Abstract
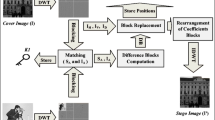
This paper presents a new efficient embedding algorithm in the wavelet domain of digital images based on the diamond encoding (DE) scheme. Current discrete wavelet transform (DWT) steganography adds an unacceptable distortion to the images and is considered as an ineffective in terms of security. Applying the DE scheme to the current DWT steganographic methods solves the problems of these methods, and reduces the distortion added to the images, and thus improves the embedding efficiency. The proposed algorithm first converts the secret image into a sequence of base-5 digits. After that, the cover image is transformed into the DWT domain and segmented into 2 × 1 coefficient pairs. The DE scheme is used then to change at most one coefficient of each coefficient pair to embed the base-5 digits. Experimental results depict that the proposed algorithm is more efficient in embedding compared to other methods in terms of embedding payload and image quality. Moreover, the proposed algorithm is attacked by well-known steganalysis software. Results are showing that the proposed algorithm is secure against the powerful universal steganalyzer “ensemble classifier” and the histogram attack. The results also reveal that the proposed algorithm is robust against different image processing attacks such as compression, added noise, and cropping attacks.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Ani ZK et al (2010) Overview: main fundamentals for steganography. J Comput 2(3):158–165
Al-Dmour H, Al-Ani A (2016) A steganography embedding method based on edge identification and XOR coding. Exp Syst Appl 46:293–306
Al-Korbi HA, Al-Ataby A, Al-Taee MA, Al-Nuaimy W (2015) High-capacity image steganography based on Haar DWT for hiding miscellaneous data. IEEE Jordan Conf Appl Electrical Eng Comput Technol (AEECT) 1:1–6
Atawneh S, Almomani A, Sumari P (2013) Steganography in digital images: common approaches and tools. IETE Tech Rev 30(4):344–358
Baby D, Thomas J, Augustine G, George E, Michael NR (2015) A novel DWT based image securing method using steganography. Procedia Comput Sci 46:612–618
Barve S, Nagaraj U, Gulabani R (2011) Efficient and secure biometric image stegnography using discrete wavelet transform. Int J Comput Sci Commun Netw 1(1):96–99
Chan C-K, Cheng L-M (2004) Hiding data in images by simple LSB substitution. Pattern Recogn 37(3):469–474
Chao RM et al (2009) A novel image data hiding scheme with diamond encoding. EURASIP J Inf Secur 2009(1):1–9
Chen M et al (2006) Analysis of current steganography tools: classifications & features. International Conference on Intelligent Information Hiding and Multimedia Signal Processing (IIH-MSP’06), California, USA
CVG image database. Available: http://decsai.ugr.es/cvg/dbimagenes/g512.php, accessed Apr. 2014
Hemalatha S et al (2013) A secure color image steganography in transform domain. Int J Cryptography Inf Secur 3(1):17–24
Kanso A, Own HS (2012) Steganographic algorithm based on a chaotic map. Commun Nonlinear Sci Numer Simul 17(8):3287–3302
Keyvanpour M, Bayat FM (2013) Blind image watermarking method based on chaotic key and dynamic coefficient quantization in the DWT domain. Math Comput Model 58(1):56–67
Kodovsky J, Fridrich J, Holub V (2012) Ensemble classifiers for steganalysis of digital media. IEEE Trans Inf Forensics and Secur 7(2):432–444
Li B et al (2011) A survey on image steganography and steganalysis. J Inf Hiding Multimed Signal Process 2(2):142–172
Mali SN, Patil PM, Jalnekar RM (2012) Robust and secured image-adaptive data hiding. Digital Signal Process 22(2):314–323
Nag A et al (2011) A novel technique for image steganography based on DWT and Huffman encoding. Int J Comput Sci Secur 4(6):561–570
Ndoundam R, Ekodeck SGR. PDF Steganography based on Chinese Remainder Theorem. J Information Security Appl, ISSN 2214–2126, Available online February 2016
Pol K (2014) Image steganography based on DWT using Huffman LWZ encoding. Int J Eng Technical Res (IJETR) 2(3):100–103
RSP image database. Available: http://dud.inf.tu-dresden.de/~westfeld/rsp/rsp.html. Accessed Feb 2014
Singh AK, Dave M, Mohan A (2014) Hybrid technique for robust and imperceptible image watermarking in DWT–DCT–SVD domain. Natl Acad Sci Lett 37(4):351–358
Singh AK, Dave M, Mohan A (2015) Hybrid technique for robust and imperceptible multiple watermarking using medical images. Multimedia Tools and Applications, pp. 1-21
Sun S (2016) A novel edge based image steganography with 2k correction and Huffman encoding. Inf Process Lett 116(2):93–99
USC-SIPI image database. Available: http://sipi.usc.edu/database/, accessed Jan. 2013
Verma A et al (2013) Implementation of image steganography using 2-level DWT technique. Int J Comput Sci Bus Inf 1(1):1–14
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix 1
Appendix 1
Table 4
Table 5
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Atawneh, S., Almomani, A., Al Bazar, H. et al. Secure and imperceptible digital image steganographic algorithm based on diamond encoding in DWT domain. Multimed Tools Appl 76, 18451–18472 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-016-3930-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-016-3930-0