Abstract
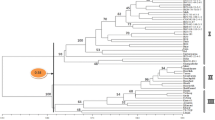
Knowledge in the area of genetic diversity could aid in providing useful information in the selection of material for breeding such as hybridization programs and quantitative trait loci mapping. To this end, 50 Nicotiana tabacum genotypes were genotyped with 21 primer combination of amplified fragment length polymorphism (AFLP). A total of 480 unambiguous DNA fragments and 373 polymorphic bands were produced with an average of 17.76 per primer combination. Also, the results revealed high polymorphic rate varing from 52.63 to 92.59 %, demonstrating that AFLP technique utilized in this research can be a powerful and valuable tool in the breeding program of N. tabacum. Cluster analysis based on complete linkage method using Jaccard’s genetic distance, grouped the 50 tobacco genotypes into eight clusters including three relatively big clusters, one cluster including Golden gift, Burly 7022 and Burly Kreuzung, one cluster consisting of two individuals (Pereg234, R9) and three single-member clusters (Pennbel69, Coker176 and Budisher Burley E), Recent genotypes showed high genetic distance from other genotypes belonging to cluster I and II. Association analysis between seven important traits and AFLP markers were performed using four statistical models. The results revealed the model containing both the factors, population structure (Q) and general similarity in genetic background arising from shared kinship (K), reduces false positive associations between markers and phenotype. According to the results nine markers were determined that could be considered to be the most interesting candidates for further studies.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achleitner A, Tinker N, Zechner E, Buerstmayr H (2008) Genetic diversity among oat varieties of worldwide origin and associations of AFLP markers with quantitative traits. Theor Appl Genet 117(7):1041–1053
Anonymous (2010) Annual reports. Tobacco Research Center of Rasht Publication
Bassam BJ, Caetano-Anolles G, Gresshoff PM (1991) Fast and sensitive silver staining of DNA in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem 196:80–83
Barrett BA, Kidwell KK (1998) AFLP-based genetic diversity assessment among wheat cultivars from the Pacific Northwest. Crop Sci 38:1261–1271
Bradbury PJ, Zhang Z, Kroon DE, Casstevens TM, Ramdoss Y, Buckler ES (2007) TASSEL: software for association mapping of complex traits in diverse samples. Bioinformatics 23:2633–2635
Bretting PK, Widrlechner MP (1995) Genetic markers and plant genetic resource management. Plant Breed Rev 13:11–86
Brookes JE (1952) The mighty leaf: tobacco through the centuries. Little, Brown, Boston, MA
Collard BCY, Jahufer MZZ, Brouwer JB, Pang ECK (2005) An introduction to markers, quantitative trait loci (QTL) mapping and marker-assisted selection for crop improvement: the basic concepts. Euphytica 142:169–196
Denduangboripant J, Piteekan T, Nantharat M (2010) Genetic polymorphism between tobacco cultivar-groups revealed by amplified fragment length polymorphism analysis. J Agric Sci 2(2):41–48
D’hoop BB, Paulo MJ, Kowitwanich K, Sengers M, Visser RGF, Van Eck HJ, Van Eeuwijk FA (2010) Population structure and linkage disequilibrium unravelled in tetraploid potato. Theor Appl Genet 121:1151–1170
Evanno G, Reganut E, Goudet J (2005) Detecting the number of clusters of individuals using the software STRUCTURE: a simulation study. Mol Ecol 14:2611–2620
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) (2009) The state of world fisheries and aquaculture 2008. http://faostat.fao.org/site/339/default.aspx
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) (2014) http://faostat.fao.org/site/567/DesktopDefault.aspx?PageID=567#ancor
Gupta PK, Sachin R, Kulwal PL (2005) Linkage disequilibrium and association studies in higher plants: present status and future prospects. Plant Mol Biol 57:461–485
Gvozdenović S, Saftić Panković D, Jocić S, Radić V (2009) Correlation between hetrosis and genetic distance based on SSR markers in sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.). J Agric Sci 54(1):1–9
Huang WK, Guo JY, Wan FH, Gao BD, Xie BY (2008) AFLP analyses on genetic diversity and structure of Eupatorium adenophorum populations in China. Chin J Agric Biotechnol 5:33–41
Hwang EY (2008) Association analysis in soybean. Ph.D. thesis, University of Maryland, College Park
Jaccard P (1908) Nouvelles recherches sur la distribution florale. Bull Soc Vaud Sci Nat 44:223–270
Meudt HM, Clarke AC (2007) Almost forgotten or latest practice? AFLP applications, analyses and advances. Trends Plant Sci 12(3):106–117
Da Silva Meyer A, Garcia AAF, De Souza AP, De Souza CLJr (2004) Comparison of similarity coefficients used for cluster analysis with dominant markers in maize (Zea mays L.). Genet Mol Biol 27:83–91
Michalski SG, Durka W, Jentsch A, Kreyling J, Pompe S, Schweiger O, Willner E, Beigerkuhnlein C (2010) Evidence for genetic differentiation and divergent selection in an autotetraploid forage grass (Arrhenatherum elatius). Theor Appl Genet 120:1151–1162
