Abstract
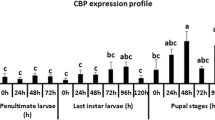
Chitin synthase is the key regulatory enzyme for chitin synthesis and excretion in insects, as well as a specific target of insecticides. The chitin synthase A gene (BmChsA) cloned from Bombyx mori, the model species of lepidopteran, is an epidermis-specific expressed gene during the molting stage. Knockdown BmChsA gene in 3rd instar larvae increased the number of non-molting and abnormal molting larvae. Exposure to nikkomycin Z, a chitin synthase inhibitor downregulated the expression of BmChsA and decreased the amount of epidermis chitin during the molting process. The thickness of the new epidermis and its dense structure varied greatly. The exogenous hormones significantly upregulated the expression of BmChsA with low levels of endogenous MH and high levels of endogenous JH immediately after molting. With low levels of endogenous hormones during the mulberry intake process, BmChsA was rarely upregulated by exogenous hormones. With high levels of endogenous MH and low levels of endogenous JH during the molting stage, we did not detect the upregulation of BmChsA by exogenous hormones. The expression of BmChsA was regulated by endocrine hormones, which directly affected the chitin synthesis-dependent epidermal regeneration and molting process.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kramer KJ, Corpuz L, Choi HK, Muthukrishnan S (1993) Sequence of a cDNA and expression of the gene encoding epidermal and gut chitinases of Manduca sexta. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 23:691–701
Bixby-Brosi AJ, Potter DA (2012) Can a chitin-synthesis-inhibiting turfgrass fungicide enhance black cutworm susceptibility to a baculovirus? Pest Manag Sci 68:324–329
Roberts SP, Harrison JF, Hadley NF (1998) Mechanisms of thermal balance in flying Centris pallida (Hymenoptera: Anthophoridae). J Exp Biol 201:2321–2331
Tellam RL, Vuocolo T, Johnson SE, Jarmey J, Pearson RD (2000) Insect chitin synthase cDNA sequence, gene organization and expression. Eur J Biochem 267:6025–6043
Cohen E (2001) Chitin synthesis and inhibition: a revisit. Pest Manag Sci 57:946–950
Merzendorfer H (2006) Insect chitin synthases: a review. J Comp Physiol B 176:1–15
Gagou ME, Kapsetaki M, Turberg A, Kafetzopoulos D (2002) Stage-specific expression of the chitin synthase DmeChSA and DmeChSB genes during the onset of Drosophila metamorphosis. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 32:141–146
Zimoch L, Merzendorfer H (2002) Immunolocalization of chitin synthase in the tobacco hornworm. Cell Tissue Res 308:287–297
Arakane Y, Muthukrishnan S, Kramer KJ, Specht CA, Tomoyasu Y, Lorenzen MD et al (2005) The Tribolium chitin synthase genes TcCHS1 and TcCHS2 are specialized for synthesis of epidermal cuticle and midgut peritrophic matrix. Insect Mol Biol 14:453–463
Shimomura M, Minami H, Suetsugu Y, Ohyanagi H, Satoh C, Antonio B et al (2009) KAIKObase: an integrated silkworm genome database and data mining tools. BMC Genom 10:486
Xia Q, Wang J, Zhou Z, Li R, Fan W, Cheng D et al (2008) The genome of a lepidopteran model insect, the silkworm Bombyx mori. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 38:1036–1045
Mita K (2009) Genome of a lepidopteran model insect, the silkworm Bombyx mori. Seikagaku 81(5):353–360
Kim MG, Shin SW, Bae KS, Kim SC, Park HY (1998) Molecular cloning of chitinase cDNAs from the silkworm, Bombyx mori and the fall webworm, Hyphantria cunea. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 28:163–171
Daimon T, Hamada K, Mita K, Okano K, Suzuki MG, Kobayashi M et al (2003) A Bombyx mori gene, BmChi-h, encodes a protein homologous to bacterial and baculovirus chitinases. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 33:749–759
Takahashi M, Kiuchi M, Kamimura M (2002) A new chitinase-related gene, BmChiR1, is induced in the Bombyx mori anterior silk gland at molt and metamorphosis by ecdysteroid. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 32:147–151
Xia Q, Cheng D, Duan J, Wang G, Cheng T, Zha X et al (2007) Microarray-based gene expression profiles in multiple tissues of the domesticated silkworm, Bombyx mori. Genome Biol 8:R162
Schefe JH, Menk M, Reinemund J, Effertz K, Hobbs RM, Pandolfi PP et al (2006) A novel signal transduction cascade involving direct physical interaction of the renin/prorenin receptor with the transcription factor promyelocytic zinc finger protein. Circ Res 99:1355–1366
Zhang J, Zhu KY (2006) Characterization of a chitin synthase cDNA and its increased mRNA level associated with decreased chitin synthesis in Anopheles quadrimaculatus exposed to diflubenzuron. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 36:712–725
Lehmann PF, White LO (1975) Chitin assay used to demonstrate renal localization and cortisone-enhanced growth of Aspergillus fumigatus mycelium in mice. Infect Immun 12:987–992
Farnesi LC, Brito JM, Linss JG, Pelajo-Machado M, Valle D, Rezende GL (2012) Physiological and morphological aspects of Aedes aegypti developing larvae: effects of the chitin synthesis inhibitor novaluron. PLoS ONE 7:e30363
Kingsbury JM, Heitman J, Pinnell SR (2012) Calcofluor white combination antifungal treatments for Trichophyton rubrum and Candida albicans. PLoS ONE 7:e39405
Xu L, Liang H, Niu YS, Wang Y, Sima YH, Xu SQ (2012) Differential expression of the Bombyx mori diapause-termination timer gene Ea4 in diapause-inducing temperature and photoperiod. Arch Insect Biochem Physiol 79:182–194
Gan LP, Zhang WY, Niu YS, Xu L, Xi J, Ji MM, Xu SQ (2010) Construction and application of an electronic spatiotemporal expression profile and gene ontology analysis platform based on the EST database of the silkworm, Bombyx mori. J Insect Sci 10:114. doi:10.1673/031.010.11401
Cui WZ, Mu ZM, Zhang YY, Duan HM, Zhou WD, Li FQ et al (1995) Studies on increasing silk amount by using juvenile hormone and ecdysone cooperatively in silkworm. Seric Sci 21:178–183
Takaki K, Sakurai S (2003) Regulation of prothoracic gland ecdysteroidogenic activity leading to pupal metamorphosis. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 33:1189–1199
Behr JB, Gourlain T, Helimi A, Guillerm G (2003) Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of hetaryl-nucleoside derivatives as inhibitors of chitin synthase. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 13:1713–1716
Acknowledgments
The present work was supported by the National High-Tech R&D Program of China (863 Program) (Grant No. 2011AA100306), National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 31172264), Provincial Key Technology R&D Program of Jiangsu (Project No. BE2011327-1), and Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhuo, W., Fang, Y., Kong, L. et al. Chitin synthase A: a novel epidermal development regulation gene in the larvae of Bombyx mori . Mol Biol Rep 41, 4177–4186 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-014-3288-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-014-3288-1