Abstract
Background
Quercetin is a natural flavonoid that is known to have numerous pharmacological activities such as antioxidative, anti-inflammatory, and neuroprotective effects against various neurological disorders. Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) is a potent endotoxin, reported causing several neurological disorders.
Aim
The present study was designed to investigate the possibility that quercetin ameliorates LPS induced oxidative stress and neuroinflammation in adult zebrafish.
Materials and methods
Zebrafish (weighing 470–530 mg) were treated with a single injection of LPS (1 mg/kg) intraperitoneally (i.p.) followed by post-treatment with quercetin (50 and 100 mg/kg; i.p.) for 7 days. After sacrificing brain was harvested and subjected for biochemical, molecular, and histological analyses.
Results
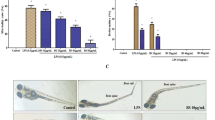
Results revealed post-treatment with quercetin was able to ameliorate the behavioral abnormalities as in novel tank diving test- time spent in the top zone (TSTZ), and the number of entries in the top zone was significantly (p < 0.01) more as compared to time spent in the bottom zone (TSBZ). In the light–dark chamber test- time spent in the light zone (TSLZ), and the number of entries in the light zone were significantly (p < 0.01) more as compared to time spent in the dark compartment (TSDC). Additionally, results of histopathology (H & E stain) studies showed less disruption in neuronal cells as compared to the LPS treated group. Moreover, the results of the molecular analysis revealed that quercetin treatment significantly (p < 0.01) decrease TNF-α and IL-1β levels as compared to LPS treated animals. Further, results of the biochemical analysis reveal that quercetin significantly (p < 0.01) reduces the level of LPO, nitrite, AChEs and increases anti-oxidant GSH.
Conclusion
Quercetin treatment helps to prevent oxidative damage and neuroinflammation in LPS treated adult zebrafish.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- LPS:
-
Lipopolysaccharide
- AD:
-
Alzheimer Disease
- PD:
-
Parkinson Disease
- MS:
-
Multiple Sclerosis
- ALS:
-
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
- TSTZ:
-
Time spent in the top zone
- TSBZ:
-
Time spent in the bottom zone
- TSLZ:
-
Time spent in the light zone
- TSDC:
-
Time spent in the dark compartment
- TNF- α:
-
Tumour necrosis factor
- IL-1β:
-
Interleukin 1 beta
- LPO:
-
Lipid peroxidation
- AChEs:
-
Acetylcholinesterase
- GSH:
-
Glutathione
- CNS:
-
Central nervous system
- QoL:
-
Quality of life
- BBB:
-
Blood–brain barrier
- DMSO:
-
Dimethylsulfoxide
- TCA:
-
Trichloroacetic acid
- TBA:
-
Thiobarbituric acid
References
I Morales L Guzmán-Martínez C Cerda-Troncoso GA Farías RB Maccioni 2014 Neuroinflammation in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. A rational framework for the search of novel therapeutic approaches Front Cell Neurosci 8 112
MT Heneka MK O'Banion 2007 Inflammatory processes in Alzheimer's disease J Neuroimmunol 184 1–2 69 91
M Rusek R Pluta M Ułamek-Kozioł SJ Czuczwar 2019 Ketogenic diet in Alzheimer’s disease Int J Mol Sci 20 16 3892
ER Dorsey A Elbaz E Nichols F Abd-Allah A Abdelalim JC Adsuar MG Ansha C Brayne JY Choi D Collado-Mateo N Dahodwala 2018 Global, regional, and national burden of Parkinson's disease, 1990–2016: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016 The Lancet Neurology 17 11 939 953
P Browne D Chandraratna C Angood H Tremlett C Baker BV Taylor AJ Thompson 2014 Atlas of multiple sclerosis 2013: a growing global problem with widespread inequity Neurology 83 11 1022 1024
A Chiò G Logroscino BJ Traynor J Collins JC Simeone LA Goldstein LA White 2013 Global epidemiology of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: a systematic review of the published literature Neuroepidemiology 41 2 118 130
