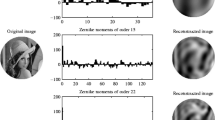
Abstract
The use of image moments as host coefficients constitutes one of the hot topics in image watermarking field due to their robust behavior. Recenlty, a new approach called separable moments (SMs) has been introduced representing an image as combinations of different orthogonal polynomials that generate a series of new moment families. The scope of the present work is to introduce the specific transformations to the image watermarking field by evaluating their security capability under a wide range of common signal processing and geometric attacks. Furthermore, their ability of carrying large binary watermark messages is also examined. The performance of the proposed moment families is evaluated by a comparison to the original moments and a state-of-the-art method. The experimental results justified that a number of the studied transformations outperforms the benchmark method and occasionally the original moment families. Moreover, specific separable moment families are free of instabilities to the higher order coefficients where the extra watermark information is carried. A significant conclusion lies on the adoption of properties (locality, stability) between the generated separable moment families that lead to the enhancement of the basic watermarking requirements (robustness, imperceptibility and capacity) of the proposed watermarking method. The present work justifies that discrete orthogonal SMs constitute a new attractive transformation for the image moment-based watermarking field.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alghoniemy M, Tewfik AH (2000) Geometric distortion correction through image normalization. Proc IEEE Int Conf Multimed Expo 3:1291–1294
Alghoniemy M, Tewfik AH (2000) Image watermarking by moment invariants. Proc IEEE Int Conf Image Process 2:73–76
Chen B, Wornell GW (2001) Quantization index modulation methods: a class of provably good methods for digital watermarking and information embedding. IEEE Trans Inf Theory 47(4):1423–1443
Deng C, Gao X, Li X, Tao D (2009) A local Tchebichef Moments-based robust image watermarking. Signal Process 89:1531–1539
Hosny KM (2011) Image representation using accurate orthogonal Gegenbauer moments. Pattern Recognit Lett 32(6):795–804
Hosny KM (2012) Fast computation of accurate Gaussian–Hermite moments for image processing applications. Digit Signal Process 22(3):476–485
Kim HS, Lee HK (2003) Invariant image watermark using Zernike moments. IEEE Trans Circ Syst Video Technol 13(8):766–775
Lee L, Ko H (2008) Gradient-based local affine invariant feature extraction for mobile robot localization in indoor environments. Pattern Recognit Lett 29(14):1934–1940
Liu ZH, Wang HX (2012) Pseudo-zernike moments-based audio content authentication algorithm robust against feature-analysed substitution attack. Multimed Tool Appl Press, doi:10.1007/s11042-012-1235-5
Moorthy AK, Bovik AC (2011) Visual quality assessment algorithms: what does the future hold? Multimed Tools Applic 51(2):675–696
Mukundan R, Ong SH, Lee PA (2001) Image analysis by Tchebichef moments. IEEE Trans Image Process 10(9):1357–1364
Papakostas GA, Karakasis EG, Koulouriotis DE (2010) Novel moment invariants for improved classification performance in computer vision applications. Pattern Recognit 43(1):58–68
Papakostas GA, Karakasis EG, Koulouriotis DE, Tourassis VD (2013) Moment-based local binary patterns: a novel local descriptor for invariant pattern recognition applications. Neurocomputing 99(1):358–371
Papakostas GA, Tsougenis ED, Koulouriotis DE (2010) Near optimum local image watermarking using Krawtchouk moments. IEEE Int Work Imaging Syst Tech (IST): 464–467
Papakostas GA, Tsougenis ED, Koulouriotis DE, Tourassis VD (2011) On the robustness of Harris detector in image watermarking attacks. Opt Commun 284(19):4394–4407
Sheng Y, Shen L (1994) Orthogonal Fourier-Mellin moments for invariant pattern recognition. J Opt Soc Am A 11(6):1748–1757
Teague MR (1980) Image analysis via the general theory of moments. Opt Soc Ame 70:920–930
Tsougenis ED, Papakostas GA, Koulouriotis DE, Tourassis VD (2012) Performance evaluation of moment-based watermarking methods: a review. J Syst Softw 85(8):1864–1884
Tsougenis ED, Papakostas GA, Koulouriotis DE, Tourassis VD (2012) Image watermarking in polar harmonic transforms domain. 19th International Conference on Systems, Signals and Image Processing (IWSSIP): ISBN 978-3-200-02588-2
Wang Z, Bovik AC, Sheikh HR (2004) Simoncelli EP, Image quality assessment: From error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE Trans Image Process 13(4):600–612
Xiang S (2012) On invariance analysis of Zernike moments in the presence of rotation with crop and loose modes. Multimed Tool Appl 57(1):29–48
Xin Y, Liao S, Pawlak M (2007) Circularly orthogonal moments for geometrically robust image watermarking. Pattern Recognit 40(12):3740–3752
Yap PT, Paramesran R (2004) Local watermarks based on Krawtchouk moments. IEEE Proc Reg Conf TENCON 2:73–76
Yap PT, Paramesran R, Ong SH (2003) Image analysis by Krawtchouk moments. IEEE Trans Image Process 12(11):1367–1377
Yap PT, Paramesran R, Ong SH (2007) Image analysis using Hahn moments. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 29:2057–2062
Zhang L, Qian G, Xiao W (2007) Geometric Distortions Invariant Blind Second Generation Watermarking Technique Based on Tchebichef Moment of Original Image. J Softw 1(9):2283–2294
Zhong S, Shi Q, Cheng MT (1994) Adaptive hierarchical vector quantization for image coding. Pattern Recognit Lett 15(12):1171–1175
Zhu H (2012) Image representation using separable two-dimensional continuous and discrete orthogonal moments. Pattern Recogn 45(4):1540–1558
Zhu H, Shu H, Zhou J, Luo L, Coatrieux JL (2007) Image analysis by discrete orthogonal dual Hahn moments. Pattern Recognit Lett 28(13):1688–1704
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tsougenis, E.D., Papakostas, G.A. & Koulouriotis, D.E. Image watermarking via separable moments. Multimed Tools Appl 74, 3985–4012 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-013-1808-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-013-1808-y