Abstract
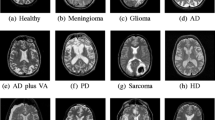
Pathological brain detection by computer vision is now attracting intense attentions from academic fields. Nevertheless, most of recent methods suffer from low-accuracy. This study combined two successful techniques: pseudo Zernike moment and kernel support vector machine. Three open datasets were downloaded and used. The 10 times of K-fold stratified cross validation showed our method using 19-order pseudo Zernike moments achieved perfect classification on the first dataset. It achieved a sensitivity of 99.93 ± 0.23%, a specificity of 98.50 ± 2.42%, and an accuracy of 99.75 ± 0.32% on the second dataset. It achieved a sensitivity of 99.64 ± 0.42%, a specificity of 98.29 ± 2.76%, and an accuracy of 99.45 ± 0.38% on the third dataset. This approach performs better than eleven state-of-the-art smart pathological brain detection methods.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdillah AA, Suwarno (2016) Diagnosis of diabetes using support vector machines with radial basis function kernels. Int J Technol 7(5):849–858. doi:10.14716/ijtech.v7i5.1370
Atangana A (2016) Application of stationary wavelet entropy in pathological brain detection. Multimedia Tools and Applications. doi:10.1007/s11042-016-3401-7
Chen X-Q (2016) Fractal dimension estimation for developing pathological brain detection system based on Minkowski-Bouligand method. IEEE Access 4:5937–5947. doi:10.1109/ACCESS.2016.2611530
Chen H (2017) Seven-layer deep neural network based on sparse autoencoder for voxelwise detection of cerebral microbleed. Multimedia Tools and Applications. doi:10.1007/s11042-017-4554-8
Chen S, Yang J-F, Phillips P (2015) Magnetic resonance brain image classification based on weighted-type fractional Fourier transform and nonparallel support vector machine. Int J Imaging Syst Technol 25(4):317–327. doi:10.1002/ima.22144
Chen Y, Zhang Y, Lu H (2016) Wavelet energy entropy and linear regression classifier for detecting abnormal breasts. Multimedia Tools and Applications. doi:10.1007/s11042-016-4161-0
Das S, Chowdhury M, Kundu MK (2013) Brain MR image classification using multiscale geometric analysis of Ripplet. Progress in Electromagnetics Research-Pier 137:1–17. doi:10.2528/pier13010105
Deng AW, Wei CH, Gwo CY (2016) Stable, fast computation of high-order Zernike moments using a recursive method. Pattern Recogn 56:16–25. doi:10.1016/j.patcog.2016.02.014
Dong Z (2014) Classification of Alzheimer disease based on structural magnetic resonance imaging by kernel support vector machine decision tree. Prog Electromagn Res 144:171–184. doi:10.2528/PIER13121310
Douglass S, Hsu SW, Cokus S, Goldberg RB, Harada JJ, Pellegrini M (2016) A naive Bayesian classifier for identifying plant microRNAs. Plant J 86(6):481–492. doi:10.1111/tpj.13180
Feng C (2015) Feed-forward neural network optimized by hybridization of PSO and ABC for abnormal brain detection. Int J Imaging Syst Technol 25(2):153–164. doi:10.1002/ima.22132
Gajovic S, Pochet R (2014) Brain extracellular matrix meets COST-Matrix for European research networks. In: Dityatev A, WehrleHaller B, Pitkanen A (eds) Brain Extracellular Matrix In Health And Disease, vol 214. Progress in Brain Research. Elsevier Science Bv, Amsterdam, pp XIX-XXIII
Ghasemi F, Fassihi A, Perez-Sanchez H, Dehnavi AM (2017) The role of different sampling methods in improving biological activity prediction using deep belief network. J Comput Chem 38(4):195–203. doi:10.1002/jcc.24671
Gorji HT, Haddadnia J (2015) A novel method for early diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease based on pseudo Zernike moment from structural MRI. Neuroscience 305:361–371. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2015.08.013
Gorriz JM, Ramírez J (2016) Wavelet entropy and directed acyclic graph support vector machine for detection of patients with unilateral hearing loss in MRI scanning. Front Comput Neurosci 10. doi:10.3389/fncom.2016.00106
Huo Y, Plassard AJ, Carass A, Resnick SM, Pham DL, Prince JL, Landman BA (2016) Consistent cortical reconstruction and multi-atlas brain segmentation. NeuroImage 138:197–210. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2016.05.030
Huo YK, Asman AJ, Plassard AJ, Landman BA (2017) Simultaneous total intracranial volume and posterior fossa volume estimation using multi-atlas label fusion. Hum Brain Mapp 38(2):599–616. doi:10.1002/hbm.23432
