Abstract
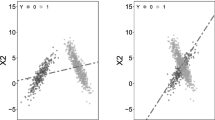
The conventional classification models implicitly assume that the distributions of data employed for training and test are identical. However, the assumption is rarely valid in many practical applications. In order to alleviate the difference between the distributions of the training and test sets, in this paper, we propose a regularized subspace learning framework based on the low-rank representation technique for unsupervised domain adaptation. Specifically, we introduce a regularization term of the subspace projection matrix to deal with the ill-conditioned problem and obtain a unique numerical solution. Meanwhile, we impose a structured sparsity-inducing regularizer on the error term so that the proposed method can filter out the outlier information, and therefore improve the performance. The extensive comparison experiments on benchmark data sets demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bruzzone L, Marconcini M (2010) Domain adaptation problems: A DASVM classification technique and a circular validation strategy. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 32(5):770–787
Cai D, He X, Han J (2007) Spectral regression for efficient regularized subspace learning. In: Proc IEEE ICCV, pp 1–8
Cai J, Candès EJ, Shen Z (2010) A singular value thresholding algorithm for matrix completion. SIAM J Optimization 20(4):1956–1982
Chen Y, Song S, Li S, Yang L, Wu C (2018) Domain space transfer extreme learning machine for domain adaptation. IEEE Trans Cybern 49(5):1909–1922
Ding Z, Nasrabadi NM, Fu Y (2018) Semi-supervised deep domain adaptation via coupled neural networks. IEEE Trans Images Process 27(11):5214–5224
Donahue J, Hoffma J, Rodner E, Saenko K, Darrell T (2013) Semi-supervised domain adaptation with instance constraints. In: Proc IEEE CVPR, pp 668–675
Donahue J, Jia Y, Vinyals O, Hoffman J, Zhang N, Tzeng E, Darrell T (2014) DeCAF: A deep convolutional activation feature for generic visual recognition. In: Proc ACM ICML, pp 647–655
Duan L, Xu D, Tsang I, Luo J (2010) Visual event recognition in videos by learning from web data. In: Proc IEEE CVPR, pp 1959–1966
Duan L, Tsang IW, Xu D (2012) Domain transfer multiple kernel learning. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 34:465–479
Duan L, Xu D, Tsang IW (2012) Domain adaptation from multiple sources: a domain-dependent regularization approach. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 23 (3):504–518
Fernando B, Habrard A, Sebban M, Tuylelaars T (2013) Unsupervised visual domain adaptation using subspace alignment. In: Proc ICCV, pp 2960–2967
Finn C, Abbeel P, Levine S (2017) Model-agnostic meta-learning for fast adaptation of deep networks. In: Proc ACM ICML, pp 1126–1135
Genc A, Ekenel HK (2019) Cross-dataset person re-identification using deep convolutional neural networks: effects of context and domain adaptation. Multimed Tools Appl 78(5):5843–5861
Ghifary M, Balduzzi D, Kleijn WB, Zhang M (2017) Scatter component analysis: A unified framework for domain adaptation and domain generalization. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 39(7):1414– 1430
Gong B, Shi Y, Sha F, Grauman K (2012) Geodesic flow kernel for unsupervised domain adaptation. In: Proc IEEE CVPR, pp 2066–2073
Gong B, Grauman K, Sha F (2013) Connecting the dots with landmarks: discriminatively learning domain-invariant features for unsupervised domain adaptation. In: Proc ACM ICML, pp 153–159
Gopalan R, Li R, Chellappa R (2011) Domain adaptation for object recognition: An unsupervised approach. In: Proc IEEE ICCV, pp 999–1006
Gretton A, Borgwardt KM, Rasch MJ, Schölkopf B, Smola A (2012) A kernel two-sample test. J Mach Learn Res 13:723–773
Hoffman J, Tzeng E, Park T, Zhu JY, Isola P, Saenko K, Efros A, Darrell T (2018) CyCADA: Cycle-consistent adversarial domain adaptation. In: Proc ACM ICML, pp 1989–1998
Hu J, Lu J, Tan Y, Zhou J (2016) Deep transfer metric learning. IEEE Trans Image Process 25(12):5576–5588
Huang Z, Xue W, Mao Q, Zhan Y (2017) Unsupervised domain adaptation for speech emotion recognition using PCAnet. Multimed Tools Appl 76(5):6785–6799
Jhuo I-H, Liu D, Lee DT, Chang S-F (2012) Robust visual domain adaptation with low-rank reconstruction. In: Proc IEEE CVPR, pp 2168–2175
