Abstract
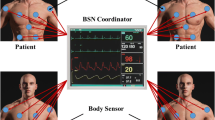
One of the most challenging jobs in designing a Medium Access Control (MAC) protocol for Body Sensor Networks (BSNs) is to achieve QoS requirements for heterogeneous traffics generated from various sensors. Increasing the energy-efficiency of the network should be kept in mind while doing this. Physiological data monitoring applications generate different types of traffic including multimedia data packets. These heterogeneous traffics should be treated differently by an underlying communication protocol, allowing the transmission schedule of these traffic types based on their priorities. In this paper, we present an energy-efficient multiconstrained QoS aware MAC protocol, namely eMC-MAC, wherein the medium access control is designed based on traffic prioritization. We have redefined the superframe structure in such a way that the critical data packets are transmitted earlier than other packets. In our proposed eMC-MAC protocol, we have introduced minislots during CFP (Contention Free Period), where requests for urgent packets are collected to the coordinator node in an energy-efficient way. We also develop an energy-efficient algorithm for preempting allocated data transmission slots to facilitate transmission of packets with higher priority. Thus, the proposed eMC-MAC protocol delivers emergency data packets to the coordinator with reduced delay. We have evaluated the effectiveness of our eMC-MAC protocol through extensive simulations in ns-3. The simulation results have shown that it outperforms a number of state-of-the-art MAC protocols for BSNs.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdur Razzaque, Md. QoS Provisioning in Wireless Sensor Network. For location aware network. VDM Verlag
Akyildiz IF, Melodia T, Chowdhury KR (2007) A survey on wireless multimedia sensor networks. Comput Netw 51(4):921–960
Akyildiz IF, Su W, Sankarasubramaniam Y, Cayirci E (2002) Wireless sensor networks: a survey. Comput Netw 38(4)
Alemdar H, Ersoy C (2010) Wireless sensor networks for healthcare: a survey. Comput Netw 54(15):2688–2710
Ameen MA, Nessa A, Kwak KS (2008) QoS issues with focus on wireless body area networks. Third 2008 international conference on convergence and hybrid information technology
Anjum I, Alam N, Abdur Razzaque Md., Hassan MM, Atif Alamri (2013) A priority based traffic load adaptive MAC protocol for QoS provisioning in body sensor networks. Int J Distrib Sensor Netw 2013
Beck C, Nagel J, Hevesi P, Bretthauer G (2012) RTS-MAC: a relative time synchronization MAC protocol for low duty cycle body sensor networks. Int J Wireless Inf Networks 19(3):163–172
Chen C, Pomalaza-Rëz C (2010) Implementing and evaluating a wireless body sensor system for automated physiological data acquisition at home. Int J Comput Sci Inf Tech 2(3)
Chen M, Gonzalez S, Vasilakos A, Cao H, Leung VC (2011) Body area networks: a survey. Mob Netw Appl 16:171–193
Gopalan SA (2010) Energy-efficient MAC protocols for wireless body area networks: survey. In: Ultra modern telecommunications and control systems and workshops (ICUMT
Hayat S, Javaid N, Khan ZA, Shareef A, Mahmood A, Bouk SH (2012) Energy efficient MAC protocols. HPCC-ICESS:1185–1192
Hossain MS, El Saddik A (2010) QoS Requirement in the multimedia transcoding service selection process. IEEE Trans Instrum Meas 59(6):1498–1506
Lai X, Liu Q, Wei X, Wang Wei, Zhou G, Han G (2013) A survey of body sensor networks. Sensors
Latre B, Braem B, Moerman I, Blondia C (2011) A survey on wireless body area networks. Wirel Netw 17:1
Li C, Hao B, Zhang K, Liu Y, Li J (2011) A novel medium access control protocol with low delay and traffic adaptivity for wireless body area networks. Springer 35:1265–1275
Monowar MM, Hassan MM, Bajaber F, Al-Hussein M, Alamri A (2012) McMAC: towards a MAC protocol with multi-constrained QoS provisioning for diverse traffic in wireless body area networks, sensors. ISSN 1424–8220
Otto C, Milenkovic A, Sanders C, Jovanov E (2006) System architecture of a wireless body area sensor network for ubiquitous health monitoring. J Mob Multimedia 1(4):307–326
Rahman Md.O, Hong CS, Lee S, Bang Y-C (2011) ATLAS: a traffic. load aware sensor MAC design for collaborative body area sensor networks. Sensors:11560–11580
Sanchez D, Alonso L, Angelidis P, Verikoukis C (2011) Secure precise clock synchronization for interconnected body area networks. EURASIP J Wirel Commun Netw 797931
Stojcev MK, Golubovic LR, Nikolic TR (2011) Clocks, power and synchronization in duty-cycled wireless sensor nodes. Ser Elec Energ 24(2):183–208
Suriyachai P, Roedig U, Scott A (2011) A survey of MAC Protocols for mission-critical-applications in wireless sensor networks. IEEE Commun Surv Tutor 14(2):240–264
The Network Simulator Version 3, ns–3. www.nsnam.org
Timmons NF, Scanlon WG (2004) Analysis of the Performance of IEEE 802.15.4 for Medical Sensor Body Area Networking. SECON: 16–24
Wireless Medium Access Control (MAC) and Physical Layer (PHY) (2003) Specifications for low-Rate Wireless Personal Area Networks (WPANs). IEEE Std 802.15.4-2006
Yoon J.S., Ahn G-S, Joo S-S, Lee MJ (2010) PNP-MAC: preemptive slot allocation and non-preemptive transmission for providing QoS in body area networks, consumer communications and networking conference (CCNC). 7th IEEE
Zhang X, Jiang H, Cheng X, Zhang L (2009) An energy efficient implementation of on-demand MAC protocol in medical wireless body sensor networks. Circuits and Systems, 2009, ISCAS 2009, IEEE International Symposium
Zhang X, Jiang H, Zhang L, Zhang C (2010) An energy-efficient ASIC for wireless body sensor networks in medical applications. Biomed Circ Systems IEEE Trans 4(1)
Zhou G, Jian L, Wan C-Y, Yarvis MD, Stankovic JA (2008) BodyQoS: adaptive and radio-agnostic QoS for body sensor networks, INFOCOM 2008. In: The 27th conference on computer communications. IEEE
Acknowledgments
We would like to pay our highest level of gratitude to the anonymous reviewers for their valuable comments and suggestions that helped a lot to enrich the quality of the paper. This work was supported by Hankuk University of Foreign Studies Research Fund of 2014.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pandit, S., Sarker, K., Razzaque, M.A. et al. An energy-efficient multiconstrained QoS aware MAC protocol for body sensor networks. Multimed Tools Appl 74, 5353–5374 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-014-1999-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-014-1999-x