision and pattern recognition workshops (CVPRW). IEEE, pp 38–43
Hong W, Kennedy A, Burgos-Artizzu XP, Zelikowsky M, Navonne SG, Perona P, Anderson DJ (2015) Automated measurement of mouse social behaviors using depth sensing, video tracking, and machine learning. Proc Natl Acad Sci 112(38):E5351–E5360
Hou YL, Pang GK (2011) People counting and human detection in a challenging situation. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern-Part A: Syst Hum 41(1):24–33
Huang SC (2011) An advanced motion detection algorithm with video quality analysis for video surveillance systems. IEEE Trans Circ Syst Video Technol 21 (1):1–14
Huang SC, Chen BH (2013) Highly accurate moving object detection in variable bit rate video-based traffic monitoring systems. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 24(12):1920–1931
Javed S, Oh SH, Heo J, Jung SK (2014) Robust background subtraction via online robust pca using image decomposition. In: Proceedings of the 2014 conference on research in adaptive and convergent systems, pp 105–110
John F, Hipiny I, Ujir H (2019) Assessing performance of aerobic routines using background subtraction and intersected image region. In: 2019 International conference on computer and drone applications (IConDA). IEEE, pp 38–41
Karnowski J, Hutchins E, Johnson C (2015) Dolphin detection and tracking. In: 2015 IEEE Winter applications and computer vision workshops. IEEE, pp 51–56
Kim K, Chalidabhongse TH, Harwood D, Davis L (2004) Background modeling and subtraction by codebook construction. In: 2004 International conference on image processing, 2004. ICIP’04, vol 5. IEEE, pp 3061–3064
Lee B, Hedley M (2002) Background estimation for video surveillance. In: 2002 Image &Vision Computing New Zealand (IVCNZ’02), pp 315–320
Li Q, Bernal EA, Shreve M, Loce RP (2016) Scene-independent feature-and classifier-based vehicle headlight and shadow removal in video sequences. In: 2016 IEEE Winter applications of computer vision workshops (WACVW). IEEE, pp 1–8
Liu Y, Shi M, Zhao Q, Wang X (2019) Point in, box out: beyond counting persons in crowds. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 6469–6478
McFarlane NJ, Schofield CP (1995) Segmentation and tracking of piglets in images. Mach Vis Appl 8(3):187–193
Mei L, Guo J, Lu P, Liu Q, Teng F (2017) Inland ship detection based on dynamic group sparsity. In: 2017 ninth international conference on advanced computational intelligence (ICACI). IEEE, pp 1–6
Moudgollya R, Midya A, Sunaniya AK, Chakraborty J (2019) Dynamic background modeling using intensity and orientation distribution of video sequence. Multimed Tools Appl 78(16):22537–22554
Muniruzzaman S, Haque N, Rahman F, Siam M, Musabbir R, Hadiuzzaman M, Hossain S (2016) Deterministic algorithm for traffic detection in free-flow and congestion using video sensor. J Built Environ Technol Eng 1:111–130
Ojala T, Pietikäinen M, Harwood D (1996) A comparative study of texture measures with classification based on featured distributions. Pattern Recognit 29(1):51–59
Ojala T, Pietikainen M, Maenpaa T (2002) Multiresolution gray-scale and rotation invariant texture classification with local binary patterns. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 24(7):971–987
Panda DK, Meher S (2018) Adaptive spatio-temporal background subtraction using improved wronskian change detection scheme in gaussian mixture model framework. IET Image Process 12(10):1832–1843
Panda DK, Meher S (2018) A new wronskian change detection model based codebook background subtraction for visual surveillance applications. J Vis Commun Image Represent 56:52–72
Pang S, Zhao J, Hartill B, Sarrafzadeh A (2016) Modelling land water composition scene for maritime traffic surveillance. Int J Appl Pattern Recognit 3(4):324–350
Perrett T, Mirmehdi M, Dias E (2016) Visual monitoring of driver and passenger control panel interactions. IEEE Trans Intell Transp Syst 18 (2):321–331
Piccardi M (2004) Background subtraction techniques: a review. In: 2004 IEEE international conference on systems, man and cybernetics, vol 4. IEEE, pp 3099–3104
Quesada J, Rodriguez P (2016) Automatic vehicle counting method based on principal component pursuit background modeling. In: 2016 IEEE international conference on image processing (ICIP). IEEE, pp 3822–3826
Roy A, Shinde S, Kang KD et al (2010) An approach for efficient real time moving object detection. In: ESA, pp 157–162
Shen W, Lin Y, Yu L, Xue F, Hong W (2018) Single channel circular sar moving target detection based on logarithm background subtraction algorithm. Remote Sens 10(5):742
Sobral A, Vacavant A (2014) A comprehensive review of background subtraction algorithms evaluated with synthetic and real videos. Comput Vis Image Underst 122:4–21
Sobral A, Bouwmans T, ZahZah EJ (2015) Double-constrained rpca based on saliency maps for foreground detection in automated maritime surveillance. In: 2015 12th IEEE international conference on advanced video and signal based surveillance (AVSS). IEEE, pp 1–6
Stauffer C, Grimson WEL (1999) Adaptive background mixture models for real-time tracking. In: IEEE computer society conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, 1999, vol 2. IEEE, pp 246– 252
Tamás B (2016) Detecting and analyzing rowing motion in videos. In: BME scientific student conference, pp 1–29
Vaswani N, Bouwmans T, Javed S, Narayanamurthy P (2018) Robust subspace learning: robust pca, robust subspace tracking, and robust subspace recovery. IEEE Signal Process Mag 35(4):32–55
Wang H, Suter D (2005) A re-evaluation of mixture of gaussian background modeling [video signal processing applications]. In: IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech, and signal processing, 2005. Proceedings.(ICASSP’05), vol 2. IEEE, pp ii–1017
Wren CR, Azarbayejani A, Darrell T, Pentland AP (1997) Pfinder: real-time tracking of the human body. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 19 (7):780–785
Wu M, Peng X (2010) Spatio-temporal context for codebook-based dynamic background subtraction. AEU-Int J Electr Commun 64(8):739–747
Yang B, Zou L (2015) Robust foreground detection using block-based rpca. Optik 126(23):4586–4590
Yang D, Zhao C, Zhang X, Huang S (2017) Background modeling by stability of adaptive features in complex scenes. IEEE Trans Image Process 27(3):1112–1125
Yousif H, Yuan J, Kays R, He Z (2017) Fast human-animal detection from highly cluttered camera-trap images using joint background modeling and deep learning classification. In: 2017 IEEE international symposium on circuits and systems (ISCAS). IEEE, pp 1–4
Zhang S, Yao H, Liu S (2008) Dynamic background modeling and subtraction using spatio-temporal local binary patterns. In: 15th IEEE international conference on image processing, 2008. ICIP 2008. IEEE, pp 1556–1559
Zhong B, Liu S, Yao H, Zhang B (2009) Multl-resolution background subtraction for dynamic scenes. In: 2009 16th IEEE international conference on image processing (ICIP). IEEE, pp 3193–3196
Zhong Z, Zhang B, Lu G, Zhao Y, Xu Y (2017) An adaptive background modeling method for foreground segmentation. IEEE Trans Intell Transp Syst 18(5):1109–1121
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mohanty, S.K., Rup, S. An adaptive background modeling for foreground detection using spatio-temporal features. Multimed Tools Appl 80, 1311–1341 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-020-09552-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-020-09552-8