Abstract
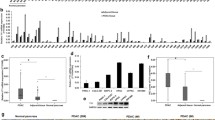
The LIM proteins (Lhx1, Lhx2, Lhx3 and Lhx4) have been report to play important roles in human development. The function role of Lhxs have been characterized in various tumor tissues as cancer suppressors or promoters in different can status and types. The aim of present study was to clarify the function role of Lhx proteins in human pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDA). The gene expression profiles of Lhxs was evaluated using real-time quantitative reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (QRT-PCR) analysis and immunohistochemistry in human PDA tissues compared with normal pancreatic tissues, which identified the gene overexpression of Lhx2 in PDA. Furthermore, we discovered that Lhx2 promoted cancer cell proliferation in vitro/vivo and elevated β-catenin levels correlated with Lhx2 expression in PDA while the Lhx2 simulated β-catenin activation was required for LMO1’s oncogenic effects. Mechanistically, Lhx2 facilitate TCF4 to bind to β-catenin and form a stable Lhx2/TCF4/β-catenin complex and trans-active its downstream target gene. Lhx2 mutations that disrupt the Lhx2-β-catenin interaction partially prevent its function in tumor cells.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barrionuevo FJ et al (2012) Genes promoting and disturbing testis development. Histol Histopathol 27(11):1361–1383
Pevny LH, Lovell-Badge R (1997) < i>Sox</i> genes find their feet. Curr Opin Genet Dev 7(3):338–344
Bowles J, Schepers G, Koopman P (2000) Phylogeny of the SOX family of developmental transcription factors based on sequence and structural indicators. Dev biol 227(2):239–255
Fu W et al (2014) Insights into HER2 signaling from step-by-step optimization of anti-HER2 antibodies. mAbs 6(4):978–990
Hobert O, Westphal H (2000) Functions of LIM-homeobox genes. Trends Genet 16(2):75–83
Hu S et al (2013) Comparison of the inhibition mechanisms of Adalimumab and Infliximab in treating tumor necrosis factor α-associated diseases from a molecular view. J Biol Chem 288(38):27059–27067
Rétaux S et al (1999) Lhx9: a novel LIM-homeodomain gene expressed in the developing forebrain. J Neurosci 19(2):783–793
Monuki ES, Porter FD, Walsh CA (2001) Patterning of the dorsal telencephalon and cerebral cortex by a roof plate-Lhx2 pathway. Neuron 32(4):591–604
Failli V, Bachy I, Rétaux S (2002) Expression of the LIM-homeodomain gene< i> Lmx1a </i>(< i> dreher </i>) during development of the mouse nervous system. Mech Dev 118(1):225–228
Murray KD, Choudary PV, Jones EG (2007) Nucleus-and cell-specific gene expression in monkey thalamus. Proc Natl Acad Sci 104(6):1989–1994
Quinlan R et al (2009) Complex and dynamic patterns of Wnt pathway gene expression in the developing chick forebrain. Neural Dev 4:35
Zhou C-J, Pinson KI, Pleasure SJ (2004) Severe defects in dorsal thalamic development in low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein-6 mutants. J Neurosci 24(35):7632–7639
Korbut E, Ptak-Belowska A, Brzozowski T (2012) Mechanisms promoting physiological cells progression into tumorigenesis. J Physiol Pharmacol 63(6):565–570
Baylin SB, Ohm JE (2006) Epigenetic gene silencing in cancer—a mechanism for early oncogenic pathway addiction? Nat Rev Cancer 6(2):107–116
Zhang W et al (2008) Epigenetic inactivation of the canonical Wnt antagonist SRY-box containing gene 17 in colorectal cancer. Cancer Res 68(8):2764–2772
Bafico A et al (2004) An autocrine mechanism for constitutive Wnt pathway activation in human cancer cells. Cancer Cell 6(5):497–506
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Feng Zhou and Shanmiao Gou have contribute equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, F., Gou, S., Xiong, J. et al. Oncogenicity of LHX2 in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Mol Biol Rep 41, 8163–8167 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-014-3716-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-014-3716-2