Abstract
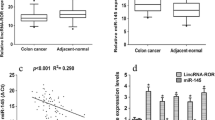
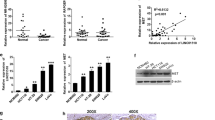
Long intergenic non-coding RNA for kinase activation (Linc-A) has been reported to enhance the occurrence and progression of breast cancer. Nevertheless, whether Linc-A is related to the tumorigenesis of colorectal cancer (CRC) remains unknown. In this study, we aimed to evaluate the expression of Linc-A in colon adenocarcinoma and explore the correlation between Linc-A and prognosis of CRC. The expression of Linc-A in human colon tissues was evaluated by qRT-PCR, which contained 15 pairs of human colon adenocarcinoma and paracancerous tissues and other 65 colon adenocarcinoma tissues. A total of 80 patients were divided into low and high expression groups according to the Linc-A levels. The levels of Linc-A in colon adenocarcinoma was higher than that in paracancerous tissues (p = 0.047). Furthermore, high expression of Linc-A was associated with advanced TNM stage (p = 0.013), positive lymph nodes (p = 0.024), low 5-year survival rate (p = 0.024) and even 10-year survival rate (p = 0.007). Besides, Linc-A, advanced age, advanced TNM stage, deep infiltration degree and positive lymph nodes were also found to be positively related to poor overall 5-year survival by Kaplan–Meier survival analysis(p < 0.05). Then, multivariable Cox regression analysis revealed that Linc-A was an independent risk factor for prognosis of colon adenocarcinoma (p = 0.047). In conclusion, high expression of Linc-A is associated with advanced TNM stage, lymphatic metastasis and poor survival in patients with CRC. Linc-A may be served as a candidate prognostic biomarker for CRC.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnold M, Sierra MS, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, Bray F (2017) Global patterns and trends in colorectal cancer incidence and mortality. Gut 66:683–691
Lawler M, Alsina D, Adams RA, Anderson AS, Brown G, Fearnhead NS, Fenwick SW, Halloran SP, Hochhauser D, Hull MA, Koelzer VH, McNair AGK, Monahan KJ, Nathke I, Norton C, Novelli MR, Steele RJC, Thomas AL, Wilde LM, Wilson RH, Tomlinson I, Bowel Cancer UK Critical Research Gaps in Colorectal Cancer Initiative (2018) Critical research gaps and recommendations to inform research prioritisation for more effective prevention and improved outcomes in colorectal cancer. Gut 67:179–193
Walsh JM, Terdiman JP (2003) Colorectal cancer screening: scientific review. JAMA 289:1288–1296
Van Schaeybroeck S, Allen WL, Turkington RC, Johnston PG (2011) Implementing prognostic and predictive biomarkers in CRC clinical trials. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 8:222–232
Mercer TR, Dinger ME, Mattick JS (2009) Long non-coding RNAs: insights into functions. Nat Rev Genet 10:155–159
Bhan A, Soleimani M, Mandal SS (2017) Long noncoding RNA and cancer: a new paradigm. Cancer Res 77:3965–3981
Lin A, Hu Q, Li C, Xing Z, Ma G, Wang C, Li J, Ye Y, Yao J, Liang K, Wang S, Park PK, Marks JR, Zhou Y, Zhou J, Hung M-C, Liang H, Hu Z, Shen H, Hawke DH, Han L, Zhou Y, Lin C, Yang L (2017) The LINK-A lncRNA interacts with PtdIns(3,4,5)P3 to hyperactivate AKT and confer resistance to AKT inhibitors. Nat Cell Biol 19:238
Xu S, Sui S, Zhang J, Bai N, Shi Q, Zhang G, Gao S, You Z, Zhan C, Liu F, Pang D (2015) Downregulation of long noncoding RNA MALAT1 induces epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition via the PI3K-AKT pathway in breast cancer. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 8:4881–4891
Lin A, Li C, Xing Z, Hu Q, Liang K, Han L, Wang C, Hawke DH, Wang S, Zhang Y, Wei Y, Ma G, Park PK, Zhou J, Zhou Y, Hu Z, Zhou Y, Marks JR, Liang H, Hung MC, Lin C, Yang L (2016) The LINK-A lncRNA activates normoxic HIF1alpha signalling in triple-negative breast cancer. Nat Cell Biol 18:213–224
Hua X, Li G, Liu Z, Niu Z (2019) LINK-A lncRNA participates in the pathogenesis of glioma by interacting with survivin. Exp Ther Med 18:1581–1586
Liu J, Song W, Li J, Li X, Zhao R, Gong T (2019) LINK-A lncRNA is upregulated in metastatic non-small cell lung cancer and is associated with poor prognosis. Oncol Lett 18:3049–3057
