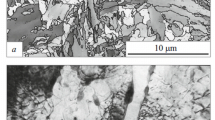
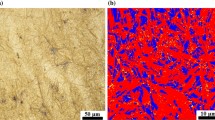
The microstructure and properties of medium-carbon steel (0.45% C) are studied after torsional severe plastic deformation (SPD) at a high quasi-hydrostatic pressure and elevated temperatures of from 300 to 450°C. The initial treatment prior to the SPD is hardening for martensite. Analysis of the results shows that the SPD is effective for raising the characteristics of strength and microhardness at satisfactory ductility.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. Z. Valiev and I. V. Aleksandrov, Bulk Nanostructured Metallic Materials [in Russian], IKTs “Akademkniga,” Moscow (2007), 398 p.
S. V. Dobatkin, A. M. Arsenkin, M. A. Popov, et al., “Fabrication of bulk nano-and submicrocrystalline materials by the method of severe plastic deformation,” Metalloved. Term. Obrab. Met., No. 5, 29 – 34 (2005).
R. Z. Valiev, R. K. Islamgaliev, and I. V. Alexandrov, Progr. Mater. Sci., 45(2), 102 – 189 (2000).
Yu. Yu. Efimova, N. V. Koptseva, and O. A. Nikitenko, “A study of the state of carbide phase after nanostructurization and subsequent drawing of low-carbon steel,” Vestn. MGTU Im. G. I. Nosova, No. 3, 45 – 48 (2009).
Yu. Ivanisenko, W. Lojkwski, R. Z. Valiev, and H.-J. Fecht, “The mechanism of formation of nanostructure and dissolution of cementite in a pearlitic steel during high pressure torsion,” Acta Mater., 51, 5555 – 5570 (2003).
J. Wang, C. Xu, Y. Wang et al, “Microstructure and properties of a low carbon steel after equal channel angular pressing,” in: M. J. Zehetbauer and R. Z. Valiev (eds.), Nanomaterials by Severe Plastic Deformation, Wiley-VCH, Vienna, Austria (2002), pp. 829 – 834.
N. Tsuji, R. Ueji, Y. Minamoto, and Y. Satio, “A new and simple process to obtain nano-structured bulk low-carbon steel with superior mechanical property,” Scr. Mater., 46, 305 – 310 (2002).
S. Dobatkin, J. Zrnik, and I. Mamuzic, “Ultrafine-grained low carbon steels by severe plastic deformation,” Metallurgija, 47(3), 181 – 186 (2008).
J. Zrnik, R. Pippan, S. Scheriau, et al., “Microstructure and mechanical properties of UFG medium carbon steel processed by HTP at increased temperature,” J. Mater. Sci., 45, 4822 – 4826 (2010).
N. Tsuji, “New routes for fabricating ultrafine-grained microstructure in bulky steels without very-high strains,” Adv. Eng. Mater., 12(8), 701 – 707 (2010).
J. Zrnik, S. Dobatkin, and O. Stejskal, “Deformation behavior and ultrafine-grained structure development in steels with different carbon content subjected to severe plastic deformation,” Key Eng. Mater., 345 – 346, 45 – 48 (2010).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Metallovedenie i Termicheskaya Obrabotka Metallov,No.4,pp.3–7, April, 2012.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Karavaeva, M.V., Nurieva, S.K., Zaripov, N.G. et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of medium-carbon steel subjected to severe plastic deformation. Met Sci Heat Treat 54, 155–159 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11041-012-9473-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11041-012-9473-8