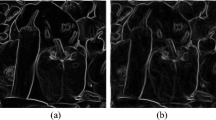
Abstract
This paper provides a robust scheme for random valued impulsive noise reduction along with edge preservation by anisotropic diffusion with improved diffusivity. The defective impulse noisy pixels are detected by Laplacian based second order pixel difference operation where these defective pixels are replaced by appropriate values with regard of the gray level of their four directional neighbors. This de-noised image undergoes the diffusion operation where diffusion coefficient function is modified to make it adaptive by incorporating local gray level variance information. The proposed modified diffusion scheme effectively restore the edges and fine details destroyed during impulse noise reduction process. The effect of proposed diffusion scheme has been studied on various images and the results are compared with some existing diffusion methods which are independently used for impulse noise reduction and edge preservation. The results shows that the prior removal of impulsive noise before the application of diffusion process is advantageous over the direct application of diffusion for removing the impulsive noise. In addition, the results of the proposed diffusion scheme are compared with some of the median filter based methods which are effectively used for impulse noise reduction without caring of edge preservation. The proposed diffusion scheme sufficiently preserves the edges without boosting of impulsive noise components on images corrupted up to 50 % of the impulsive noise density.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brownrigg D (1984) The weighted median filter. Commun ACM 27(8):807–818
Cai JF, Chan RH, Nikolova M (2010) Fast two-phase image deblurring under impulse noise. J Math Imaging 36:46–53
Catte F, Lions PL, Morel JM, Coll T (1992) Image selective smoothing and edge-detection by nonlinear diffusion. SIAM J Numer Anal 29:182–193
Chao SM, Tsai DM (2010) An improved anisotropic diffusion model for detail and edge preserving smoothing. Pattern Recogn Lett 31:2012–2023
Chen T, Wu HR (2001) Adaptive impulse detection using center weighted median filters. IEEE Signal Process Lett 8(1):1–3
Chen Y, Barcelos C, Mair B (2001) Smoothing and edge detection by time-varying coupled nonlinear diffusion equations. Comp Vision Image Underst 82:85–100
Chen Q, Wu D (2010) Image denoising by bounded block matching and 3D filtering. Signal Process 90:2778–2783
Chao LT (2007) A new adaptive center weighted median filter for suppressing impusive noise in images. Inf Sci 177:1073–1087
Crnojevic V, Senk V, Tropovski Z (2004) Advanced impulse detection based on pixel-wise MAD. IEEE Signal Process Lett 11(7):589–592
Delon J, Desolneux A (2012) A patch-based approach for random-valued impulse noise removal. In: Proceedings of 2012 IEEE international conference on acoustic, speech and signal processing, (ICASSP 2012). Kyoto, Japan, 25–30 March 2012, pp 1093–1096
Dong Y, Xu S (2007) A new directional weighted median filter for removal of random valued impulsive noise. IEEE Signal Process Lett 14(3):193–196
Fang D, Nanning Z, Jianru X (2008) Image smoothing and sharpening based on nonlinear diffusion equation. Signal Process 88:2850–2855
Gonzalez RC, Woods RE (2008) Digital image processing, ch 3, pp 144–168. Prentice Hall
Ji Z, Chen Q, Sun QS, Xia DS (2009) A moment-based nonlocal-means algorithm for image denoising. Inf Process Lett 109:1238–1244
Khan NU, Arya KV, Pattanaik M (2010) An efficient image noise removal and enhancement method. In: Proceedings of 2010 IEEE international conference on systems, man and cybernetics, (SMC 2010). Istanbul, Turkey, 10–13 October 2010, pp 3735–3740
Khan NU, Arya KV, Pattanaik M (2012) Fuzzy based diffusion coefficient function in anisotropic diffusion for impulse noise removal. In: Proceedings of 8th Indian conference on vision, graphics and image processing, (ICVGIP 2012). Bombay, India, 16–19 December 2012, pp 3735–3740
Perona P, Malik J (1990) Scale space and edge detection using anisotropic diffusion. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 12(8):629–639
Pinho AJ, Almeida AB (1996) Figures of merit for quality assessment of binary edge maps. In: Proceedings of 3rd IEEE international conference on image processing, (ICIP 96), vol 3. Lausanne, Swittzerland, 16–19 September 1996, pp 591–594
Smolka B, Chydzinski A (2005) Fast detection and impulsive noise removal in color images. J Real-Time Imaging 11(5):389–402
Smolka B (2010) Peer group switching filter for impulse noise reduction in color images. Pattern Recogn Lett 31(6):484–495
Tschumperle D, Deriche R (2005) Vector-valued image regularization with PDEs: a common framework for different application. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 27(4):506–517
Wang Y, Zhang L, Li P (2007) Local variance-controlled forward-and-backward diffusion for image enhancement and noise reduction. IEEE Trans Image Process 16(7):1854–1864
Wang S, Liu Q, Xia Y, Dong P, Luo J, Huang Q, Feng DD (2013) Dictionary learning based impulse noise removal via L1-L1 minimization. Signal Process 93:2696–2708
Witkin AP (1983) Scale-space filtering. In: Proceedings of 8th international joint conference on artificial intelligence, pp 1019–1022
Wu J, Tang C (2011) PDE-based random-valued impulse noise removal based on new class of controlling functions. IEEE Trans Image Process 20(9):2428–2438
Xiao Y, Zeng T, Yu J, Ng MK Restoration of images corrupted by mixed gaussian-impulse noise via L1-L0 minimization. Pattern Recogn 44:1708–1720
You Y, Kaveh M (2000) Fourth-order partial differential equations for noise removal. IEEE Trans Image Process 9(10):1723–1730
Yu J, Wang Y, Shen Y (2008) Noise reduction and edge detection via kernel anisotropic diffusion. Pattern Recogn Lett 29:1496–1503
Zheng K, Feng W, Chen H (2010) An adaptive nonlocal-means algorithm for image denoising via pixel region growing and merging. In: Proceedings of 2010 3rd international congress on image and signal processing. Yantai, China, 16–18 October 2010, pp 621–625
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khan, N.U., Arya, K.V. & Pattanaik, M. Edge preservation of impulse noise filtered images by improved anisotropic diffusion. Multimed Tools Appl 73, 573–597 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-013-1620-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-013-1620-8