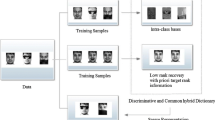
Abstract
Sparse representation based classification (SRC) and collaborative representation based classification (CRC) have demonstrated impressive performance for visual recognition. SRC and CRC assume that the training samples in each class contribute equally to the dictionary and thus generate the dictionary that consists of the training samples in the corresponding class. This may lead to high residual error and instability, to the detriment of recognition performance. One solution is to use the class specific dictionary learning (CSDL) algorithm, which has greatly improved the classification accuracy. However, the CSDL algorithm fails to consider the constraints to sparse codes. In particular, it cannot guarantee that the sparse codes in the same class will be concentrated based on the learned dictionary for each class. Such concentration is actually beneficial to classification. To address these limitations, in this paper, we propose a class specific centralized dictionary learning (CSCDL) algorithm to simultaneously consider the desired characteristics for both dictionary and sparse codes. The blockwise coordinate descent algorithm and Lagrange multipliers are used to optimize the corresponding objective function. Extensive experimental results on face recognition benchmark datasets demonstrate the superior performance of our CSCDL algorithm compared with conventional approaches.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Belhumeur PN, Hespanha JP, Kriegman D (1997) Eigenfaces vs. fisherfaces: Recognition using class specific linear projection. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intel 19(7):711–720
Bertsekas DP (1999) Nonlinear programming. Athena Scientific Belmont, MA
Castrodad A, Sapiro G (2012) Sparse modeling of human actions from motion imagery. Int J Comput Vis 100(1):1–15
Chang CC, Lin CJ (2011) Libsvm: a library for support vector machines. ACM Transactions on Intelligent Systems and Technology (TIST) 2(3):27
Duda RO, Hart PE, Stork DG (2001) Pattern classification. A Wiley-Interscience:373–378
Elad M, Aharon M (2006) Image denoising via sparse and redundant representations over learned dictionaries. IEEE Trans Image Process 15(12):3736–3745
Gao S, Tsang IW-H, Yi M (2014) Learning category-specific dictionary and shared dictionary for fine-grained image categorization. IEEE Trans Image Process 23 (2):623–634
Georghiades AS, Belhumeur PN, Kriegman DJ (2001) From few to many: Illumination cone models for face recognition under variable lighting and pose. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence 23(6):643–660
He X, Yan S, Yuxiao H, Niyogi P, Zhang H-J (2005) Face recognition using laplacianfaces. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence 27(3):328–340
Ho J, Yang MH, Lim J, Lee KC, Kriegman D (2003) Clustering appearances of objects under varying illumination conditions. In: Proceedings of 16th CVPR, vol 1, pp 1–11
Lee H, Battle A, Raina R, Ng A (2006) Efficient sparse coding algorithms. In: Proceedings of Advances in neural information processing systems, pp 801–808
Liu B-D, Shen B, Li X (2015) Locality sensitive dictionary learning for image classification. In: Proceedings of the 22nd ICIP
Liu B-D, Shen B, Wang Y-X (2014) Class specific dictionary learning for face recognition. In: Proceedings of ICSPAC, pp 229–234
Liu B-D, Wang Y-X, Shen B, Zhang Y-J, Hebert M (2014) Self-explanatory sparse representation for image classification. In: Proceedings of the 13th ECCV 2014, pp 600–616
Liu B-D, Wang Y-X, Shen B, Zhang Y-J, Wang Y-J (2014) Blockwise coordinate descent schemes for sparse representation. In: Proceedings of the 39th ICASSP, pp 5304–5308
Liu B-D, Wang Y-X, Zhang Y-J, Shen B (2013) Learning dictionary on manifolds for image classification. Pattern Recogn 46(7):1879–1890
Liu B-D, Wang Y-X, Zhang Y-J, Zheng Y (2012) Discriminant sparse coding for image classification. In: Proceedings of 37th ICASSP, pp 2193–2196
