Abstract
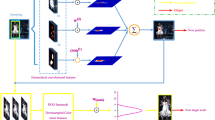
Robust and accurate visual tracking is a challenging problem in computer vision. In this paper, we exploit spatial and semantic convolutional features extracted from convolutional neural networks in continuous object tracking. The spatial features retain higher resolution for precise localization and semantic features capture more semantic information and less fine-grained spatial details. Therefore, we localize the target by fusing these different features, which improves the tracking accuracy. Besides, we construct the multi-scale pyramid correlation filter of the target and extract its spatial features. This filter determines the scale level effectively and tackles target scale estimation. Finally, we further present a novel model updating strategy, and exploit peak sidelobe ratio (PSR) and skewness to measure the comprehensive fluctuation of response map for efficient tracking performance. Each contribution above is validated on 50 image sequences of tracking benchmark OTB-2013. The experimental comparison shows that our algorithm performs favorably against 12 state-of-the-art trackers.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Babenko B, Yang MH, Belongie S (2011) Robust object tracking with online multiple instance learning. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 33(8):1619–1632
Bertinetto L, Valmadre J, Henriques JF, et al. (2016) Fully-convolutional siamese networks for object tracking. in Proc. Eur. Conf. Comput. Vis., Amsterdam. 850–865
Bertinetto L, Valmadre J, Golodetz S, et al. (2016) Staple: Complementary learners for real-time tracking. in Proc. Eur. Conf. Comput. Vis., Las Vegas. 1401–1409
Bolme DS, Beveridge JR, Draper BA, et al. (2010) Visual object tracking using adaptive correlation filters. in Proc. IEEE Conf. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit., San Francisco. 2544–2550
Danelljan M, Khan FS, Felsberg M, et al (2014) Adaptive Color Attributes for Real-Time Visual Tracking. in Proc. IEEE Conf. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit. Columbus. 1090–1097
Danelljan M, Häger G, Khan F, et al. (2014) Accurate scale estimation for robust visual tracking. In Proc. Br. Mach. Vis. Conf. 1–5
Danelljan M, Hager G, Shahbaz Khan F, et al. (2015) Convolutional features for correlation filter based visual tracking. in Proc IEEE Int Conf Comput Vis., Santiago, Chile. 58–66
Danelljan M, Hager G, Shahbaz Khan F, et al. (2015) Learning spatially regularized correlation filters for visual tracking. in Proc IEEE Int Conf Comput Vis., Santiago. 4310–4318
Hare S, Saffari A, Torr PHS (2016) Struck: structured output tracking with kernels. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 38(10):2096–2109
He K, Zhang X, Ren S, et al. (2016) Deep residual learning for image recognition. in Proc. IEEE Conf. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit., Las Vegas. 770–778
Held D, Thrun S, Savarese S (2016) Learning to track at 100 fps with deep regression networks. in Proc. Eur. Conf. Comput. Vis., Amsterdam. 749–765
Henriques JF, Caseiro R, Martins P, et al. (2012) Exploiting the circulant structure of tracking-by-detection with kernels. in Proc. Eur. Conf. Comput. Vis., Florence. 702–715
Henriques JF, Caseiro R, Martins P et al (2015) High-speed tracking with kernelized correlation filters. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 37(3):583–596
Hong S, You T, Kwak S, et al. (2015) Online tracking by learning discriminative saliency map with convolutional neural network. Int. Conf. Mach. Learn., Lile. 597–606
Kalal Z, Mikolajczyk K, Matas J. Tracking-learning-detection. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell, vol. 34, no. 7, pp. 1409–1422, July. 2012
Krizhevsky A, Sutskever I, Hinton GE (2017) Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Commun ACM 60(6):84–90
Li Y, Zhu J (2014) A Scale Adaptive Kernel Correlation Filter Tracker with Feature Integration. in Proc. Eur. Conf. Comput. Vis., Zurich. 254–265
Li P, Wang D, Wang L et al (2018) Deep visual tracking: review and experimental comparison [J]. Pattern Recogn 76:323–338
Lv Y (2018) Alcoholism detection by data augmentation and convolutional neural network with stochastic pooling. J Med Syst 42(1):2
Ma C, Huang JB, Yang X, et al. (2015) Hierarchical convolutional features for visual tracking. in Proc IEEE Int Conf Comput Vis., Santiago. 3074–3082
Ma C, Yang X, Zhang C, et al. (2015) Long-term correlation tracking. in Proc. Eur. Conf. Comput. Vis., Boston. 5388–5396
Nam H, Han B (2016) Learning multi-domain convolutional neural networks for visual tracking. in Proc. IEEE Conf. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit., Las Vegas. 4293–4302
Ning J, Yang J, Jiang S, et al. (2016) Object tracking via dual linear structured SVM and explicit feature map. in Proc. IEEE Conf. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit. 4266–4274
