Abstract
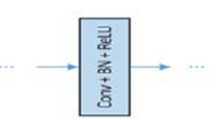
Elimination of combined Gaussian and impulse noises in digital image processing with preservation of image details and suppression of noise are challenging problem. For this purpose, a new filter which is median filters combined with convolutional neural network for Gaussian and salt & pepper noises. The previous methods are application dependents; some used for impulse noise and other employed only for Gaussian noise. The elimination of Gaussian and impulse noise completed into two steps. First the detection of impulse noise with the rejection of noise by employed of 3 × 3 and 5 × 5 window size median filters. In the second step removal of Gaussian noise performed by residual learning denoising convolutional neural network. It is very favorable and the ability of learning and denoising performance in the field of digital image processing. Denoising convolutional neural network also has active Gaussian noise with an unknown level of noise. Experimental work showed that the proposed method can achieve low loss and root mean square error during training, high peak signal to noise ratio, low mean square error, image quality assessment with good quality and mean absolute error for close prediction between denoised and original color images.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aiswarya K, Jayaraj V, Ebenezer D (2010) A new and efficient algorithm for the removal of high-density salt and pepper noise in images and videos. In: IEEE second international conference on computer modeling and simulation, Sanya, Hainan, China, pp 409–413
Chen P, Lien C (2008) An efficient edge-preserving algorithm for removal of salt-and-pepper noise. IEEE Signal Process Lett 15:833–836
Demirkaya O (2004) Smoothing impulsive noise using nonlinear diffusion filtering. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Desolneu A, Delon J (2013) A patch-based approach for removing mixed Gaussian-impulse noise. J Imaging Sci 6:1140–1174
Ioffe S, Szegedy C (2015) Batch normalization: accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift. arXiv:1502.03167v3
Khmou Y (2012) Mathworks, 28 Aug 2012. [Online]. Available: https://www.mathworks.com/matlabcentral/fileexchange/37691-psnr-for-rgb-images?s_tid=srchtitle
Kingma D, Ba J (2014) Adam: a method for stochastic optimization. arXiv preprint arXiv:1412.6980
Kirchner M, Fridrich J (2010) On detection of median filtering in digital images. Proc. SPIE 7541, Media Forensics and Security II, 754110. https://doi.org/10.1117/12.839100
Lehmman EL, George C (1998) Theory of point estimation, 2nd edn. Springer, New York
Lim JS (1990) Two-dimensional signal and image processing. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs
Lin T-C (2007) A new adaptive center weighted median filter for suppressing impulse noise in images. Information Sciences Elsevier 177(4):1073–1087
Luo W (2006) Efficient removal of impulse noise from digital images. IEEE Trans Consum Electron 52(2):523–527
Ng PE, Ma KK (2006) A switching median filter with boundary discriminative noise detection for extremely corrupted images. IEEE Trans Image Process 15(6):1506–1516
Pham TD et al. (2007) Double adaptive filtering of gaussian noise degraded images., in springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Pratt WK (1991) Digital Image Processing. Wiley-Interscience, New York
Srinivasan KS, Ebenezer D (2007) A new fast and efficient decision-based algorithm for removal of high density impulse noises. IEEE Signal Process Lett 14(3):189–192
Toh KKV, Mat Isa NA (2010) Noise adaptive fuzzy switching median filter for salt-and-pepper noise reduction. IEEE Signal Process Lett 17(3):281–284
Toh KKV, Ibrahim H, Mahyuddi MN (2008) Salt-and-pepper noise detection and reduction using fuzzy switching median filter. IEEE T Consum Electr 54(4):1956–1961
Willmott CJ, Matsuura K (2005) Advantage of the mean absolute error (MAE) over the root mean square error (RMSE) in assessing average model performance. Clim Res 30(1):79–82
Zhang S, Karim MA (2002) A new impulse detector for switching median filters. IEEE Signal Process Lett 9(11):360–363
Zhang K, ZuoW CY, Meng D (2017) Beyond a gaussian denoising: residual learning of deep CNN for image denoising. IEEE Trans Image Process 26(7):3142–3155
Zhang K, Zuo W, Zhang L (2018) FFDNet: toward a fast and flexible solution for CNN-based image denoising. IEEE T Image Process 27(9):4608–4622
Zhou W, Bovik AC, Sheikh HR, Simoncelli EP (2014) Image quality assessment: from error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE T Image Process 13(4):600–612
Acknowledgments
This Paper is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, China [Grand number:61671185].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Noor, A., Zhao, Y., Khan, R. et al. Median filters combined with denoising convolutional neural network for Gaussian and impulse noises. Multimed Tools Appl 79, 18553–18568 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-020-08657-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-020-08657-4