Abstract
Background
Nitrogen (N) and phosphorous (P) play a very important role in the growth and development of wheat as well as major constituents of biological membranes. To meet the plant’s nutritional demand these nutrients are applied in the form of fertilizers. But the plant can utilize only half of the applied fertilizer whereas the rest is lost through surface runoff, leaching and volatilization. Thus, to overcome the N/P loss we need to elucidate the molecular mechanism behind the N/P uptake.
Methods
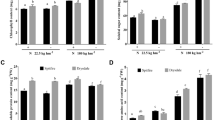
In our study, we used DBW16 (low NUE), and WH147 (high NUE) wheat genotypes under different doses of N, whereas HD2967 (low PUE) and WH1100 (high PUE) genotypes were studied under different doses of P. To check the effect of different doses of N/P, the physiological parameters like total chlorophyll content, net photosynthetic rate, N/P content, and N/PUE of these genotypes were calculated. In addition, gene expression of various genes involved in N uptake, utilization, and acquisition such as Nitrite reductase (NiR), Nitrate transporter 1/Peptide transporter family (NPF2.4/2.5), Nitrate transporter (NRT1) and NIN Like Protein (NLP) and induced phosphate starvation (IPS), Phosphate Transporter (PHT1.7) and Phosphate 2 (PHO2) acquisition was studied by quantitative real-time PCR.
Results
Statistical analysis revealed a lower percent reduction in TCC, NPR, and N/P content in N/P efficient wheat genotypes (WH147 & WH1100). A significant increase in relative fold expression of genes under low N/P concentration was observed in N/P efficient genotypes as compared to N/P deficient genotypes.
Conclusion
Significant differences in physiological data and gene expression among N/ P efficient and deficient wheat genotypes could be useful for future improvement of N/P use efficiency.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Ct:
-
Threshold cycle
- DMSO:
-
Dimethyl sulphoxide
- GPP:
-
Grain yield per plant
- IPS:
-
induced phosphate starvation
- NiR:
-
Nitrate reductase
- NLP:
-
NIN Like protein
- NO3− :
-
Nitrate
- NPF:
-
Nitrate transporter 1/Peptide transporter family
- NPR:
-
Net photosynthetic rate
- NRT:
-
Nitrate transporter
- NUE:
-
Nitrogen use efficiency
- PHO2:
-
Phosphate 2
- PHT:
-
Phosphate Transporter
- PUE:
-
Phosphorous use efficiency
- qRT-PCR:
-
Quantitative real time PCR
- TCC:
-
Total chlorophyll content
References
Venske E, Dos Santos RS, Busanello C, Gustafson P, de Oliveira AC (2019) Bread wheat: a role model for plant domestication and breeding. Hereditas 156(1):1–11. https://doi.org/10.1186/s41065-019-0093-9
Hirel B, Tétu T, Lea PJ, Dubois F (2011) Improving nitrogen use efficiency in crops for sustainable agriculture. Sustainability 3(9):1452–1485. https://doi.org/10.3390/su3091452
Motsara MR (2002) Promoting Balanced fertilization in India–Policies and Economic Issues. Fertilizer News 47:15–21
Hari-Gowthem G, Kaur S, Sekhon BS, Sharma P, Chhuneja P (2019) Genetic variation for phosphorus-use efficiency in diverse wheat germplasm. J Crop Improv 33(4):536–550. https://doi.org/10.1080/15427528.2019.1627633
Moll RH, Kamprath EJ, Jackson WA (1982) Analysis and interpretation of factors which contribute to efficiency of nitrogen utilization 1. Agronomy 74(3):562–564. https://doi.org/10.2134/agronj1982.00021962007400030037x
Balyan HS, Gahlaut V, Kumar A, Jaiswal V, Dhariwal R, Tyagi S et al (2016) Nitrogen and phosphorus use efficiencies in wheat: physiology, phenotyping, genetics and breeding. Plant Breed Rev 40:167–234
Bosquet CL, Rossella A, Joscb-Luis A, Salvador N (2009) Photosynthetic capacity of fieldgrown durum wheat under different N availabilities: a comparative study from leaf so canopy. Environ Exp Bot 67(1):145–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2009.06.004
Ghafoor I, Habib-ur-Rahman M, Ali M, Afzal M, Ahmed W, Gaiser T, Ghaffar A (2021) Slow-release nitrogen fertilizers enhance growth, yield, NUE in wheat crop and reduce nitrogen losses under an arid environment. Environ Sci Pollut Res 1–16. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-13700-4
El-Sobky ESE (2021) Response of wheat to micronutrients foliar application, compost, and N fertilizer level. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 1–17. https://doi.org/10.1080/00103624.2021.1885694
Fontana M, Bélanger G, Hirte J, Ziadi N, Elfouki S, Bragazza L, Sinaj S (2021) Critical plant phosphorus for winter wheat assessed from long-term field experiments. Eur J Agron 126:126263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eja.2021.126263
