Abstract
Background
Low temperature plasma (LTP) is a developing field in recent years to play important roles of sterilization, material modification and wound healing. Breast cancer is a common gynecological malignant tumor. Recent studies have shown that LTP is a promising selective anti-cancer treatment. The effect of LTP on breast cancer is still unclear. In this study, We treated breast cancer cell lines with low temperature plasma for different periods of time and analyzed the relevant differences.
Methods and results
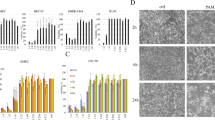
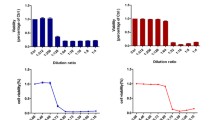
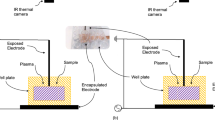
SK-BR-3 cell nutrient solution was firstly treated by ACP for 0, 10, 20, 40, 80 and 120 s, which was next used to cultivateSK-BR-3cells for overnight.we found that LTP was able to suppress cell vitality, proliferation, invasion and migration of SK-BR-3 cells. Also, SK-BR-3 apoptosis was induced by LTP in a time-dependent manner.
Conclusion
These evidences suggest the negative effect of LTP on malignant development of SK-BR-3 cells, and LTP has the potential clinical application for breast cancer treatment.




Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
All data are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- LTP:
-
Low temperature plasma
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- MAPK:
-
Mitogen-activated proteinkinase
- Erks:
-
Extracellular signal-regulated kinases
- NF-κB:
-
Nuclear factor kappa-B
- PCNA:
-
Proliferating Cell Nuclear Antigen
- BAX:
-
BCL2-associated X protein
- BCL-2:
-
B-cell lymphoma-2
- MMP2:
-
Matrix metalloproteinase 2
- MMP9:
-
Matrix metalloproteinase 9
References
Hirst AM, Frame FM, Arya M, Maitland NJ, O’Connell D (2016) Low temperature plasmas as emerging cancer therapeutics: the state of play and thoughts for the future. Tumour biology: the journal of the International Society for Oncodevelopmental Biology and Medicine 37:7021–7031
Tanaka H, Mizuno M, Ishikawa K, Toyokuni S, Kajiyama H, Kikkawa F et al (2021) Cancer treatments using low-temperature plasma. Curr Med Chem 28:8549–8558
Xu D, Luo X, Xu Y, Cui Q, Yang Y, Liu D et al (2016) The effects of cold atmospheric plasma on cell adhesion, differentiation, migration, apoptosis and drug sensitivity of multiple myeloma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 473:1125–1132
Voloaca OM, Greenhalgh CJ, Cole LM, Clench MR, Managh AJ, Haywood-Small SL (2020) Laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry as a novel clinical imaging tool to detect asbestos fibres in malignant mesothelioma. Rapid Commun mass spectrometry: RCM 34:e8906
Bunz O, Mese K, Funk C, Wulf M, Bailer SM, Piwowarczyk A et al (2020) Cold atmospheric plasma as antiviral therapy - effect on human herpes simplex virus type 1. J Gen Virol 101:208–215
Eggers B, Marciniak J, Memmert S, Kramer FJ, Deschner J, Nokhbehsaim M (2020) The beneficial effect of cold atmospheric plasma on parameters of molecules and cell function involved in wound healing in human osteoblast-like cells in vitro. Odontology 108:607–616
Feizollahi E, Misra NN, Roopesh MS (2021) Factors influencing the antimicrobial efficacy of Dielectric Barrier Discharge (DBD) Atmospheric Cold Plasma (ACP) in food processing applications. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 61:666–689
Frias E, Iglesias Y, Alvarez-Ordonez A, Prieto M, Gonzalez-Raurich M, Lopez M (2020) Evaluation of Cold Atmospheric Pressure Plasma (CAPP) and plasma-activated water (PAW) as alternative non-thermal decontamination technologies for tofu: impact on microbiological, sensorial and functional quality attributes. Food Res Int 129:108859
Bernhardt T, Semmler ML, Schafer M, Bekeschus S, Emmert S, Boeckmann L (2019) Plasma medicine: applications of cold atmospheric pressure plasma in dermatology. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity
Kleineidam B, Nokhbehsaim M, Deschner J, Wahl G (2019) Effect of cold plasma on periodontal wound healing-an in vitro study. Clin Oral Invest 23:1941–1950
Keidar M, Yan D, Beilis II, Trink B, Sherman JH (2018) Plasmas for treating cancer: opportunities for adaptive and self-adaptive approaches. Trends Biotechnol 36:586–593
Ikeda JI, Tanaka H, Ishikawa K, Sakakita H, Ikehara Y, Hori M (2018) Plasma-activated medium (PAM) kills human cancer-initiating cells. Pathol Int 68:23–30
Adachi T, Tanaka H, Nonomura S, Hara H, Kondo S, Hori M (2015) Plasma-activated medium induces A549 cell injury via a spiral apoptotic cascade involving the mitochondrial-nuclear network. Free Radic Biol Med 79:28–44
Vaquero J, Judee F, Vallette M, Decauchy H, Arbelaiz A, Aoudjehane L et al (2020) Cold-atmospheric plasma induces tumor cell death in preclinical in vivo and in vitro models of human cholangiocarcinoma. Cancers 12
Li Y, Tang T, Lee H, Song K (2021) Cold atmospheric pressure plasma-activated medium induces selective cell death in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells independently of singlet oxygen, hydrogen peroxide, nitric oxide and nitrite/nitrate. International journal of molecular sciences 22.