Ji G (2014) Fruit classification using computer vision and feedforward neural network. J Food Eng 143:167–177. doi:10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2014.07.001
Johnson KA, Becker JA (2016) The whole brain atlas. http://www.med.harvard.edu/AANLIB/home.html
Kahyaei S, Moin MS (2016) Robust Matching of Fingerprints Using Pseudo-Zernike Moments. In: 4th International Conference on Control, Instrumentation, And Automation (ICCIA), Qazvin, IRAN. IEEE, pp 116–120
Liu A (2015) Magnetic resonance brain image classification via stationary wavelet transform and generalized eigenvalue proximal support vector machine. J Med Imaging Health Inform 5(7):1395–1403. doi:10.1166/jmihi.2015.1542
Liu G, Phillips P, Yuan T-F (2016) Detection of Alzheimer's disease by three-dimensional displacement field estimation in structural magnetic resonance imaging. J Alzheimers Dis 50(1):233–248
Lu HM (2016) Facial emotion recognition based on biorthogonal wavelet entropy, fuzzy support vector machine, and stratified cross validation. IEEE Access 4:8375–8385. doi:10.1109/ACCESS.2016.2628407
Marathe AS, Vyas V, Chavhan M (2016) Petrographic image classification using Optimized Radial Basis Function Support Vector Machine & Validation of its asymptotic behavior. In: International Conference on Signal Processing, Communications And Computing (ICSPCC), Hong Kong, P R China. IEEE, pp 6–11
Nayak DR (2017) Detection of unilateral hearing loss by stationary wavelet entropy. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets 16(1). doi:10.2174/1871527315666161026115046
Nayak R, Patra D (2016) Super resolution image reconstruction using weighted combined pseudo-Zernike moment invariants. AEU-Int J Electron Commun 70(11):1496–1505. doi:10.1016/j.aeue.2016.09.001
Nayak DR, Dash R, Majhi B (2016) Brain MR image classification using two-dimensional discrete wavelet transform and AdaBoost with random forests. Neurocomputing 177:188–197. doi:10.1016/j.neucom.2015.11.034
Pham BT, Bui DT, Prakash I, Dholakia MB (2017) Hybrid integration of multilayer perceptron neural networks and machine learning ensembles for landslide susceptibility assessment at Himalayan area (India) using GIS. Catena 149:52–63. doi:10.1016/j.catena.2016.09.007
Phillips P (2016) Three-dimensional Eigenbrain for the detection of subjects and brain regions related with Alzheimer's disease. J Alzheimers Dis 50(4):1163–1179. doi:10.3233/jad-150988
Phillips P, Dong Z, Yang J (2015) Pathological brain detection in magnetic resonance imaging scanning by wavelet entropy and hybridization of biogeography-based optimization and particle swarm optimization. Prog Electromagn Res 152:41–58. doi:10.2528/PIER15040602
Scott J, Geoffroy PA, Sportiche S, Brichant-Petit-Jean C, Gard S, Kahn JP, Azorin JM, Henry C, Etain B, Bellivier F (2017) Cross-validation of clinical characteristics and treatment patterns associated with phenotypes for lithium response defined by the Alda scale. J Affect Disord 208:62–67. doi:10.1016/j.jad.2016.08.069
Singh SP, Urooj S (2016) An improved CAD system for breast cancer diagnosis based on generalized pseudo-Zernike moment and Ada-DEWNN classifier. J Med Syst 40(4). doi:10.1007/s10916-016-0454-0
Singh C, Aggarwal A, Ranade SK (2017) A new convolution model for the fast computation of Zernike moments. AEU-Int J Electron Commun 72:104–113. doi:10.1016/j.aeue.2016.11.014
Soman K, Sathiya A, Suganthi N (2014) Classification of Stress of Automobile Drivers using Radial Basis Function Kernel Support Vector Machine. In: International Conference on Information Communication And Embedded Systems (ICICES), Chennai, India. IEEE, pp 5–10
Sun P (2015) Pathological brain detection based on wavelet entropy and Hu moment invariants. Biomed Mater Eng 26(s1):1283–1290. doi:10.2528/PIER13121310
Sun Y (2016) A multilayer perceptron based smart pathological brain detection system by fractional Fourier entropy. J Med Syst 40(7). doi:10.1007/s10916-016-0525-2
Wang S-H (2016) Single slice based detection for Alzheimer’s disease via wavelet entropy and multilayer perceptron trained by biogeography-based optimization. Multimedia Tools and Applications. doi:10.1007/s11042-016-4222-4
Wang H, Lv Y (2016) Smart pathological brain detection system by predator-prey particle swarm optimization and single-hidden layer neural-network. Multimedia Tools and Applications. doi:10.1007/s11042-016-4242-0
Wang S, Lu S, Dong Z, Yang J, Yang M, Zhang Y (2016) Dual-Tree Complex Wavelet Transform and Twin Support Vector Machine for Pathological Brain Detection. Appl. Sci. 2016, 6(6):169. doi:10.3390/app6060169"10.3390/app6060169