Li P, Weng J, Zhang Q, Yu L, Yao Q, Chang L, Niu Q (2018) Physiological and biochemical responses of Cucumis melo L. chloroplasts to low-phosphate stress. Front Plant sci 9:1525. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2018.01525
Prathap V, Kumar A, Maheshwari C, Tyagi A (2022) Phosphorus homeostasis: acquisition, sensing, and long-distance signaling in plants.Mol. Biol. Rep.1–16
Sagwal V, Sihag P, Singh Y, Mehla S, Kapoor P, Balyan P, Kumar U, Heredity (2022)1–11. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41437-022-00506-4
Aung K, Lin SI, Wu CC, Huang YT, Su CL, Chiou TJ (2006) pho2, a phosphateoveraccumulator, is caused by a nonsense mutation in a microRNA399 target gene. Plant Physiol 141:1000–1011. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.106.078063
Zhao M, Ding H, Zhu JK, Zhang F, Li WX (2011) Involvement of miR169 in the nitrogen-starvation responses in Arabidopsis. New Phytol 190(4):906–915. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2011.03647.x
He H, Liang G, Li Y, Wang F, Yu D (2014) Two young microRNAs originating from target duplication mediate nitrogen starvation adaptation via regulation of glucosinolate synthesis in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Physiol 164(2):853–865. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.113.228635
Olsen AN, Ernst HA, Leggio LL, Skriver K (2005) NAC transcription factors: structurally distinct, functionally diverse. Trends Plant Sci 10(2):79–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2004.12.010
Li M, Wang T, Zhang H, Liu S, Li W, Abou Elwafa SF, Tian H (2022) Tanrt2. 1-6b is a dual-affinity nitrate transporter contributing to nitrogen uptake in bread wheat under both nitrogen deficiency and sufficiency. J Crop Sci 10(4):9931005. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cj.2021.11.012
Kumar A, Batra R, Gahlaut V, Gautam T, Kumar S, Sharma M, Gupta PK (2018) Genome-wide identification and characterization of gene family for RWP-RK transcription factors in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.).PloS one, 13(12), e0208409
Arnon DI (1949) Copper enzymes in isolated chloroplasts. Polyphenoloxidase in Beta vulgaris. Plant physiol 24(1):1. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.24.1.1
Subbiah BV, Asija GL (1956) A rapid procedure for the determination of available nitrogen in soils. Curr Sci 26:259–260
Koenig RA, Johnson CR (1942) Colorimetric determination of P in biological materials. Ind Eng Chem Anal 14:155–156. https://doi.org/10.1021/i560102a026
Olsen SR (1954) Estimation of available phosphorus in soils by extraction with sodium bicarbonate (No. 939). US Department of Agriculture
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2– ∆∆CT method. Methods 25(4):402–408. https://doi.org/10.1006/meth.2001.1262
Pandey M, Shrestha J, Subedi S, Shah KK (2020) Role of nutrients in wheat: a review. TRAB 1(1):18–23
Amjadian E, Zeinodini A, Doğan H (2021) Effect of fertilizer management systems on growth and balance of nutrients in wheat cultivation. Asian J Plant Sci 1(2):56–69. https://doi.org/10.22034/CAJPSI.2021.02.01
Folina A, Tataridas A, Mavroeidis A, Kousta A, Katsenios N, Efthimiadou A, Kakabouki I (2021) Evaluation of various nitrogen indices in N-Fertilizers with inhibitors in field crops: a review. Agronomy 11(3):418. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11030418
Hawkesford MJ (2014) Reducing the reliance on nitrogen fertilizer for wheat production. J Cereal Sci 59(3):276–283. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcs.2013.12.001
Marschner H, Kirkby EA, Cakmak I (1996) Effect of mineral nutritional status on shoot-root partitioning of photoassimilates and cycling of mineral nutrients. J Exp Bot 47(3):1255–1263. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/47
Schlichting AF, Bonfim-Silva EM, Silva MDC, Pietro-Souza W, da Silva TJ, Farias LDN (2015) Efficiency of portable chlorophyll meters in assessing the nutritional status of wheat plants. Rev Bras Eng Agric Ambient 19:1148–1151. https://doi.org/10.1590/1807-1929/agriambi.v19n12p1148-1151
Akhter MM, Hossain A, Timsina J, TEIXEIRA DSJA, Islam MS (2016) Chlorophyll meter-a decision-making tool for nitrogen application in wheat under light soils. Int J Plant Prod 10(3):289–302
Xu HX, Weng XY, Yang Y (2007) Effect of phosphorus deficiency on the photosynthetic characteristics of rice plants. Russ J Plant Physiol 54(6):741–748