R Zakaria WM Wan Yaacob Z Othman I Long AH Ahmad B Al-Rahbi 2017 Lipopolysaccharide-induced memory impairment in rats: a model of Alzheimer's disease Physiol Res 1 66
YC Lu WC Yeh PS Ohashi 2008 LPS/TLR4 signal transduction pathway Cytokine 42 2 145 151
AC Oliveira de NM Yousif HS Bhatia J Hermanek M Huell BL Fiebich 2016 Poly (I: C) increases the expression of mPGES-1 and COX-2 in rat primary microglia J Neuroinflammation 13 1 1 1
L Yao EM Kan C Kaur ST Dheen A Hao J Lu EA Ling 2013 Notch-1 signaling regulates microglia activation via the NF-κB pathway after hypoxic exposure in vivo and in vitro PLoS ONE 8 11 e78439
YM Bradford S Toro S Ramachandran L Ruzicka DG Howe A Eagle P Kalita R Martin SA Taylor Moxon K Schaper M Westerfield 2017 Zebrafish models of human disease: gaining insight into the human disease at ZFIN ILAR J 58 1 4 16
CH Williams CC Hong 2011 Multi-step usage of in vivo models during rational drug design and discovery Int J Mol Sci 12 4 2262 2274
K Howe MD Clark CF Torroja J Torrance C Berthelot M Muffato JE Collins S Humphray K McLaren L Matthews S McLaren 2013 The zebrafish reference genome sequence and its relationship to the human genome Nature 496 7446 498 503
S Saleem RR Kannan 2018 Zebrafish: an emerging real-time model system to study Alzheimer's disease and neurospecific drug discovery Cell Death Discov 4 45 https://doi.org/10.1038/s41420-018-0109-7forline5-7"
AV Kalueff AM Stewart R Gerlai 2014 Zebrafish as an emerging model for studying complex brain disorders Trends Pharmacol Sci 35 2 63 75
GJ Lieschke PD Currie 2007 Animal models of human disease: zebrafish swim into view Nat Rev Genet 8 5 353 367
ZJ Zhang LC Cheang MW Wang SM Lee 2011 Quercetin exerts a neuroprotective effect through inhibition of the iNOS/NO system and pro-inflammation gene expression in PC12 cells and in zebrafish Int J Mol Med 27 2 195 203
IUH Bhat R Bhat 2021 Quercetin: a bioactive compound imparting cardiovascular and neuroprotective benefits: scope for exploring fresh produce, their wastes, and by-products Biology (Basel) 10 7 586 https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10070586.PMID:34206761;PMCID:PMC8301140
SK Richetti M Blank KM Capiotti AL Piato MR Bogo MR Vianna CD Bonan 2011 Quercetin and rutin prevent scopolamine-induced memory impairment in zebrafish Behav Brain Res 217 1 10 15
Q Cai RO Rahn R Zhang 1997 Dietary flavonoids, quercetin, luteolin and genistein, reduce oxidative DNA damage and lipid peroxidation and quench free radicals Cancer Lett 119 1 99 107
SR Husain J Cillard P Cillard 1987 Hydroxyl radical scavenging activity of flavonoids Phytochemistry 26 9 2489 2491
J Bournival M Plouffe J Renaud C Provencher MG Martinoli 2012 Quercetin and sesamin protect dopaminergic cells from MPP+-induced neuroinflammation in a microglial (N9)-neuronal (PC12) coculture system Oxid Med Cell Longev https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/921941
S Singh S Jamwal P Kumar 2017 Neuroprotective potential of Quercetin in combination with piperine against 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1, 2, 3, 6-tetrahydropyridine-induced neurotoxicity Neural Regen Res 12 7 1137
B Zhang PP Wang KL Hu LN Li X Yu Y Lu HS Chang 2019 Antidepressant-like effect and mechanism of action of honokiol on the mouse lipopolysaccharide (LPS) depression model Molecules 24 11 2035
JL Zhang M Liu W Cui L Yang CN Zhang 2020 Quercetin affects shoaling and anxiety behaviors in zebrafish: Involvement of neuroinflammation and neuron apoptosis Fish Shellfish Immunol 1 105 359 368
Stewart A, Cachat JM, Suciu C, Hart PC, Gaikwad S, Utterback E, DiLeo J, Kalueff AV. Intraperitoneal injection as a method of psychotropic drug delivery in adult zebrafish. In Zebrafish neurobehavioral protocols 2011 (pp. 169–179). Humana Press.