Pan C (2018) Abnormal breast identification by nine-layer convolutional neural network with parametric rectified linear unit and rank-based stochastic pooling. J Comput Sci 27:57–68
Qi Y, Zhang S, Qin L, et al. (2016) Hedged deep tracking. in Proc. IEEE Conf. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit., Las Vegas, 4303–4311
K Simonyan, A Zisserman (2014) Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. [Online]. Available: https://arxiv.org/abs/1409.1556
Song Y, Ma C, Gong L, et al. (2017) Crest: Convolutional residual learning for visual tracking. in Proc IEEE Int Conf Comput Vis., Venice. 2574–2583
Sun J (2017) Polarimetric synthetic aperture radar image segmentation by convolutional neural network using graphical processing units. J Real-Time Image Proc. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11554-017-0717-0
Sun C, Wang D, Lu H, et al. (2018) Correlation Tracking via Joint Discrimination and Reliability Learning [C]. Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 489–497
Tu Y, Lin Y, Wang J et al (2018) Semi-supervised learning with generative adversarial networks on digital signal modulation classification [J]. Comput Material Continua 55(2):243–254
Valmadre J, Bertinetto L, Henriques J, et al. (2017) End-to-End Representation Learning for Correlation Filter Based Tracking. in Proc. IEEE Conf. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit., Honolulu. 5000–5008
Wang N, Yeung DY (2013) Learning a deep compact image representation for visual tracking. Adv. neural inf. proces. syst., Lake Tahoe. 809–817
Wang L, Ouyang W, Wang X, et al. (2015) Visual Tracking with fully convolutional networks. in Proc IEEE Int Conf Comput Vis., Santiago. 3119–3127
Wang M, Liu Y, Huang Z (2017) Large margin object tracking with circulant feature maps. in Proc. IEEE Conf. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit., Honolulu. 4800–4808
Wang SH, Sun J, Phillips P et al Polarimetric synthetic aperture radar image segmentation by convolutional neural network using graphical processing units [J]. J Real-Time Image Proc 2017(4):1–12
Wu Y, Lim J, Yang M-H (2015) Object tracking benchmark. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 37(9):1834–1848
Wu Y, Jia N, Sun J (2015) Real-time multi-scale tracking based on compressive sensing. Vis Comput 31(4):471–484
Yan C, Xie H, Liu S et al (2018) Effective Uyghur language text detection in complex background images for traffic prompt identification [J]. IEEE Trans Intell Transp Syst 19(1):220–229
Yan C, Xie H, Chen J et al (2018) An effective Uyghur text detector for complex background images [J]. IEEE Trans Multimed. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMM.2018.2838320
Zhang K, Zhang L, Yang MH (2012) Real-time compressive tracking. in Proc. Eur. Conf. Comput. Vis., Florence, Italy. 864–877
Zhang J, Ma S, Sclaroff S (2014) MEEM: robust tracking via multiple experts using entropy minimization. in Proc. Eur. Conf. Comput. Vis., Zurich, Switzerland. 188–203
Zhang K, Zhang L, Yang MH, et al. (2014) Fast tracking via spatio-temporal context learning. in Proc. Eur. Conf. Comput. Vis., Zurich. 127–141
Zhang YD, Zhang Y, Hou XX et al (2018) Seven-layer deep neural network based on sparse autoencoder for voxelwise detection of cerebral microbleed. Multimed Tools Appl 77(9):10521–10538
Zhang YD, Muhammad K, Tang C (2018) Twelve-layer deep convolutional neural network with stochastic pooling for tea category classification on GPU platform. Multimed Tools Appl. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-018-5765-3
Zhang S, Wang H, Huang W et al (2018) Plant diseased leaf segmentation and recognition by fusion of superpixel, K-means and PHOG [J]. Optik-Int J Light Electron Optics 157:866–872
Zhang S, Wang H, Huang W et al (2018) Combining modified LBP and weighted SRC for palmprint recognition [J]. SIViP. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-018-1246-4
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This work was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant 61402053, Grant 61772454, Grant 61811530332 in part by the Scientific Research Fund of Hunan Provincial Education Department under Grant 16A008,in part by the Scientific Research Fund of Hunan Provincial Transportation Department under Grant 201446, in part by the Industry-University Cooperation and Collaborative Education Project of Department of Higher Education of Ministry of Education under Grant 201702137008, in part by the Undergraduate Inquiry Learning and Innovative Experimental Fund of CSUST under Grant 2018-6-119, and in part by the Postgraduate Course Construction Fund of CSUST under Grant KC201611.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, J., Jin, X., Sun, J. et al. Spatial and semantic convolutional features for robust visual object tracking. Multimed Tools Appl 79, 15095–15115 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-018-6562-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-018-6562-8