Zhang W, Chen XX, Liu YM, Liu DY, Du YF, Chen XP, Zou CQ (2018) The role of phosphorus supply in maximizing the leaf area, photosynthetic rate, coordinated to grain yield of summer maize. Field Crops Res 219:113–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2018.01.031
Meng X, Liang Z, Dai X, Zhang Y, Mahboub S, Ngu DW et al (2021) Predicting transcriptional responses to cold stress across plant species. PNAS 118(10):1073. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2026330118
Abedi T, Alemzadeh A, Kazemeini SA (2011) Wheat yield and grain protein response to nitrogen amount and timing. Aust J Crop Sci 5(3):330–336
Tan Y, Chai Q, Li G, Zhao C, Yu A, Fan Z, Tian X (2021) Improving wheat grain yield via promotion of water and nitrogen utilization in arid areas. Sci Rep 11(1):1–12. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-92894-6
Haroon M, Idrees F, Naushahi HA, Afzal R, Usman M, Qadir T, Rauf H (2019) Nitrogen use efficiency: farming practices and sustainability. J Exp Agric Int 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1080/15427528.2019.1627633
Sandaña P, Pinochet D (2014) Grain yield and phosphorus use efficiency of wheat and pea in a high yielding environment. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 14(4):973–986. https://doi.org/10.4067/S0718-95162014005000076
Bilal HM, Aziz T, Maqsood MA, Farooq M, Yan G (2018) Categorization of wheat genotypes for phosphorus efficiency. PLoS ONE 13(10):e0205471. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0205471
Zhao M, Ding H, Zhu JK, Zhang F, Li WX (2011) Involvement of miR169 in the nitrogen-starvation responses in Arabidopsis. New Phytol 190(4):906–915. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2011.03647.x
Wang H, Wan Y, Buchner P, King R, Ma H, Hawkesford MJ (2020) Phylogeny and gene expression of the complete NITRATE TRANSPORTER 1/PEPTIDE TRANSPORTER FAMILY in Triticum aestivum. J Exp Bot 71(15):4531–4546. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/eraa210
Sun J, Bankston JR, Payandeh J, Hinds TR, Zagotta WN, Zheng N (2014) Crystal structure of the plant dual-affinity nitrate transporter NRT1. 1. Nature 507(7490):73–77
Guo T, Xuan H, Yang Y, Wang L, Wei L, Wang Y, Kang G (2014) Transcription analysis of genes encoding the wheat root transporter NRT1 and NRT2 families during nitrogen starvation. J Plant Growth Regul 33(4):837–848. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-014-9435-z
Jagadhesan B, Sathee L, Meena HS, Jha SK, Chinnusamy V, Kumar A, Kumar S (2020) Genome wide analysis of NLP transcription factors reveals their role in nitrogen stress tolerance of rice. Sci Rep 10(1):1–16. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-66338-6
Kumar A, Sharma M, Kumar S, Tyagi, Wani SH, Gajula MP, Singh KP (2018a) Functional and structural insights into candidate genes associated with nitrogen and phosphorus nutrition in wheat (Triticum aestivum L). Int J biol macromol 118:76–91
Oono Y, Kobayashi F, Kawahara Y, Yazawa T, Handa H, Itoh T, Matsumoto T (2013) Characterisation of the wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) transcriptome by de novo assembly for the discovery of phosphate starvation-responsive genes: gene expression in Pi-stressed wheat. BMC Genom 14(1):1–14
Baek D, Kim MC, Chun HJ, Kang S, Park HC, Shin G et al (2013) Regulation of miR399f transcription by AtMYB2 affects phosphate starvation responses in Arabidopsis. Plant physiol 161(1):362–373. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.112.205922
Ouyang X, Hong X, Zhao X, Zhang W, He X, Ma W, Tong Y (2016) Knock out of the PHOSPHATE 2 gene TaPHO2-A1 improves phosphorus uptake and grain yield under low phosphorus conditions in common wheat. Sci Rep 6(1):1–11. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep29850
Acknowledgements
The corresponding author is highly grateful to the Head, Department of Molecular Biology & Biotechnology, and Directorate of Research, CCS Haryana Agricultural University for providing all the necessary facilities during the course of this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
UK conceived the idea and designed the experiment. VS and PS carried out the experiments. YS, PB, and KPS analysed the data. UK, VS and YS drafting and editing the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sagwal, V., Kumar, U., Sihag, P. et al. Physiological traits and expression profile of genes associated with nitrogen and phosphorous use efficiency in wheat. Mol Biol Rep 50, 5091–5103 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-023-08413-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-023-08413-5