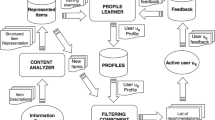
Abstract
The efficiency of personal video suggestions generated by recommender systems is highly dependent on the quality of the obtained user feedback. This feedback has to reflect the personal interest in the content of the viewed video, to obtain accurate results. However, user feedback might undesirably be influenced by additional aspects such as the loading speed or the quality of the video. To date, this issue has received very little research attention. Therefore, this study investigates the direct influence of audio-visual quality parameters on explicit user feedback for the first time to our knowledge via a mobile, Living Lab experiment. This paper proposes a feedback model which takes the Quality of Service (QoS) parameters of the mobile network into account. This model can be used as an additional feedback filter for video recommendation systems that could help to eliminate the influences of QoS on explicit user feedback.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aljukhadar M, Senecal S, Daoust CE (2010) Information overload and usage of recommendations. In: Proceedings of the ACM RecSys 2010 workshop on User-Centric Evaluation of Recommender Systems and Their Interfaces (UCERSTI). CEUR-WS.org
Bell RM, Koren Y (2007) Lessons from the netflix prize challenge. SIGKDD Explor Newsl 9(2):75–79. doi:10.1145/1345448.1345465
Breese J, Heckerman D, Kadie C (1998) Empirical analysis of predictive algorithms for collaborative filtering. In: Proceedings of the 14th conference on uncertainty in artificial intelligence. Madison, USA, pp 43–52
Cha M, Kwak H, Rodriguez P, Ahn YY, Moon S (2007) I tube, you tube, everybody tubes: analyzing the world’s largest user generated content video system. In: IMC ’07: Proceedings of the 7th ACM SIGCOMM conference on Internet measurement. ACM, New York, pp 1–14. doi: 10.1145/1298306.1298309
Chung ET, Du Q, Zou J (2007) Video quality experts group, “Final report from the video quality experts group on the validation of objective models of video quality assessment,” vqeg, 2000. Available at ftp://ftp.its.bldrdoc.gov/dist/ituvidq. URL: http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/summary?doi=?doi=10.1.1.15.7470
Claypool M, Gokhale A, Miranda T, Murnikov P, Netes D, Sartin M (1999) Combining content-based and collaborative filters in an online newspaper. In: Proceedings of ACM SIGIR workshop on recommender systems
De Moor K, Ketyko I, Joseph W, Deryckere T, De Marez L, Martens L, Verleye G (2010) Proposed framework for evaluating quality of experience in a mobile, testbed-oriented living lab setting. Mobile Networks and Applications 15:378–391. doi:10.1007/s11036-010-0223-0. URL: http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s11036-010-0223-0
De Pessemier T, Deryckere T, Martens L (2009) Context aware recommendations for user-generated content on a social network site. In: EuroITV ’09: Proceedings of the seventh european conference on European interactive television conference. ACM, New York, pp 133–136. doi:10.1145/1542084.1542108
Følstad A (2008) Living labs for innovation and development of information and communication technology: a literature review. The Electronic Journal for Virtual Organizations and Networks (Special Issue on Living Labs) 10:99–131
Good, N, Schafer JB, Konstan JA, Borchers A, Sarwar B, Herlocker J, Riedl J (1999) Combining collaborative filtering with personal agents for better recommendations. In: Proceedings of the sixteenth national conference on artificial intelligence, pp 439–446
Heckerman D, Chickering DM, Meek C, Rounthwaite R, Kadie C (2001) Dependency networks for inference, collaborative filtering, and data visualization. J Mach Learn Res 1:49–75. doi:10.1162/153244301753344614. URL: http://dx.doi.org/10.1162/153244301753344614
Jacobson V (1989) “tcpdump packet analyzer”. The tcpdump manual page
Jumisko SH, Ilvonen VP, Vaananen-Vainio-Mattila KA (2005) Effect of tv content in subjective assessment of video quality on mobile devices. SPIE, Bellingham, pp 243–254. doi:10.1117/12.596503. URL: http://link.aip.org/link/?PSI/5684/243/1
Jumisko-Pyykkö S (2008) “I would like to see the subtitles and the face or at least hear the voice”: effects of picture ratio and audio—video bitrate ratio on perception of quality in mobile television. Multimedia Tools Appl 36:167–184. doi:10.1007/s11042-006-0080-9. URL: http://portal.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=1327423.1327428
Jumisko-Pyykkö S, Häkkinen J (2005) Evaluation of subjective video quality of mobile devices. In: MULTIMEDIA ’05: Proceedings of the 13th annual ACM international conference on multimedia. ACM, New York, pp 535–538. doi:10.1145/1101149.1101270
Karypis G (2001) Evaluation of item-based top-n recommendation algorithms. In: CIKM ’01: Proceedings of the tenth international conference on information and knowledge management. ACM, New York, pp 247–254. doi:10.1145/502585.502627
Knoche H, McCarthy JD, Sasse MA (2005) Can small be beautiful?: assessing image resolution requirements for mobile tv. In: MULTIMEDIA ’05: Proceedings of the 13th annual ACM international conference on multimedia. ACM, New York, pp 829–838. doi:10.1145/1101149.1101331
Korhonen J, Reiter U, Myakotnykh E (2010) On the relative importance of audio and video in the presence of packet losses. In: 2010 second international workshop on Quality of Multimedia Experience (QoMEX), pp 64–69. doi:10.1109/QOMEX.2010.5518112