Kan M, Wu J, Shan S, Chen X (2014) Domain adaptation for face recognition: Targetize source domain bridged by common subspace. Int J Comput Vis 109(1):94–109
Krizhevsky A, Sutskever I, Hinton GE (2012) Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In: Proc NIPS, pp 1097–1105
Li J, Zhao J, Lu K (2016) Joint feature selection and structure preservation for domain adaptation. In: Proc IJCAI, pp 1697–1703
Li J, Wu Y, Lu K (2017) Structured domain adaptation. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 27(8):1700–1713
Li S, Song S, Huang G, Ding Z, Wu C (2018) Domain invariant and class discriminative feature learning for visual domain adaptation. IEEE Trans Image Process 27(9):4260–4273
Liu G, Lin Z, Yan S, Sun J, Yu Y, Ma Y (2013) Robust recovery of subspace structures by low-rank representation. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 35(1):171–184
Liu L, Yang L, Zhu B (2018) Sparse feature space representation: A unified framework for semi-supervised and domain adaptation learning. Knowledge-Based Syst 156:43–61
Long M, Wang J, Ding G, Sun J, Yu PS (2013) Transfer feature learning with joint distribution adaptation. In: Proc IEEE ICCV, pp 2200–2207
Long M, Wang J, Ding G, Sun J, Yu PS (2014) Transfer joint matching for unsupervised domain adaptation. In: Proc IEEE CVPR, pp 1410–1417
Long M, Cao Y, Wang J, Jordan M (2015) Learning transferable features with deep adaptation networks. In: Proc ACM ICML, pp 97–105
Mozafari AS, Jamzad M (2016) A SVM-based model-transferring method for heterogeneous domain adaptation. Pattern Recognit 56:142–158
Nuricumbo JR, Ali H, Márton Z-C, Grzegorzek M (2016) Improving object classification robustness in RGB-D using adaptive SVMs. Multimed Tools Appl 75(12):6829–6847
Pan SJ, Tsang IW, Kwol JT, Yang Q (2011) Domain adaptation via transfer component analysis. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 22(2):199–210
Pereira LAM, Torres RDS (2018) Semi-supervised transfer subspace for domain adaptation. Pattern Recognit 75:235–249
Razzaghi P, Razzaghi P, Abbasi K (2019) Transfer subspace learning via low-rank and discriminative reconstruction matrix. Knowledge-Based Syst 163:174–185
Saenko K, Kulis B, Fritz M, Darrell T (2010) Adapting visual category models to new domains. In: Proc ECCV, pp 213–226
Shao M, Kit D, Fu Y (2014) Generalized transfer subspace learning through low-rank constraint. Int J Comput Vis 109(1):74–93
Si S, Tao D, Geng B (2010) Bregman divergence-based regularization for transfer subspace learning. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 22(7):929–942
Tzeng E, Hoffman J, Zhang N, Saenko K, Darrell T (2014) Deep domain confusion: Maximizing for domain invariance, Technical report. arXiv:1412.3474
Tzeng E, Hoffman J, Saenko K, Darrell T (2017) Adversarial discriminative domain adaptation. In: Proc IEEE CVPR, pp 7167–7176
Uzair M, Mian A (2017) Blind domain adaptation with augmented extreme learning machine features. IEEE Trans Cybern 47(3):651–660
Wang X, Ren J, Liu S (2018) Distribution adaptation and manifold alignment for complex processes fault diagnosis. Knowledge-Based Syst 156:100–112
Xu Y, Fang X, Wu J, Li X, Zhang D (2016) Discriminative transfer subspace learning via low-rank and sparse representation. IEEE Trans Images Process 25(2):850–863
Yan K, Kou L, Zhang D (2017) Learning domain-invariant subspace using domain features and independence maximization. IEEE Trans Cybern 48(1):288–299
Yang J, Yin W, Zhang Y, Wang Y (2009) A fast algorithm for edge-preserving variational multichannel image restoration. SIAM J Imaging Sci 2(2):569–592
Zhang L, Wang P, Wei W, Lu H, Shen C, Hengel AVD, Zhang Y (2018) Unsupervised domain adaptation using robust class-wise matching. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 29(5):1339–1349
Acknowledgments
The work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 61872368). The authors also gratefully acknowledge the helpful comments and suggestions of the reviewers, which have improved the presentation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, L., Men, M., Xue, Y. et al. Low-rank representation-based regularized subspace learning method for unsupervised domain adaptation. Multimed Tools Appl 79, 3031–3047 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-019-08474-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-019-08474-4