Wang S, Chen M, Li Y, Shao Y, Zhang Y, Du S, Wu J (2016) Morphological analysis of dendrites and spines by hybridization of ridge detection with twin support vector machine. PeerJ 4:e2207. doi:10.7717/peerj.2207. eCollection 2016
Wei L (2015) Fruit classification by wavelet-entropy and feedforward neural network trained by fitness-scaled chaotic ABC and biogeography-based optimization. Entropy 17(8):5711–5728. doi:10.3390/e17085711
Wu L (2011) A hybrid method for MRI brain image classification. Expert Syst Appl 38(8):10049–10053
Wu L (2012) An MR brain images classifier via principal component analysis and kernel support vector machine. Prog Electromagn Res 130:369–388
Wu X (2016) Smart detection on abnormal breasts in digital mammography based on contrast-limited adaptive histogram equalization and chaotic adaptive real-coded biogeography-based optimization. SIMULATION 92(9):873–885. doi:10.1177/0037549716667834
Wu J (2016) Fruit classification by biogeography-based optimization and feedforward neural network. Expert Syst 33(3):239–253. doi:10.1111/exsy.12146
Yang J (2015) Preclinical diagnosis of magnetic resonance (MR) brain images via discrete wavelet packet transform with Tsallis entropy and generalized eigenvalue proximal support vector machine (GEPSVM). Entropy 17(4):1795–1813. doi:10.3390/e17041795
Yang J (2015) Identification of green, oolong and black teas in China via wavelet packet entropy and fuzzy support vector machine. Entropy 17(10):6663–6682. doi:10.3390/e17106663
Yang J (2017) Pathological brain detection in MRI scanning via Hu moment invariants and machine learning. Journal of Experimental & Theoretical Artificial Intelligence 29(2):299–312. doi:10.1080/0952813X.2015.1132274
Yang JF, Sun P (2016) Magnetic resonance brain classification by a novel binary particle swarm optimization with mutation and time-varying acceleration coefficients. Biomed Eng-Biomed Tech 61(4):431–441. doi:10.1515/bmt-2015-0152
Yang X, Sun P, Dong Z, Liu A, Yuan T-F (2015) Pathological brain detection by a novel image feature—fractional Fourier entropy. Entropy 17(12):8278–8296. doi:10.3390/e17127877
Zhan TM, Chen Y (2016) Multiple sclerosis detection based on biorthogonal wavelet transform, RBF kernel principal component analysis, and logistic regression. IEEE Access 4:7567–7576. doi:10.1109/ACCESS.2016.2620996
Zhang Y (2014) Binary PSO with mutation operator for feature selection using decision tree applied to spam detection. Knowledge-Based Syst 64:22–31
Zhang YD, Wang SH, Yang XJ, Dong ZC, Liu G, Phillips P, Yuan TF (2015) Pathological brain detection in MRI scanning by wavelet packet Tsallis entropy and fuzzy support vector machine. SpringerPlus 4:716. doi:10.1186/s40064-015-1523-4. eCollection 2015.
Zhou X-X (2016) Comparison of machine learning methods for stationary wavelet entropy-based multiple sclerosis detection: decision tree, k-nearest neighbors, and support vector machine. SIMULATION 92(9):861–871. doi:10.1177/0037549716666962
Zhou XX, Zhang GS (2016) Detection of abnormal MR brains based on wavelet entropy and feature selection. IEEJ Trans Electr Electron Eng 11(3):364–373. doi:10.1002/tee.22226
Zhou X-X, Yang J-F, Sheng H, Wei L, Yan J, Sun P (2016) Combination of stationary wavelet transform and kernel support vector machines for pathological brain detection. SIMULATION 92(9):827–837. doi:10.1177/0037549716629227
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (61602250), Open fund for Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Advanced Manufacturing Technology (HGAMTL1601), Open fund of Key Laboratory of Guangxi High Schools Complex System and Computational Intelligence (2016CSCI01), Leading Initiative for Excellent Young Researcher (LEADER) of Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology-Japan (16809746), Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (BK20150983), Open fund of Key Laboratory of Guangxi High Schools Complex System and Computational Intelligence (2016CSCI01), Opening Project of State Key Laboratory of Digital Publishing Technology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, YD., Jiang, Y., Zhu, W. et al. Exploring a smart pathological brain detection method on pseudo Zernike moment. Multimed Tools Appl 77, 22589–22604 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-017-4703-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-017-4703-0