RJ Egan CL Bergner PC Hart JM Cachat PR Canavello MF Elegante SI Elkhayat BK Bartels AK Tien DH Tien S Mohnot 2009 Understanding behavioral and physiological phenotypes of stress and anxiety in zebrafish Behav Brain Res 205 1 38 44
A Singh N Subhashini S Sharma BN Mallick 2013 Involvement of the α1-adrenoceptor in sleep–waking and sleep loss-induced anxiety behavior in zebrafish Neuroscience 15 245 136 147
S Dubey A Ganeshpurkar D Bansal N Dubey 2015 Protective effect of rutin on impairment of cognitive functions of due to antiepileptic drugs on zebrafish model Indian journal of pharmacology 47 1 86
Stewart A, Maximino C, De Brito TM, Herculano AM, Gouveia A, Morato S, Cachat JM, Gaikwad S, Elegante MF, Hart PC, Kalueff AV. Neurophenotyping of adult zebrafish using the light/dark box paradigm. In Zebrafish neurobehavioral protocols 2011 (pp. 157–167). Humana Press
T Gupta MC Mullins 2010 Dissection of organs from the adult zebrafish Journal of visualized experiments: JoVE. https://doi.org/10.3791/1717
E Wills 1966 Mechanisms of lipid peroxide formation in animal tissues Biochemical journal 99 3 667 676
GL Ellman 1959 Tissue sulfhydryl groups Arch Biochem Biophys 82 1 70 77
RF Itzhaki DM Gill 1964 A micro-biuret method for estimating proteins Anal Biochem 9 4 401 410
GL Ellman KD Courtney V Andres Jr RM Featherstone 1961 A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity Biochem Pharmacol 7 2 88 95
GL Peterson 1977 A simplification of the protein assay method of Lowry et al. which is more generally applicable Anal Biochem 83 2 346 356
A Singh A Kumar 2015 Microglial inhibitory mechanism of coenzyme Q10 against Aβ (1–42) induced cognitive dysfunctions: possible behavioral, biochemical, cellular, and histopathological alterations Front Pharmacol 9 6 268
SP Fu JF Wang WJ Xue HM Liu BR Liu YL Zeng SN Li BX Huang QK Lv W Wang JX Liu 2015 Anti-inflammatory effects of BHBA in both in vivo and in vitro Parkinson’s disease models are mediated by GPR109A-dependent mechanisms J Neuroinflammation 12 1 1 4
CR Raetz C Whitfield 2002 Lipopolysaccharide endotoxins Annu Rev Biochem 71 1 635 700
K Sulakhiya P Kumar SS Gurjar CC Barua NK Hazarika 2015 Beneficial effect of honokiol on lipopolysaccharide induced anxiety-like behavior and liver damage in mice Pharmacol Biochem Behav 1 132 79 87
D Hwang BC Jang G Yu M Boudreau 1997 Expression of mitogen-inducible cyclooxygenase induced by lipopolysaccharide: mediation through both mitogen-activated protein kinase and NF-kB signaling pathways in macrophages Biochem Pharmacol 54 1 87 96
DB Rosemberg EP Rico BH Mussulini 2011 Differences in spatio-temporal behavior of zebrafish in the open tank paradigm after a short-period confinement into dark and bright environments PLoS ONE 6 5 e19397
NJ Mezzomo A Silveira GS Giuliani VA Quadros DB Rosemberg 2016 The role of taurine on anxiety-like behaviors in zebrafish: a comparative study using the novel tank and the light–dark tasks Neurosci Lett 2 613 19 24
X Peng J Lin Y Zhu X Liu Y Zhang Y Ji X Yang Y Zhang N Guo Q Li 2016 Anxiety-related behavioral responses of pentylenetetrazole-treated zebrafish larvae to light-dark transitions Pharmacol Biochem Behav 1 145 55 65
PK Sahoo LK Pradhan S Aparna K Agarwal A Banerjee SK Das 2020 Quercetin abrogates bisphenol A induced altered neurobehavioral response and oxidative stress in zebrafish by modulating brain antioxidant defence system Environ ToxicolPharmacol 80 103483 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etap.2020.103483 Epub 2020 Aug 29 PMID: 32866630
A Wach K Pyrzyńska M Biesaga 2007 Quercetin content in some food and herbal samples Food Chem 100 2 699 704