Schneider C, Arndt S, Zimmermann JL, Li YF, Karrer S, Bosserhoff AK (2019) Cold atmospheric plasma treatment inhibits growth in colorectal cancer cells. Biol Chem 400:111–122
Li W, Yu H, Ding D, Chen Z, Wang Y, Wang S et al (2019) Cold atmospheric plasma and iron oxide-based magnetic nanoparticles for synergetic lung cancer therapy. Free Radic Biol Med 130:71–81
Golubitskaya EA, Troitskaya OS, Yelak EV, Gugin PP, Richter VA, Schweigert IV et al (2019) Cold Physical plasma decreases the viability of lung adenocarcinoma cells. Acta naturae 11:16–19
Verloy R, Privat-Maldonado A, Smits E, Bogaerts A (2020) Cold atmospheric plasma treatment for pancreatic cancer-the importance of pancreatic stellate cells. Cancers 12
Van Loenhout J, Flieswasser T, Freire Boullosa L, De Waele J, Van Audenaerde J, Marcq E et al (2019) Cold atmospheric plasma-treated PBS eliminates immunosuppressive pancreatic stellate cells and induces immunogenic cell death of pancreatic cancer cells. Cancers 11.
Yang X, Chen G, Yu KN, Yang M, Peng S, Ma J et al (2020) Cold atmospheric plasma induces GSDME-dependent pyroptotic signaling pathway via ROS generation in tumor cells. Cell Death Dis 11:295
Guo L, Zhao Y, Liu D, Liu Z, Chen C, Xu R et al (2018) Cold atmospheric-pressure plasma induces DNA-protein crosslinks through protein oxidation. Free Radic Res 52:783–798
Yousfi M, Merbahi N, Pathak A, Eichwald O (2014) Low-temperature plasmas at atmospheric pressure: toward new pharmaceutical treatments in medicine. Fundam Clin Pharmacol 28:123–135
Mahmood N, Arakelian A, Cheishvili D, Szyf M, Rabbani SA (2020) S-adenosylmethionine in combination with decitabine shows enhanced anti-cancer effects in repressing breast cancer growth and metastasis. J Cell Mol Med 24:10322–10337
Murphy BL, Yi M, Arun BK, Gutierrez Barrera AM, Bedrosian I (2020) Contralateral risk-reducing mastectomy in breast cancer patients who undergo multigene panel testing. Ann Surg Oncol 27:4613–4621
Co N, Iglesias D, Celestino J, Kwan S, Mok S, Schmandt R et al (2014) Loss of LKB1 in high-grade endometrial carcinoma: LKB1 is a novel transcriptional target of p53. Cancer 120:3457–3468
Naji S, Issa K, Eid A, Iratni R, Eid AH (2019) Cadmium induces migration of colon cancer cells: roles of reactive oxygen species, P38 and Cyclooxygenase-2. Cell Physiol Biochem 52:1517–1534
Li W, Li Y, Tian W, Han X, Zhao J, Xin Z et al (2020) 2-methylbenzoyl berbamine, a multi-targeted inhibitor, suppresses the growth of human osteosarcoma through disabling NF-kappaB, ERK and AKT signaling networks. Aging 12:15037–15049
Libson S, Lippman M (2014) A review of clinical aspects of breast cancer. Int Rev psychiatry 26:4–15
Jiang K, Liu P, Xu H, Liang D, Fang K, Du S et al (2020) SASH1 suppresses triple-negative breast cancer cell invasion through YAP-ARHGAP42-actin axis. Oncogene 39:5015–5030
Green D, Eyre H, Singh A, Taylor JT, Chu J, Jeys L et al (2020) Targeting the MAPK7/MMP9 axis for metastasis in primary bone cancer. Oncogene 39:5553–5569
Winerdal ME, Krantz D, Hartana CA, Zirakzadeh AA, Linton L, Bergman EA et al (2018) Urinary bladder cancer tregs suppress MMP2 and potentially regulate invasiveness. Cancer Immunol Res 6:528–538
Qin H, Liu X, Li F, Miao L, Li T, Xu B et al (2017) PAD1 promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis in triple-negative breast cancer cells by regulating MEK1-ERK1/2-MMP2 signaling. Cancer Lett 409:30–41
Wang ZC, Li Y, Wang KL, Wang L, You BS, Zhao DF et al (2020) miR-5089-5p suppresses castration-resistant prostate cancer resistance to enzalutamide and metastasis via miR-5089-5p/SPINK1/ MAPK/MMP9 signaling. Aging 12:14418–14433
D’Arcy MS (2019) Cell death: a review of the major forms of apoptosis, necrosis and autophagy. Cell Biol Int 43:582–592