Kortum P (2004) Content is king: the effect of content on the perception of video quality. Human Factors and Ergonomics Society Annual Meeting Proceedings 48(5):1910–1914. URL: http://www.ingentaconnect.com/content/hfes/hfproc/2004/00000048/00000016/art00025
Kortum P (2010) The effect of content desirability on subjective video quality ratings. Human Factors: The Journal of the Human Factors and Ergonomics Society 52(14):105–118. URL: http://www.ingentaconnect.com/content/hfes/hf/2010/00000052/00000001/art00009
Linden G, Smith B, York J (2003) Amazon.com recommendations: item-to-item collaborative filtering. Internet Computing, IEEE 7(1):76–80. doi:10.1109/MIC.2003.1167344
Miller BN, Albert I, Lam SK, Konstan JA, Riedl J, Miller BN, Albert I, Lam SK, Riedl JAKJ (2003) Movielens unplugged: experiences with a recommender system on four mobile devices. In: Proceedings of the 2003 conference on intelligent user interfaces
Mooney RJ, Roy L (2000) Content-based book recommending using learning for text categorization. In: Proceedings of the fifth ACM conference on digital libraries, DL ’00. ACM, New York, pp 195–204. doi:10.1145/336597.336662. URL: http://doi.acm.org/10.1145/336597.336662
Oard D, Kim J (1998) Implicit feedback for recommender systems. URL: http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/summary?doi=10.1.1.49.3097
Pennock DM, Lawrence S, Popescul R, Ungar LH (2001) Probabilistic models for unified collaborative and content-based recommendation in sparse-data environments
Pfeiffer S, Srinivasan U (2000) Tv anytime as an application scenario for mpeg-7. In: MULTIMEDIA ’00: Proceedings of the 2000 ACM workshops on multimedia. ACM, New York, pp 89–92. doi:10.1145/357744.357885
Resnick P, Varian HR (1997) Recommender systems. Commun ACM 40:56–58. doi:10.1145/245108.245121. URL: http://doi.acm.org/10.1145/245108.245121
Sarwar BM, Karypis G, Konstan JA, Riedl JT (2000) Application of dimensionality reduction in recommender system—a case study. URL: http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/summary?doi=?doi=10.1.1.38.744
Schein AI, Popescul A, Ungar LH, Pennock DM (2002) Methods and metrics for cold-start recommendations. In: SIGIR ’02: Proceedings of the 25th annual international ACM SIGIR conference on research and development in information retrieval. ACM, New York, pp 253–260. doi:10.1145/564376.564421
Schumacher J, Feurstein K, Pitkänen O, Niitamo VP (2008) European living labs: a new approach for human centric regional innovation. Wissenschaftlicher, Berlin
Schuurman D, Evens T, De Marez L (2009) A living lab research approach for mobile tv. In: EuroITV ’09: Proceedings of the seventh European conference on European interactive television conference. ACM, New York, pp 189–196. doi:10.1145/1542084.1542122
Senter HF (2008) Applied linear statistical models, 5th edn. In: Kutner MH, Nachtsheim CJ, Neter J, Li W (eds) Journal of the American Statistical Association, vol 103, pp 880–880. URL: http://econpapers.repec.org/RePEc:bes:jnlasa:v:103:y:2008:m:june:p:880-880
Sullivan M, Pratt J, Kortum P (2008) Practical issues in subjective video quality evaluation: human factors vs. psychophysical image quality evaluation. In: UXTV ’08: Proceeding of the 1st international conference on designing interactive user experiences for TV and video. ACM, New York, pp 1–4. doi:10.1145/1453805.1453807
Tseng BL, Yung Lin C, Smith JR (2002) Video summarization and personalization for pervasive mobile devices. In: SPIE electronic imaging—storage & retrieval for media databases, pp 359–370
Ungar LH, Foster DP (1998) Clustering methods for collaborative filtering. URL: http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/summary?doi=?doi=10.1.1.44.7783
Wang HC, Lee CS, Ho TH (2007) Combining subjective and objective qos factors for personalized web service selection. Expert Syst Appl 32(2):571–584. doi:10.1016/j.eswa.2006.01.034. URL: http://www.scienced irect.com/science/article/B6V03-4J84RXD-4/2/0ec2a61005d6175e995650b2d6968ab1
Yu Z, Lin N, Nakamura Y, Kajita S, Mase K (2007) Fuzzy recommendation towards qos-aware pervasive learning. In: 21st international conference on advanced information networking and applications, 2007. AINA ’07, pp 604–610. doi:10.1109/AINA.2007.73
Yu Z, Zhou X (2004) Tv3p: an adaptive assistant for personalized tv. IEEE Trans Consum Electron 50(1):393–399. doi:10.1109/TCE.2004.1277889
Yu Z, Zhou X, Hao Y, Gu J (2006) Tv program recommendation for multiple viewers based on user profile merging. User Model User-Adapt Interact 16:63–82. doi:10.1007/s11257-006-9005-6. URL: http://portal.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=1146521.1146531
Zhang H, Zheng S, Yuan J (2005) A personalized tv guide system compliant with mhp. IEEE Trans Consum Electron 51(2):731–737. doi:10.1109/TCE.2005.1468026
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank the Research Foundation—Flanders (FWO), for the research position of Toon De Pessemier (pre-doctoral fellow) and Wout Joseph (post-doctoral fellow). Besides, this work was supported by the IBBT / UGent (Interdisciplinary institute for BroadBand Technology / Ghent University) through the GR@SP-project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
De Pessemier, T., De Moor, K., Ketykó, I. et al. Investigating the influence of QoS on personal evaluation behaviour in a mobile context. Multimed Tools Appl 57, 335–358 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-010-0712-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-010-0712-y