Abstract
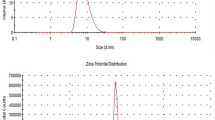
To evaluate the relationship between oxidative stress, DNA damage, and suppression of tumor growth induced by lipoic acid free and nano-capsule. Lipoic acid nano-capsule was assessed by transmission electron microscopy (TEM). The antitumor activity of lipoic acid free and nano-capsule was investigated in Ehrlich solid tumor bearing mice. The endpoints measured were superoxide dismutase (SOD) enzyme activity, malondialdehyde (MDA) levels, DNA damage (comet assay), histopathological examination of tissues and tumor growth volume. Treatment with α-lipoic acid (A-LA) free and nano-capsule (1.2, 2.4 mg/kg) showed a significant depression (67–28%) in MDA levels and elevated (38–98%) in SOD activity. Additionally, A-LA free and nano-capsule caused a 3-10-fold increase in comet parameters such as % tail DNA and suppressed Ehrlich solid tumor growth in mice. In conclusion, the present study revealed that A-LA free and nano-capsule have antitumor activity. This might be possible via its redox activity.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kozlov AV, Gille L, Staniek K, Nohl H (1999) Dihydrolipoic acid maintains ubiquinone in the antioxidant active form by two-electron reduction of ubiquinone and one-electron reduction of ubisemiquinone. Arch Biochem Biophys 363:148
Roy SS, Packer L (1998) Redox regulation of cell functions by alpha lipoate: biochemical and molecular aspects. BioFactors 8:17
Novotny L, Rauko P, Cojocel C (2008) Alpha-lipoic acid—the potential for use in cancer therapy. Neoplasma 55:81
Korotchkina LG, Sidhu S, Patel MS (2004) Adverse effects of high doses of intravenous alpha lipoic acid on liver mitochondria. Free Radic Res 38:1083
Chiumiento L, Bruschi F (2009) Enzymatic antioxidant systems in helminth parasites. Parasitol Res 105:593
Dal-Pizzol F, Klamt F, Frota ML Jr, Andrades ME, Caregnato FF, Vianna MM, Schröder N, Quevedo J, Izquierdo I, Archer T, Moreira JC (2001) Neonatal iron exposure induces oxidative stress in adult Wistar rat. Brain Res Dev Brain Res 130:109
Gackowski D, Banaszkiewicz Z, Rosalski R, Jawien A, Olinski R (2002) Persistent oxidative stress in colorectal carcinoma patients. Int J Cancer 101:395
Glaab WE, Hill RB, Skopek TR (2001) Suppression of spontaneous and hydrogen peroxide-induced mutagenesis by the antioxidant ascorbate in mismatch repair-deficient human colon cancer cells. Carcinogenesis 22:1709
Forsberg L, de Faire U, Morgenstern R (2001) Oxidative stress, human genetic. Arch Biochem Biophys 389:84
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A (2016) Cancer statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin 66:7
Ferreira E, da Silva AE, Serakides R, Gomes MG, Cassali GD (2007) Ehrlich tumor as model to study artificial hyperthyroidism influence on breast cancer. Pathol Res Prac 203:39
Newman DJ, Cragg GM, Snader KM (2003) Natural products as sources of new drugs over the period 1981–2002. J Nat Prod 66:1022
Bergfeld SA, Blavier L, DeClerck YA (2014) Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stromal cells promote survival and drug resistance in tumor cells. Mol Cancer Ther 13:962
Hill GW, Morest DK, Parham K (2008) Cisplatin-induced ototoxicity: effect of intratympanic dexamethasone injections. Otol Neurotol 29:1005
Ashour AE, Abdel-Hamied HE, Korashy HM, Al-Shabanah AO, Abd-Allah ARA (2011) Alpha-lipoic acid rebalances redox and immune-testicular milieu in septic rats. Chem Biol Interact 189:198
Moreira PI, Harris PLR, Zhu X, Santos MS, Oliveira CR, Smith MA, Perry G (2007) Lipoic acid and N-acetyl cysteine decrease mitochondrial-related oxidative stress in Alzheimer disease patient fibroblasts. J Alzheimer’s Dis 12:195
Wenzel U, Nickel A, Daniel H (2005) α-lipoic acid induces apoptosis in human colon cancer cells by increasing mitochondrial respiration with a concomitant O2 –-generation. Apoptosis 10:359
Yoo TH, Lee JH, Chun HS, Chi SG (2013) α-lipoic acid prevents p53 degradation in colon cancer cells by blocking NF-κB induction of RPS6KA4. Anticancer Drugs 24:555
Jankowska AK, Ponikowska MG, Wozniak MM (2017) Lipoic acid decreases the viability of breast cancer cells and activity of PTP1B and SHP2. Anticancer Res 37:2893
Kim JI, Cho SR, Lee CM, Park ES, Kim KN, Kim HC, Lee HY (2012) Induction of ER stress-mediated apoptosis by α-lipoic acid in A549 cell lines. Korean J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 45:1
Feuerecker B, Pirsig S, Seidl C, Aichler M, Feuchtinger A, Bruchelt G, Senekowitsch-Schmidtke R (2012) Lipoic acid inhibits cell proliferation of tumor cells in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Biol Ther 13:1425
Teichert J, Hermann R, Ruus P, Preiss R (2003) Plasma kinetics, metabolism, and urinary excretion of alpha-lipoic acid following oral administration in healthy volunteers. J Clin Pharmacol 43:1257
Kofuji K, Nakamura M, Isobe T, Murata Y, Kawashima S (2008) Stabilization of α-lipoic acid by complex formation with chitosan. Food Chem 109:167
Souto EB, Müller RH, Gohla S (2005) A novel approach based on lipid nanoparticles (SLN®) for topical delivery of α-lipoic acid. J Microencapsul 22:581