Huang ZY, Zhang LH, Zhao C, Liu R, Tong H, Gan C, Lan T, Tang CW, Gao JH (2018) High HIF-1 alpha expression predicts poor prognosis of patients with colon adenocarcinoma. Int J Clin Exp Patho 11:5635–5646
Ganesh K, Stadler ZK, Cercek A, Mendelsohn RB, Shia J, Segal NH, Diaz LA Jr (2019) Immunotherapy in colorectal cancer: rationale, challenges and potential. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 16:361–375
Robertson DJ, Ladabaum U (2019) Opportunities and challenges in moving from current guidelines to personalized colorectal cancer screening. Gastroenterology 156:904–917
Dekker E, Rex DK (2018) Advances in CRC prevention: screening and surveillance. Gastroenterology 154:1970–1984
Vacante M, Borzì AM, Basile F, Biondi A (2018) Biomarkers in colorectal cancer: current clinical utility and future perspectives. World J Clin Cases 6:869–881
Wang L, Cho KB, Li Y, Tao G, Xie Z, Guo B (2019) Long noncoding RNA (lncRNA)-mediated competing endogenous RNA networks provide novel potential biomarkers and therapeutic targets for colorectal cancer. Int J Mol Sci 20(22):5758
Stottrup C, Tsang T, Chin YR (2016) Upregulation of AKT3 confers resistance to the AKT inhibitor MK2206 in breast cancer. Mol Cancer Ther 15:1964–1974
Li ZB, Chu HT, Jia M, Li L (2020) Long noncoding RNA LINC01139 promotes the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma by upregulating MYBL2 via competitively binding to miR-30 family. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 525:581–588
Zhao W, Li W, Dai W, Huang N, Qiu J (2018) LINK-A promotes cell proliferation through the regulation of aerobic glycolysis in non-small-cell lung cancer. Onco Targets Ther 11:6071–6080
Chen X, Lingala S, Khoobyari S, Nolta J, Zern MA, Wu J (2011) Epithelial mesenchymal transition and hedgehog signaling activation are associated with chemoresistance and invasion of hepatoma subpopulations. J Hepatol 55:838–845
Park MY, Kim KR, Park HS, Park BH, Choi HN, Jang KY, Chung MJ, Kang MJ, Lee DG, Moon WS (2007) Expression of the serum response factor in hepatocellular carcinoma: implications for epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Int J Oncol 31:1309–1315
Zhang W, Yuan W, Song J, Wang S, Gu X (2017) LncRna CPS1-IT1 suppresses cell proliferation, invasion and metastasis in colorectal cancer. Cell Physiol Biochem 44:567–580
Padua Alves C, Fonseca AS, Muys BR, de Barros ELBR, Burger MC, de Souza JE, Valente V, Zago MA, Silva WA Jr (2013) Brief report: The lincRNA Hotair is required for epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and stemness maintenance of cancer cell lines. Stem Cells 31:2827–2832
Xu W, Yang Z, Lu N (2015) A new role for the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in the epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Cell Adh Migr 9:317–324
Alzahrani AS (2019) PI3K/Akt/mTOR inhibitors in cancer: at the bench and bedside. Semin Cancer Biol 59:125–132
Ma J, Xue M (2018) LINK-A lncRNA promotes migration and invasion of ovarian carcinoma cells by activating TGF-β pathway. Biosci Rep. https://doi.org/10.1042/BSR20180936
Barbagallo C, Brex D, Caponnetto A, Cirnigliaro M, Scalia M, Magnano A, Caltabiano R, Barbagallo D, Biondi A, Cappellani A, Basile F, Di Pietro C, Purrello M, Ragusa M (2018) lncrna UCA1, upregulated in CRC biopsies and downregulated in serum exosomes, controls mRNA expression by RNA-RNA interactions. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids 12:229–241
Acknowledgements
This study is supported by Natural Science Fund of China (U1702281, 81670551 and 81873584), National Key R&D Program of China (2017YFA0205404). The abstract has been presented in 26th United European Gastroenterology Week Vienna 2018 as a poster.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare no conflict of interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, C., Gan, C., Xiao, Y. et al. High expression of long non-coding RNA Linc-A associates with poor survival in patients with colorectal cancer. Mol Biol Rep 47, 7497–7504 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-020-05809-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-020-05809-5