AK Grewal TG Singh D Sharma V Sharma M Singh MH Rahman A Najda M Walasek-Janusz M Kamel GM Albadrani MF Akhtar A Saleem MM Abdel-Daim 2021 Mechanistic insights and perspectives involved in neuroprotective action of quercetin Biomed Pharmacother 140 111729 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111729 Epub 2021 May 25 PMID: 34044274
Y Yang X Liu T Wu W Zhang J Shu Y He SJ Tang 2018 Quercetin attenuates AZT-induced neuroinflammation in the CNS Sci Rep 8 1 1 8
AW Boots H Li RP Schins R Duffin JW Heemskerk A Bast GR Haenen 2007 The quercetin paradox Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 222 1 89 96
TS Pês EM Saccol GM Ourique ÉP Londero LT Gressler JI Golombieski WG Glanzner SF Llesuy PB Gonçalves JR Neto B Baldisserotto 2016 Quercetin in the diet of silver catfish: effects on antioxidant status, blood parameters and pituitary hormone expression Aquaculture 1 458 100 106
G Patki N Solanki F Atrooz F Allam S Salim 2013 Depression, anxiety-like behavior and memory impairment are associated with increased oxidative stress and inflammation in a rat model of social stress Brain Res 20 1539 73 86
LE Page 1999 Benznidazole, a drug employed in the treatment of Chagas' disease, down-regulates the synthesis of nitrite and cytokines by murine stimulated macrophages Clin Exp Immunol 118 2 271 277
E Tyagi R Agrawal C Nath R Shukla 2008 Influence of LPS-induced neuroinflammation on acetylcholinesterase activity in rat brain J Neuroimmunol 205 1–2 51 56
C Unsal M Kanter C Aktas M Erboga 2015 Role of quercetin in cadmium-induced oxidative stress, neuronal damage, and apoptosis in rats Toxicol Ind Health 31 12 1106 1115
MA Ansari HM Abdul G Joshi WO Opii DA Butterfield 2009 Protective effect of quercetin in primary neurons against Aβ (1–42): relevance to Alzheimer's disease J Nutr Biochem 20 4 269 275
VF Prado C Martins-Silva BM Castro de RF Lima DM Barros E Amaral AJ Ramsey TD Sotnikova MR Ramirez HG Kim JI Rossato 2006 Mice deficient for the vesicular acetylcholine transporter are myasthenic and have deficits in object and social recognition Neuron 51 5 601 612
J Dai RM Buijs W Kamphorst DF Swaab 2002 Impaired axonal transport of cortical neurons in Alzheimer’s disease is associated with neuropathological changes Brain Res 948 1–2 138 144
JM Fasolo AF Vizuete EP Rico RB Rambo NS Toson E Santos DL Oliveira de CA Gonçalves EE Schapoval AT Heriques 2021 Anti-inflammatory effect of rosmarinic acid isolated from Blechnum brasiliense in adult zebrafish brain Comp Biochem Physiol C: Toxicol Pharmacol 239 108874
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to the Institute, for providing a research facility. Biorender.com for the preparation of figures.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SS did the research and drafts the manuscript, KS and LK helped in data collection, CS helped in editing the manuscript, AS designs the layout and critically revises the manuscript. The authors declare that all data were generated in-house and that no paper mill was used.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors confirm and declare no competing financial interests.
Research involving human participants and/or animals
Our study protocol involving animals have been approved by the Institutional Biosafety Committee.
Informed consent
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, S., Sahu, K., Kapil, L. et al. Quercetin ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced neuroinflammation and oxidative stress in adult zebrafish. Mol Biol Rep 49, 3247–3258 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-022-07161-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-022-07161-2