Tiziana MGP, Teresa M, Lucrezia M, Massimo F, Rosario P (2016) Evaluation of Eudragit® retard polymers for the microencapsulation of alpha-lipoic acid. Curr Drug Deliv 13:1165
Vidović BB, Milašinović NZ, Kotur-Stevuljević JM, Dilber SP, Kalagasidis Krušić MT, Dordević BI, Knežević-Jugović ZD (2016) Encapsulation of α-lipoic acid into chitosan and alginate/gelatin hydrogel microparticles and its in vitro antioxidant activity. Hem ind 70:49
Segall A, Sosa M, Alami A, Enero C, Hormaechea F, Pizzorno MT, Bregni C, Serrao R (2004) Stability study of lipoic acid in the presence of vitamins A and E in o/w emulsions for cosmetic application. J Cosmet Sci 55:449
Sridharan V, Seawright JW, Antonawich FJ, Garnett M, Cao M, Singh P, Boerma M (2017) Late administration of a palladium lipoic acid complex (POLY-MVA) modifies cardiac mitochondria but not functional or structural manifestations of radiation-induced heart disease in a rat model. Rad Res 187:361
Nishiura H, Sugimoto K, Akiyama K, Musashi M, Kubota Y, Yokoyama Ti, Yamashita Y, Kuriki T, Yamaguchi Y (2013) A novel nano-capsule of lipoic acid as a template of core-shell structure constructed by self-assembly. J Nanomed Nanotechol 4:155
National Research Council (1996) Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. National Academy Press, Washington, DC
Food and Drug Administration, Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER) (2005) Estimating the maximum safe starting dose in initial clinical trials for therapeutics in adult healthy volunteers. Pharmacol Toxicol 40:185–206
Singh NP, McCoy MT, Tice RR, Schneider EL (1988) A simple technique for quantitation of low levels of DNA damage in individual cells. Exp Cell Res 175:184
Tice RR, Agurell E, Anderson D, Burlinson B, Hartmann A, Kobayashi H, Miyamae Y, Rojas E, Ryu JC, Sasaki YF (2000) Single cell gel/comet assay: guidelines for in vitro and in vivo genetic toxicology testing. Environ Mol Mutagen 35:206
Kudryavtseva AV, Krasnov GS, Dmitriev AA, Alekseev BY, Kardymon OL, Sadritdinova AF, Fedorova MS, Pokrovsky AV, Melnikova NV, Kaprin AD, Moskalev AA, Snezhkina AV (2016) Mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress in aging and cancer. Oncotarget 7:44879
Sinclair AJ, Barnett AH, Lunec J (1990) Free radicals and antioxidant systems in health and disease. Br J Hosp Med 43:334
Ahmed MI, Fayed ST, Hossein H, Tash FM (1999) Lipid peroxidation and antioxidant status in human cervical carcinoma. Dis Markers 15:283
Saad EA, Hassanien MM, El-lban FW (2017) Nickel (II) diacetyl monoxime-2-pyridyl hydrazone complex can inhibit Ehrlich solid tumor growth in mice: a potential new antitumor drug. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 484:579
Patra S, Muthuraman MS, Prabhu ATJ, Priyadharshini RR, Parthiban S (2015) Evaluation of antitumor and antioxidant activity of Sargassum tenerrimum against Ehrlich ascites carcinoma in mice. APJCP 16:915
Michiels C, Raes M, Toussaint O, Remacle J (1994) Importance of SE-glutathione peroxidase, catalase, and CU/ZN-SOD for cell survival against oxidative stress. Free Radic Biol Med 17:235
Castro LSEPW, Kviecinski MR, Ourique F, Parisotto EB, Grinevicius VMAS, Correia JFG, Wilhelm Filho D, Pedrosa RC (2016) Albendazole as a promising molecule for tumor control. Redox Biol 10:90
Moller P, Knudsen LE, Loft S, Wallin H (2000) The comet assay as a rapid test in biomonitoring occupational exposure to DNA-damaging agents and effect of confounding factors. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 9:1005
Georgieva E, Ivanova D, Zhelev Z, Bakalova R, Gulubova M, Aoki I (2017) Mitochondrial dysfunction and redox imbalance as a diagnostic marker of “free radical diseases”. Anticancer Res 10:5373
Kafara P, Icard P, Guillamin M, Schwartz L, Lincet H (2015) Lipoic acid decreases Mcl-1, Bcl-xL and up regulates Bim on ovarian carcinoma cells leading to cell death. J Ovarian Res 8:36
Al Abdan M (2012) Alfa-lipoic acid controls tumor growth and modulates hepatic redox state in Ehrlich-ascites-carcinoma-bearing mice. Sci World J 2012:509838
Rageh MM, El-Gebaly RH, Afifi MM (2018) Antitumor activity of silver nanoparticles in Ehrlich carcinoma-bearing mice. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch Pharmacol 391:1421
Michikoshi H, Nakamura T, Sakai K, Suzuki Y, Adachi E, Matsugo S et al (2013) Alpha-lipoic acid-induced inhibition of proliferation and met phosphorylation in human non-small cell lung cancer cells. Cancer Lett 335:472
Schwartz L, Guais A, Israel M, Junod B, Steyaert JM, Crespi E et al (2013) Tumor regression with a combination of drugs interfering with the tumor metabolism: efficacy of hydroxycitrate, lipoic acid and capsaicin. Invest New Drugs 31:256
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors state that there are no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rageh, M.M., El-Gebaly, R.H. Antioxidant activities of α-lipoic acid free and nano-capsule inhibit the growth of Ehrlich carcinoma. Mol Biol Rep 46, 3141–3148 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-019-04769-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-019-04769-9