Abstract
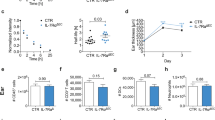
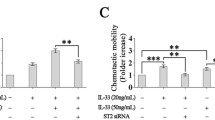
Elucidation of the events responsible for the interaction between lymphatic endothelial cells (LECs) and mast cells (MCs) may prove to be a valuable source for controlling lymphangiogenesis. In the present study, we compared immunohistochemical and RT-PCR findings of the popliteal lymph node (PLN) and footpad skin in C57BL/6J and WBB6F1 mice, the MC-deficient strain. The results indicated that MCs play certain role in complete Freund’s adjuvant-induced intranodal lymphangiogenesis. VEGF-A, VEGFR-2 and TNF-α were crucial factors in lymphangiogenesis both in the PLN and skin. Moreover, the in vivo administration of the specific mTOR inhibitor, rapamycin inhibited lymphangiogenesis independent of MCs in PLN rather than in the skin. Further study on anti-lymphangiogenic effect will contribute to our understanding of LEC and MC modulation in pathological lymphangiogenesis.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ji RC (2006) Lymphatic endothelial cells, lymphangiogenesis, and extracellular matrix. Lymphat Res Biol 4:83–100
Ji RC (2012) Macrophages are important mediators of either tumor- or inflammation-induced lymphangiogenesis. Cell Mol Life Sci 69:897–914
Ishizuka T, Terada N, Gerwins P, Hamelmann E, Oshiba A, Fanger GR, Johnson GL, Gelfand EW (1997) Mast cell tumor necrosis factor alpha production is regulated by MEK kinases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:6358–6363
Detoraki A, Staiano RI, Granata F, Giannattasio G, Prevete N, de Paulis A, Ribatti D, Genovese A, Triggiani M, Marone G (2009) Vascular endothelial growth factors synthesized by human lung mast cells exert angiogenic effects. J Allergy Clin Immunol 123:1142–1149
Kobayashi S, Kishimoto T, Kamata S, Otsuka M, Miyazaki M, Ishikura H (2007) Rapamycin, a specific inhibitor of the mammalian target of rapamycin, suppresses lymphangiogenesis and lymphatic metastasis. Cancer Sci 98:726–733
Patel V, Marsh CA, Dorsam RT, Mikelis CM, Masedunskas A, Amornphimoltham P, Nathan CA, Singh B, Weigert R, Molinolo AA, Gutkind JS (2011) Decreased lymphangiogenesis and lymph node metastasis by mTOR inhibition in head and neck cancer. Cancer Res 71:7103–7112
Lesma E, Eloisa C, Isaia E, Grande V, Ancona S, Orpianesi E, Di Giulio AM, Gorio A (2012) Development of a lymphangioleiomyomatosis model by endonasal administration of human TSC2 (−/−) smooth muscle cells in mice. Am J Pathol 181:947–960
Ji RC, Eshita Y, Kato S (2007) Investigation of intratumoural and peritumoural lymphatics expressed by podoplanin and LYVE-1 in the hybridoma-induced tumours. Int J Exp Pathol 88:257–270
Ji RC, Eshita Y, Xing L, Miura M (2010) Multiple expressions of lymphatic markers and morphological evolution of newly formed lymphatics in lymphangioma and lymph node lymphangiogenesis. Microvasc Res 80:195–201
Ji RC (2009) Lymph node lymphangiogenesis: a new concept for modulating tumor metastasis and inflammatory process. Histol Histopathol 24:377–384
Angeli V, Ginhoux F, Llodrà J, Quemeneur L, Fenette PS, Skobe M, Jessberger R, Merad M, Randolph GJ (2006) B cell-driven lymphangiogenesis in inflamed lymph nodes enhances dendritic cell mobilization. Immunity 24:203–215
Giraudo E, Primo L, Audero E, Gerber HP, Koolwijk P, Soker S, Klagsbrun M, Ferrara N, Bussolino F (1998) Tumor necrosis factor-alpha regulates expression of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 and of its co-receptor neuropilin-1 in human vascular endothelial cells. J Biol Chem 273:22128–22135
