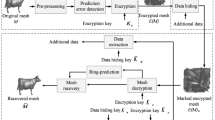
Abstract
This study proposes a reversible data hiding (RDH) algorithm for 3D mesh models based on the optimal three-dimensional prediction-error histogram (PEH) modification with recursive construction coding (RCC). Firstly, we design a double-layered prediction scheme to divide all the vertices of 3D mesh model into the “embedded” set and the “referenced” set, according to the odd-even property of indices into the vertex list. Thanks to the geometrical similarity among neighboring vertices, we obtain the prediction errors (PEs) with a sharp histogram. Then we combine every three adjacent PEs into one prediction-error triplet (PET) and construct the three-dimensional PEH with smaller entropy than one-dimensional PEH by utilizing the correlation among PEs. Next we project the three-dimensional PEH into one-dimensional space for scalar PET sequence which is suitable for using RCC. And also, we define the distortion metrics for 3D mesh models, by which we can estimate the optimal probability transition matrix (OTPM) indicating the optimal PEH modification manner. After that, we modify the PET sequence and embed data by RCC according to OTPM. The experimental results show that our method is superior to two state-of-the-art spatial-domain RDH algorithms for 3D mesh models a lot.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Coltuc D (2012) Low distortion transform for reversible watermarking. IEEE Trans Image Process 21(1):412–417
Chou D, Jhou CY, Chu SC (2009) Reversible watermark for 3D vertices based on data hiding in mesh formation. Int J Innov Comput Inf Control 5(7):1893–1901
Fridrich J, Goljan M, Du R (2002) Lossless data embedding for all image formats. In: International Society for Optics and Photonics, pp 572-583
Hu Y, Lee HK, Li J (2009) DE-based reversible data hiding with improved overflow location map. IEEE Trans Circ Syst Vid Technol 19(2):250–260
Hu X, Zhang W, Hu X et al (2013) Fast estimation of optimal marked-signal distribution for reversible data hiding. IEEE Trans Inf Forensic Secur 8(5):779–788
Huang YH, Tsai YY (2015) A reversible data hiding scheme for 3D polygonal models based on histogram shifting with high embedding capacity. 3D Res 6(2):1–12
Kalker T, Willems FMJ (2003) Capacity bounds and constructions for reversible data-hiding. In: International Society for Optics and Photonics, Electronic Imaging, pp 604–611
Luo L, Chen Z, Chen M (2010) Reversible image watermarking using interpolation technique. IEEE Trans Inf Forensic Secur 5(1):187–193
Li X, Yang B, Zeng T (2011) Efficient reversible watermarking based on adaptive prediction-error expansion and pixel selection. IEEE Trans Image Process 20(12):3524–3533
Lin SJ, Chung WH (2012) The scalar scheme for reversible information-embedding in gray-scale signals: Capacity evaluation and code constructions. IEEE Trans Inf Forensic Secur 7(4):1155–1167
Lu ZM, Li Z (2007) High capacity reversible data hiding for 3D meshes in the PVQ domain. In: Digital Watermarking, Springer Berlin Heidelberg, pp 233–243
Luo H, Lu ZM, Pan JS (2006) A reversible data hiding scheme for 3D point cloud model. In: IEEE International Symposium on Signal Processing and Information Technology, pp 863–867
Luo H, Pan JS, Lu ZM (2006) Reversible data hiding for 3D point cloud model. In: IEEE International Conference on Intelligent Information Hiding and Multimedia Signal Processing(IIH-MSP), pp 487–490
Ni Z, Shi YQ, Ansari N (2006) Reversible data hiding. IEEE Trans Circ Syst Video Technol 16(3):354–362
Ou B, Li X, Zhao Y (2013) Pairwise prediction-error expansion for efficient reversible data hiding. IEEE Trans Image Process 22(12):5010–5021
Sachnev V, Kim HJ, Nam J (2009) Reversible watermarking algorithm using sorting and prediction. IEEE Trans Circ Syst Video Technol 19(7):989–999
Sun Z, Lu ZM, Li Z (2006) Reversible data hiding for 3D meshes in the PVQ-compressed domain. In: IEEE International Conference on Intelligent Information Hiding and Multimedia Signal Processing(IIH-MSP), pp 593–596
Tian J (2003) Reversible data embedding using a difference expansion. IEEE Trans Circ Syst Vid Technol 13(8):890–896
Thodi DM, Rodrguez JJ (2007) Expansion embedding techniques for reversible watermarking. IEEE Trans Image Process 16(3):721–730
Tsai P, Hu YC, Yeh HL (2009) Reversible image hiding scheme using predictive coding and histogram shifting. Signal Process 89(6):1129–1143
Wu H, Dugelay JL (2008) Reversible watermarking of 3D mesh models by prediction-error expansion. In: IEEE 10th Workshop on Multimedia Signal Processing, pp 797–802
Wu H, Cheung Y (2005) A reversible data hiding approach to mesh authenticationWeb Intelligence. In: The 2005 IEEE/WIC/ACM International Conference on Proceedings, pp 774–777
Zhang W, Chen B, Yu N (2012) Improving various reversible data hiding schemes via optimal codes for binary covers. IEEE Trans Image Process 21(6):2991–3003
Zhang W, Hu X, Li X et al (2013) Recursive histogram modification: establishing equivalency between reversible data hiding and lossless data compression. IEEE Trans Image Process 22(7):2775–2785
Zhang W, Hu X, Li X, et al (2015) Optimal transition probability of reversible data hiding for general distortion metrics and its applications. IEEE Trans Image Process 24(1):294–304
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by the Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant U1636201, 61572452, 61502007, and in part by the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation under Grant 2015M582015.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, R., Zhang, W., Hou, D. et al. Reversible data hiding for 3D mesh models with three-dimensional prediction-error histogram modification. Multimed Tools Appl 77, 5263–5280 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-017-4430-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-017-4430-6