Mohammadi SA, Shokrpour M, Moghaddam M, Javanshir A (2011) AFLP-based molecular characterization and population structure analysis of Silybum marianum L. Plant Genet Resour Charact Util 9(3):445–453
Moon H, Nicholson JS (2007) AFLP and SCAR markers linked to tomato spotted wilt virus resistance in tobacco. Crop Sci 47:1887–1894
Moon HS, Nifong JM, Nicholson JS, Heineman A, Lion K, van der Hoeven R, Hayes AJ, Lewis RS (2009) Microsatellite-based analysis of tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum L.) genetic resources. Crop Sci 49:1–11
Pritchard JK, Stephens M, Donnelly P (2000) Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data. Genetics 155:945–959
Ren N, Timko MP (2001) AFLP analysis of genetic polymorphism and evolutionary relationships among cultivated and wild Nicotiana species. Genome 44(4):559–571
Rohlf FJ (2000) NTSYSpc: numerical taxonomy and multivariate analysis system. Version 2.02. Exeter Software, Setauket, NY
Roldain-Ruiz I, Calsyn E, Gilliand TJ, Coll R, van Eijk MJT, De Loose M (2000) Estimating genetic conformity between related ryegrass (Lolium) varieties, 2. AFLP characterization. Mol Breed 6:593–602
SaghiMaroof MA, Biyashev RM, Yang GP, Zhang Q, Allard RW (1994) Extraordinarily polymorphic microsatillate DNA in barely species diversity, choromosomal location, and population dynamics. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:5466–5570
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425
Sarala K, Rao RVS (2008) Genetic diversity in Indian FCV and Burley tobacco cultivars. J Genet 87:159–163
Sesli M, Yegenoglu ED (2010) Comparison of similarity coefficients used for cluster analysis based on RAPD markers in wild olives. Genet Mol Res 9(4):2248–2253
Shannon CE, Weaver W (1963) The mathematical theory of communication. University of Illinois Press, Urbana, IL
Sisson V (2002) The nicotiana catalogue, compilation of international tobacco germplasm holdings. Cooperation Centre for Scientific Research Relative to Tobacco (CORESTA)
Siva Raju K, Madhav MS, Sharma RK, Murthy TGK, Mohapatra T (2008) Genetic polymorphism of Indian tobacco types as revealed by amplified fragment length polymorphism. Curr Sci 94:633–639
Sneath PHA, Sokal RR (1973) Numerical taxonomy: the principle and practice of numerical classification. W. H. Freeman, San Francisco
Spataro G, Tiranti B, Arcaleni P, Bellucci E, Attene G, Papa R, Spagnoletti Zeuli P, Negri V (2011) Genetic diversity and structure of a worldwide collection of Phaseolus coccineus L. Theor Appl Genet 122:1281–1291
Spooner D, Van Treuren R, de Vicente MC (2005) Molecular Markers for genebank management. IPGRI technical bulletin no. 10. International Plant Genetic Resources Institute, Rome, Italy
Subudhi PK, Parami NP, Harrison SA, Materne MD, Murphy JP, Nash D (2005) An AFLP-based survey of genetic diversity among accessions of sea oats (Uniola paniculata, Poaceae) from the southeastern Atlantic and Gulf coast states of the United States. Theor Appl Genet 111:1632–1641
Tatikonda L, Wani SP, Kannan S, Beerelli N, Sreedevi TK, Hoisington DA, Devi P, Varshney RK (2009) AFLP-based molecular characterization of an elite germplasm collection of Jatropha curcas L., a biofuel plant. Plant Sci 176:505–513
Van Berloo R (1999) GGT: software for the display of graphical genotypes. J Hered 90:328–329
Van Berloo R, Aalbers H, Werkman A, Niks ER (2001) Resistance QTL confirmed through development of QTL–NILs for burley leaf rust resistance. Mol Breed 8(3):187–195
Vos P, Hogers R, Bleeker M, Reijans M, van de Lee T, Hornes M, Frijters A, Pot J, Paleman J, Kuiper M, Zabeau M (1995) AFLP: a new technique for DNA fingerprinting. Nucleic Acids Res 23(21):4407–4414
Wei P, Feng H, Feng Z, Li C, Liu Z, Wang Y, Ji R, Zou T, Ji S (2009) Identification of AFLP markers linked to Ms, a genetic multiple allele inherited male-sterile gene in Chinese cabbage. Breed Sci 59:333–339
Yeh FC, Yang R-C, Boyle TJB, Ye Z-H, Mao JX (1997) POPGENE, the user-friendly shareware for population genetic analysis. University of Alberta, Edmonton
Yu J, Pressoir G, Briggs WH, Vroh Bi I, Yamasaki M, Doebley JF, McMullen MD, Gaut BS, Nielsen DM, Holland JB, Kresovich S, Buckler ES (2006) A unified mixed-model method for association mapping that accounts for multiple levels of relatedness. Nat Genet 38:203–208
Zhang HY, Liu XZ, He CS, Yang YM (2008) Genetic diversity among flue-cured tobacco based on RAPD and AFLP markers. Braz Arch Biol Technol 51:1097–1101
Zhang HY, Liu XZ, Li TS, Yang YM (2006) Genetic diversity among flue-cured tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum L.) revealed by amplified fragment length polymorphism. Bot Stud 47:223–229
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dadras, A.R., Sabouri, H., Nejad, G.M. et al. Association analysis, genetic diversity and structure analysis of tobacco based on AFLP markers. Mol Biol Rep 41, 3317–3329 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-014-3194-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-014-3194-6