Mairal J, Ponce J, Sapiro G, Zisserman A, Bach FR (2009) Supervised dictionary learning. In: Proceedings of advances in neural information processing systems. MIT Press, pp 1033–1040
Martinez AM (1998) The ar face database. CVC Technical Report:24
Sim T, Baker S, Bsat M (2002) The cmu pose, illumination, and expression (pie) database. In: Proceedings of the 5th international conference on automatic face and gesture recognition , pp 46–51
Sprechmann P, Sapiro G (2010) Dictionary learning and sparse coding for unsupervised clustering. In: Proceedings of the 35th ICASSP, pp 2042–2045
Tao D, Li X, Xindong W, Maybank SJ (2009) Geometric mean for subspace selection. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intel 31(2):260–274
Tseng P (2001) Convergence of a block coordinate descent method for nondifferentiable minimization. J Optimiz Theory App 109(3):475–494
Turk M, Pentland A (1991) Eigenfaces for recognition. J Cogn Neurosci 3 (1):71–86
Wang C, Yan S, Zhang L, Zhang H (2009) Multi-label sparse coding for automatic image annotation. In: Proceedings of the 22nd CVPR, pp 1643–1650
Wang H, Yuan C, Weiming H, Sun C (2012) Supervised class-specific dictionary learning for sparse modeling in action recognition. Pattern Recognition 45 (11):3902–3911
Wang Y-X, Gui L-Y, Zhang Y-J (2012) Neighborhood preserving non-negative tensor factorization for image representation. In: Proceedings of the 37th ICASSP, pp 3389–3392
Wang Y-X, Hebert M (2015) Model recommendation: generating object detectors from few samples. In: Proceedings of the 28th CVPR, pp 1619–1628
Wang Y-X, Hebert M (2016) Learned by transferring from unsupervised universal sources. In: Proceedings of the 30th AAAI
Wang Y-X, Zhang Y-J (2011) Image inpainting via weighted sparse non-negative matrix factorization. In: Proceedings of the 18th ICIP, pp 3409–3412
Wang Y-X, Zhang Y-J (2013) Nonnegative matrix factorization: a comprehensive review. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 25(6):1336–1353
Wright J, Yang AY, Ganesh A, Sastry S, Ma Y (2009) Robust face recognition via sparse representation. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intel 31 (2):210–227
Yan Y, Wang H, Suter D (2014) Multi-subregion based correlation filter bank for robust face recognition. Pattern Recognition 47(11):3487–3501
Yang M, Zhang L, Feng X, Zhang D (2014) Sparse representation based fisher discrimination dictionary learning for image classification. Int J Comput Vis 109 (3):209–232
Yang M, Zhang L, Yang J, Zhang D (2010) Metaface learning for sparse representation based face recognition. In: Proceedings of the 17th ICIP, pp 1601–1604
Zhang D, Yang M, Feng X (2011) Sparse representation or collaborative representation: which helps face recognition?. In: Proceedings of the 13th ICCV, pp 471–478
Zhang Q, Li B (2010) Discriminative k-svd for dictionary learning in face recognition. In: Proceedings of 23rd CVPR, pp 2691–2698
Zhao W, Chellappa R, Phillips JP, Rosenfeld A (2003) Face recognition: A literature survey. Acm Computing Surveys (CSUR) 35(4):399–458
Zhou N, Yi S, Jinye P, Fan J (2012) Learning inter-related visual dictionary for object recognition. In: Proceedings of 25th CVPR, pp 3490–3497
Acknowledgment
This paper is supported partly by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 61402535, No. 61271407), the Natural Science Foundation for Youths of Shandong Province, China (Grant No. ZR2014FQ001) , Qingdao Science and Technology Project (No. 14-2-4-111-jch), and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, China University of Petroleum (East China) (Grant No. 14CX02169A).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, BD., Gui, L., Wang, Y. et al. Class specific centralized dictionary learning for face recognition. Multimed Tools Appl 76, 4159–4177 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-015-3042-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-015-3042-2