Bhat TA, Chaudhary AK, Kumar S, O’Malley J, Inigo JR, Kumar R et al (2017) Endoplasmic reticulum-mediated unfolded protein response and mitochondrial apoptosis in cancer. Biochim et Biophys acta Reviews cancer 1867:58–66
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel R, Torre L, Jemal A (2018) Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. Cancer J Clin 68:394–424
Chlebowski R, Anderson G, Aragaki A, Manson J, Stefanick M, Pan K et al (2020) Association of menopausal hormone therapy with breast cancer incidence and mortality during long-term follow-up of the women’s health initiative randomized clinical trials. JAMA 324:369–380
Fahad Ullah M (2019) Breast cancer: current perspectives on the disease status. Adv Exp Med Biol 1152:51–64
Manai M, Finetti P, Mejri N, Athimni S, Birnbaum D, Bertucci F et al (2019) Inflammatory breast cancer in 210 patients: a retrospective study on epidemiological, anatomo-clinical features and therapeutic results. Mol Clin Oncol 10:223–230
Xu X, Zhang M, Xu F, Jiang S (2020) Wnt signaling in breast cancer: biological mechanisms, challenges and opportunities. Mol Cancer 19:165
Yan D, Cui H, Zhu W, Talbot A, Zhang LG, Sherman JH et al (2017) The strong cell-based hydrogen peroxide generation triggered by cold atmospheric plasma. Sci Rep 7:10831
Yang Y, Li D, Li Y, Jiang Q, Sun R, Liu J et al (2020) Low-temperature plasma suppresses proliferation and induces apoptosis in lung cancer cells by regulating the miR-203a/BIRC5 axis. OncoTargets and therapy 13:5145–5153
Duarte S, Panariello BHD (2020) Comprehensive biomedical applications of low temperature plasmas. Arch Biochem Biophys 693:108560
Kumar N, Attri P, Choi EH, Uhm HS (2015) Influence of water vapour with non-thermal plasma jet on the apoptosis of SK-BR-3 breast cancer cells. RSC Adv 5:14670–14677
Wagner EF, Nebreda ÁR (2009) Signal integration by JNK and p38 MAPK pathways in cancer development. Nat Rev Cancer 9:537–549
de la Torre AV, Junyent F, Folch J, Pelegri C, Vilaplana J, Auladell C et al (2013) PI3 k/akt inhibition induces apoptosis through p38 activation in neurons. Pharmacol Res 70:116–125
He HT, Qiao KY, Wang C, Yang WH, Xu Z, Zhang ZL et al (2021) Hydrazinocurcumin induces apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells through the p38 mapk pathway. Cts-Clinical and Translational Science 14:2075–2084
Feng XJ, Sun TZ, Bei YC, Ding S, Zheng W, Lu Y et al (2013) S-nitrosylation of ERK inhibits ERK phosphorylation and induces apoptosis. Sci Rep3
Acknowledgements
None.
Funding
This research was supported by the fund from National Key R&D Program of China to Guohua Ni (grant number 2019YFC0119000), National Natural Science Foundation of China to Dong Wang, Guohua Ni and Qiying Shen (grant number 31800702, 11875295, 11535003 and 81902003), funds from Anhui Medical University to Dong Wang [grant number XJ201603 and 2017xkj003].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XL: Conceptualization, Methodology, Writing Original draft preparation, Supervision. TS: Software, Data curation Writing-Reviewing. QS: Editing. CH: Data curation. XZ: Visualization. DW: Investigation. GN: Validation.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
The Ethical Committee of Anhui Medical University approved this research.
Consent for publication
All authors have given consents for publication.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, X., Sun, T., Zhang, X. et al. Low temperature plasma suppresses proliferation, invasion, migration and survival of SK-BR-3 breast cancer cells. Mol Biol Rep 50, 2025–2031 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-022-08026-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-022-08026-4