Baluk P, Yao LC, Feng J, Romano T, Jung SS, Schreiter JL, Yan L, Shealy DJ, McDonald DM (2009) TNF-alpha drives remodeling of blood vessels and lymphatics in sustained airway inflammation in mice. J Clin Investig 119:2954–2964
McColl BK, Paavonen K, Karnezis T, Harris NC, Davydova N, Rothacker J, Nice EC, Harder KW, Roufail S, Hibbs ML, Rogers PA, Alitalo K, Stacker SA, Achen MG (2007) Proprotein convertases promote processing of VEGF-D, a critical step for binding the angiogenic receptor VEGFR-2. FASEB J 21:1088–1098
Karnezis T, Shayan R, Caesar C, Roufail S, Harris NC, Ardipradja K, Zhang YF, Williams SP, Farnsworth RH, Chai MG, Rupasinghe TW, Tull DL, Baldwin ME, Sloan EK, Fox SB, Achen MG, Stacker SA (2012) VEGF-D promotes tumor metastasis by regulating prostaglandins produced by the collecting lymphatic endothelium. Cancer Cell 21:181–195
Dalton DK, Noelle RJ (2012) The roles of mast cells in anticancer immunity. Cancer Immunol Immunother 61:1511–1520
Soucek L, Lawlor ER, Soto D, Shchors K, Swigart LB, Evan GI (2007) Mast cells are required for angiogenesis and macroscopic expansion of Myc-induced pancreatic islet tumors. Nat Med 13:1211–1218
Kunder CA, St John AL, Abraham SN (2011) Mast cell modulation of the vascular and lymphatic endothelium. Blood 118:5383–5393
Grimbaldeston MA, Chen CC, Piliponsky AM, Tsai M, Tam SY, Galli SJ (2005) Mast cell-deficient W-sash c-kit mutant Kit W-sh/W-sh mice as a model for investigating mast cell biology in vivo. Am J Pathol 167:835–848
Mèndez R, Myers MG Jr, White MF, Rhoads RE (1996) Stimulation of protein synthesis, eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E phosphorylation, and PHAS-I phosphorylation by insulin requires insulin receptor substrate 1 and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. Mol Cell Biol 16:2857–2864
Guba M, von Breitenbuch P, Steinbauer M, Koehl G, Flegel S, Hornung M, Bruns CJ, Zuelke C, Farkas S, Anthuber M, Jauch KW, Geissler EK (2002) Rapamycin inhibits primary and metastatic tumor growth by antiangiogenesis: involvement of vascular endothelial growth factor. Nat Med 8:128–135
Mäkinen T, Veikkola T, Mustjoki S, Karpanen T, Catimel B, Nice EC, Wise L, Mercer A, Kowalski H, Kerjaschki D, Stacker SA, Achen MG, Alitalo K (2001) Isolated lymphatic endothelial cells transduce growth, survival and migratory signals via the VEGF-C/D receptor VEGFR-3. EMBO J 20:4762–4773
Salameh A, Galvagni F, Bardelli M, Bussolino F, Oliviero S (2005) Direct recruitment of CRK and GRB2 to VEGFR-3 induces proliferation, migration, and survival of endothelial cells through the activation of ERK, AKT, and JNK pathways. Blood 106:3423–3431
Huber S, Bruns CJ, Schmid G, Hermann PC, Conrad C, Niess H, Huss R, Graeb C, Jauch KW, Heeschen C, Guba M (2007) Inhibition of the mammalian target of rapamycin impedes lymphangiogenesis. Kidney Int 71:771–777
Luo Y, Liu L, Rogers D, Su W, Odaka Y, Zhou H, Chen W, Shen T, Alexander JS, Huang S (2012) Rapamycin inhibits lymphatic endothelial cell tube formation by downregulating vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 3 protein expression. Neoplasia 14:228–237
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ji, RC., Eshita, Y. Rapamycin inhibition of CFA-induced lymphangiogenesis in PLN is independent of mast cells. Mol Biol Rep 41, 2217–2228 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-014-3073-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-014-3073-1